Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):233-233
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):233-234
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):233-240
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005333
To assess the effect of tibolone on mammary tissue of castrated rats over 3
different periods of time.
Sixty virgin female Wistar rats were submitted to oophorectomy. Twenty-one days
after surgery, with hypoestrogenism confirmed, the experimental rats were randomly
assigned to six groups: Tibolone 1 (n=10) received tibolone 1 mg/day for 23 days,
tibolone 2 (n=10) for 59 days and tibolone 3 (n=10) for 118 days. The groups
control 1 (n=8), control 2 (n=7) and control 2 (n=10) received distilled water for
23, 59 and 118 days, respectively. After treatment, all six pairs of mammary
glands were removed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) for histological
analysis after euthanasia. The histological parameters evaluated were: epithelial
cell proliferation and secretory activity. The variables were analyzed
statistically, with the level of significance set at 0.05.
Histological changes were observed in 20/55 rats, mild epithelial hyperplasia in
7/55, moderate epithelial hyperplasia in 5/55, alveolar-nodular hyperplasia in
7/55, atypia without epithelial proliferation in 1/55, and no cases of severe
epithelial hyperplasia were found. Secretory activity was observed in 31/55 rats.
The secretory activity was significantly higher in the tibolone groups compared to
control at all the time points assessed (p=0,001). The histological changes were
did not show significance when the control and tibolone groups were compared. The
time of exposure to tibolone did not show significance when the three different
periods of evaluation were compared.
No relation between histological modification and tibolone treatment was verified
after short-, medium- and long-term treatment.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(4):233-239
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000400004
Purpose: to analyze sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and the likelihood ratio of transvaginal ultrasound and hysteroscopy when compared with the histopathologic examination of the endometrium in women with breast cancer who have been treated with tamoxifen. Methods: transversal study with 30 women in whom transvaginal ultrasound evaluated the echogenic pattern of endometrial echo and its thickness. Hyteroscopy was performed and described as normal (normal or atrophic endometrium) or abnormal (thickening, polyps, leiomyoma, synechia). Material for histopathology was obtained from endometrial biopsy and the findings were considered normal (irregular endometrial maturation and/or atrophy) or abnormal (polyps, simple or complex hyperplasia, leiomyoma or endometrial carcinoma). Results: the general diagnosis of endometrial modifications was present in 36.6% of patients. The most frequent results were cystic atrophy (46.6%) and endometrial polyps (26.6%). Through the ROC curve the best cutoff of 8 mm of endometrial thickness measure was determined. This measure showed sensitivity of 72.7%, specificity of 72.9%, positive predictive value of 66.6%, negative predictive value of 83.3% and likelihood ratio of 3.4. Hysteroscopy showed sensitivity of 90.9%, specificity of 68.4%, positive predictive value of 62.5%, negative prediction value of 92.8% and likelihood ratio of 2.8. Conclusions: the most frequent endometrial modifications were cystic atrophy followed by polyps. Transvaginal ultrasound showed a higher rate of false-positive (42.1%), when the cutoff for the thickness of the endometrium was 5 mm; however acuracy improved when the measure of 8 mm was used. The cutoff of 8 mm was determined through the ROC curve.
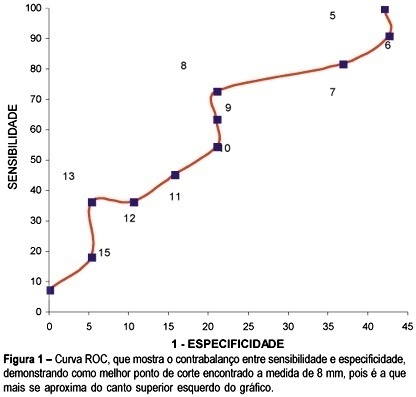
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):234-239
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000900003
PURPOSE: To analyze comparatively the conditions of birth in Portugal and Brazil from 1975 to 2007. METHODS: Indicators of maternal and child health: rates of maternal death and neonatal mortality, cesarean rate and public spending on health were retrospectively collected from electronic databases of health information from the Unified Health System (DATASUS) and the National Institute of Statistics of Portugal (INE), among others. Their values were descriptively analyzed in terms of trends and the temporal sanitary scenarios were presented and discussed, comparing, when possible, the information from the two countries. RESULTS: Births in Portugal were characterized by lower maternal mortality (12.2x76.2/100.000) and neonatal mortality (2.2x14.6/1000), compared to Brazil, considering the average of the years from 2004 to 2007. The history of the conquest of maternal and child indicators of excellence in Portugal involved a phase that paralleled the significant socio-economic improvements and the increasing contribution of public health, followed by another from the 1990s, involving better equipped health care units. In Brazil, rates of maternal and neonatal mortality are declining, but satisfactory values have not yet been achieved. The historical difference in the amount of social spending on health, both in current and historical values, was a crucial difference between countries. Despite the disparities in maternal and neonatal outcomes, cesarean section rates were equally ascendant (34.5% in Portugal and 45.5% in Brazil), considering the average for the period from 2004 to 2007. CONCLUSION: The indicators of maternal and neonatal death in Portugal and Brazil have aligned themselves to social, economic and contributions of public investments in health. The increasing rates of caesarean section do not explain the discrepancies in maternal and neonatal outcome between countries.
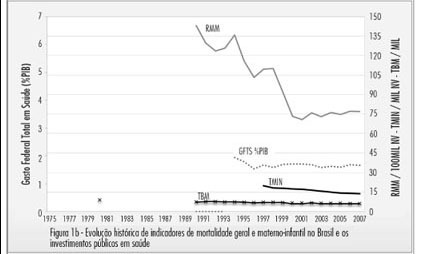
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(5):234-240
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) on female sexual dysfunctions. METHODS: twenty-six women with a diagnosis of sexual dysfunction (sexual desire, arousal, orgasmic disorders and/or dyspareunia) were included in a clinical trial with a before/after approach . The assessment was carried out before, during (after five sessions) and at the end of the treatment (after ten sessions) by two-digit palpation (assessment of pelvic floor muscle, PFM, strength), intravaginal electromyography (EMG) (capture of PFM contraction amplitudes) and Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI, a questionnaire for the evaluation of sexual function). The women underwent PFMT in different positions for ten sessions (once or twice a week). For statistical analysis, absolute and relative frequencies were used for clinical characteristics and PFM strength. The Friedman test was used to compare the FSFI domain scores and EMG values, the Students t-test was used to determine the association between these values and the characteristics of the women, and the Wilcoxon test for percent modification of the EMG. The Mann-Whitney test permitted us to compare these values with clinical characteristics. The Spearman correlation test was used to correlate the EMG values with mean total score. Results were considered statistically significant if p<0.05. RESULTS: a significant improvement (p<0.0001) of FSFI scores was observed at the end of treatment compared to the values observed before and in the middle of treatment. Regarding the EMG, the amplitudes of tonic and phasic contractions increased significantly during treatment (p<0.0001). Pelvic floor strength increased, which 69% of the women presenting grade 4 or 5 at the end of treatment, with a total improvement of sexual complaints. CONCLUSIONS: the PFMT improved muscle strength and electromyography contraction amplitudes, with improved sexual function, indicating that this physiotherapy approach may be successfully used for the treatment of female sexual dysfunctions.
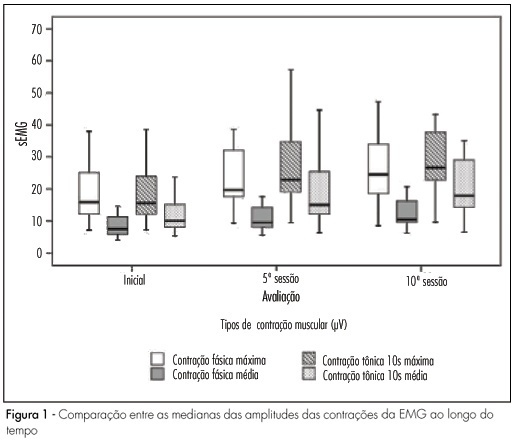
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):235-240
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500006
PURPOSE: to study infection prevalence by Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG), among adolescent and young women in a family planning outpatient clinic. METHODS: a total of 230 women up to 24 years old and history of up to four sexual partners have been followed-up for 48 months, with urine collection to search CT and NG, by the polymerase chain reaction method at the 1st, 12nd, 24th, 36th and 48th months. The variables studied were age group, schooling, marital status, number of gestations, abortions and children alive, age at the onset of sexual life, previous and present use of condom, previous use of intrauterine device, number of sexual partners in the previous six months and follow-up time. Bivariate analysis of variables according to positive tests for CT and NG, and multiple analyses by logistic regression were done. RESULTS: the ratio of infections by CT was 13.5% and by NG, 3%. Two women presented both tests as positive. The previous intrauterine device use was associated with positive tests for NG. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of infections by CT and NG was higher among the age group studied and the screening of young women must be taken into consideration in our services, to control the dissemination of sexually transmitted diseases and prevention of sequels.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):235-242
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000500008
PURPOSE: To evaluate the survival and complications associated with prematurity of infants with less than 32 weeks of gestation. METHODS: It was done a prospective cohort study. All preterm infants with a gestational age between 25 and 31 weeks and 6 days, born alive without congenital anomalies and admitted to the NICU between August 1st, 2009 and October 31st, 2010 were included. Newborns were stratified into three groups: G25, 25 to 27 weeks and 6 days; G28, 28 to 29 weeks and 6 days; G30, 30 to 31 weeks and 6 days, and they were followed up to 28 days. Survival at 28 days and complications associated with prematurity were evaluated. Data were analyzed statistically by c² test, analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis test, odds ratio with confidence interval (CI) and multiple logistic regression, with significance set at 5%. RESULTS: The cohort comprised 198 preterm infants (G25=59, G28=43 and G30=96). The risk of death was significantly higher in G25 and G28 compared to G30 (RR=4.14, 95%CI 2.23-7.68 and RR=2.84, 95%CI: 1.41-5.74). Survival was 52.5%, 67.4% and 88.5%, respectively. Survival was greater than 50% in preterm >26 weeks and birth weight >700 g. Neonatal morbidity was inversely proportional to gestational age, except for necrotizing enterocolitis and leukomalacia, which did not differ among groups. Logistic regression showed that pulmonary hemorrhage (OR=3.3, 95%CI 1.4-7.9) and respiratory distress syndrome (OR=2.5, 95%CI 1.1-6.1) were independent risk factors for death. There was a predominance of severe hemorrhagic brain lesions in G25. CONCLUSION: Survival above 50% occurred in infants with a gestational age of more than 26 weeks and >700 g birth weight. Pulmonary hemorrhage and respiratory distress syndrome were independent predictors of neonatal death. It is necessary to identify the best practices to improve the survival of extreme preterm infants.