Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(4):217-223
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000400005
Purpose: to identify recurrent spontaneous abortion- associated factors. Subjects: one hundred seventy-five outpatients were investigated from March 1993 to March 1997 at the "Ambulatório de Aborto Recorrente CAISM/UNICAMP". All of them had had three or more consecutive spontaneous abortions and/or two abortions and were 35 years or more old. Methods: the investigation protocol included: couple's karyotype; hysterosalpingography, serial plasma progesterone levels and/or endometrial biopsy; toxoplasmosis, listeriosis, brucelosis, lues and cytomegalovirus serum tests; Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma hominis cultures of cervical discharge; TSH and thyroid hormone levels; fasting glucose; autoantibody panel, anti-HLA antibody search by microlymphocytotoxicity crossmatch and one-way mixed lymphocyte culture with inhibitor factor detection. Husband's evaluation included: physical evaluation, lues, Chagas' disease, B and C hepatitis and AIDS serum tests, microlymphocytotoxicity crossmatch and one-way mixed lymphocyte culture with inhibitor factor detection. Results: alloimmune etiology was the most frequently found factor (86.3% of studied patients), represented by negative crossmatch and one-way mixed lymphocyte culture with inhibitor factor below 50%. The second most frequently found factor was cervical incompetence (22.8%), followed by hormonal factor (21.2%), mainly represented by luteal insufficiency. Some patients were found to have more than one etiologic factor. Conclusion: the investigation of recurrent spontaneous abortion-associated factors must include alloimmune etiology. Most cases will remain unexplained without this investigation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):217-223
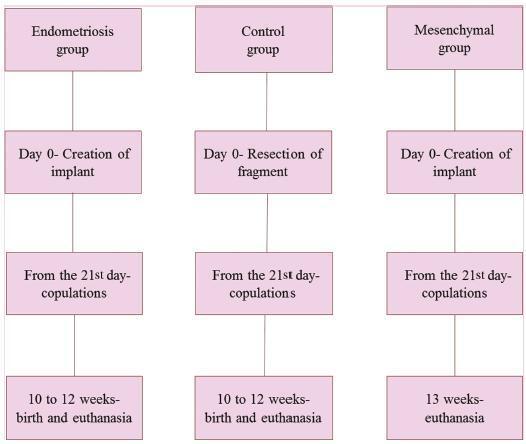
To evaluate the effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on fertility in experimental retrocervical endometriosis.
A total of 27 New Zealand rabbits were divided into three groups: endometriosis, in which endometrial implants were created; mesenchymal, in which MSCs were applied in addition to the creation of endometrial implants; and control, the group without endometriosis. Fisher’s exact test was performed to compare the dichotomous qualitative variables among the groups. The quantitative variables were compared by the nonparametric Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis tests. The MannWhitney test was used for post-hoc multiple comparison with Boniferroni correction.
Regarding the beginning of the fertile period, the three groups had medians of 14±12.7, 40±5, and 33±8.9 days respectively (p = 0.005). With regard to fertility (number of pregnancies), the endometriosis and control groups showed a rate of 77.78%, whereas the mesenchymal group showed a rate of 11.20% (p = 0.015). No differences in Keenan’s histological classification were observed among the groups (p = 0.730). With regard to the macroscopic appearance of the lesions, the mesenchymal group showed the most pelvic adhesions.
The use of MSCs in endometriosis negatively contributed to fertility, suggesting the role of these cells in the development of this disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(4):217-221
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000400004
Purpose: to evaluate the influence of pregnancy, habit of smoking, and the contraceptive method in HPV infection and the frequency of cytologic findings in adolescent women with HPV infection. Methods: a total of 54,985 cytologic examinations of patients seen between July, 1993 and December, 1998 were retrospectively analyzed. Of this total, 6,498 (11.8%) examinations were from patients under 20 years old. Of the total of 6,498 cytologic examinations, 326 (5.9%) presented signs of HPV infection, with or without grade I cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Patients with diagnosis of grade II and III CIN were excluded. The control group consisted of 333 patients paired by age, without cytological signs of HPV infection. Results: in adolescents, HPV infection was more frequent in oral contraceptive users (16.9% versus 13.8%, p<0.01) and in those who presented with clue cells in cytologic smears (22.4% versus 14.7%, p<0.001). The frequency of HPV infection in couples who used condom was 0% versus 2.1% in the control group (p<0.01). The difference in the number of pregnant women (41.1% versus 44.1%) and smokers (21.8% versus 16.5%) was not statistically significant. Conclusions: HPV infection is more frequent in adolescent women in use of oral contraceptive and with clue cells as cytologic finding. HPV infection did not occur in couples who used condom. Gestation and the habit of smoking did not influence the incidence of HPV infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400007
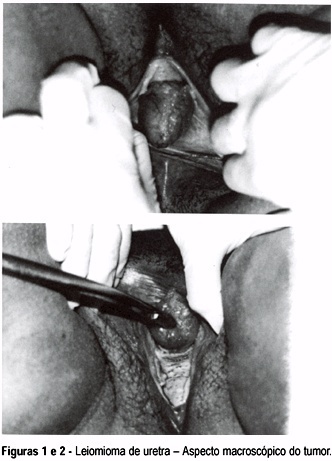
A case of urethral leiomyoma - a mass of approximately 5 cm in diameter - located on the anterior wall of the vaginal lower third is reported. The patient was submitted to a surgical tumor excision. Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies indicated leiomyoma, which is always a benign, unusual neoplasm, rarely relapsing after excision. Its pathogenesis and clinical features are also focused on.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(5):218-224
To evaluate whether women with endometriosis have different ovarian reserves and reproductive outcomes when compared with women without this diagnosis undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection ( IVF/ ICSI), and to compare the reproductive outcomes between women with and without the diagnosis considering the ovarian reserve assessed by antral follicle count ( AFC ).
This retrospective cohort study evaluated all women who underwent IVF/ ICSI in a university hospital in Brazil between January 2011 and December 2012. All patients were followed up until a negative pregnancy test or until the end of the pregnancy. The primary outcomes assessed were number of retrieved oocytes and live birth. Women were divided into two groups according to the diagnosis of endometriosis, and each group was divided again into a group that had AFC 6 (poor ovarian reserve) and another that had AFC 7 (normal ovarian reserve). Continuous variables with normal distribution were compared using unpaired t-test, and those without normal distribution, using Mann-Whitney test. Binary data were compared using either Fisher's exact test or Chi-square (2) test. The significance level was set as p < 0.05.
787 women underwent IVF/ICSI (241 of which had endometriosis). Although the mean age has been similar between women with and without the diagnosis of endometriosis (33.8 4 versus 33.7 4.4 years, respectively), poor ovarian reserves were much more common in women with endometriosis (39.8 versus 22.7%). The chance of achieving live birth was similar between women with the diagnosis of endometriosis and those without it (19.1 versus 22.5%), and also when considering only women with a poor ovarian reserve (9.4 versus 8.9%) and only those with a normal ovarian reserve (25.5 versus 26.5%).
Women diagnosed with endometriosis are more likely to have a poor ovarian reserve; however, their chance of conceiving by IVF/ICSI is similar to the one observed in patients without endometriosis and with a comparable ovarian reserve.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):218-227
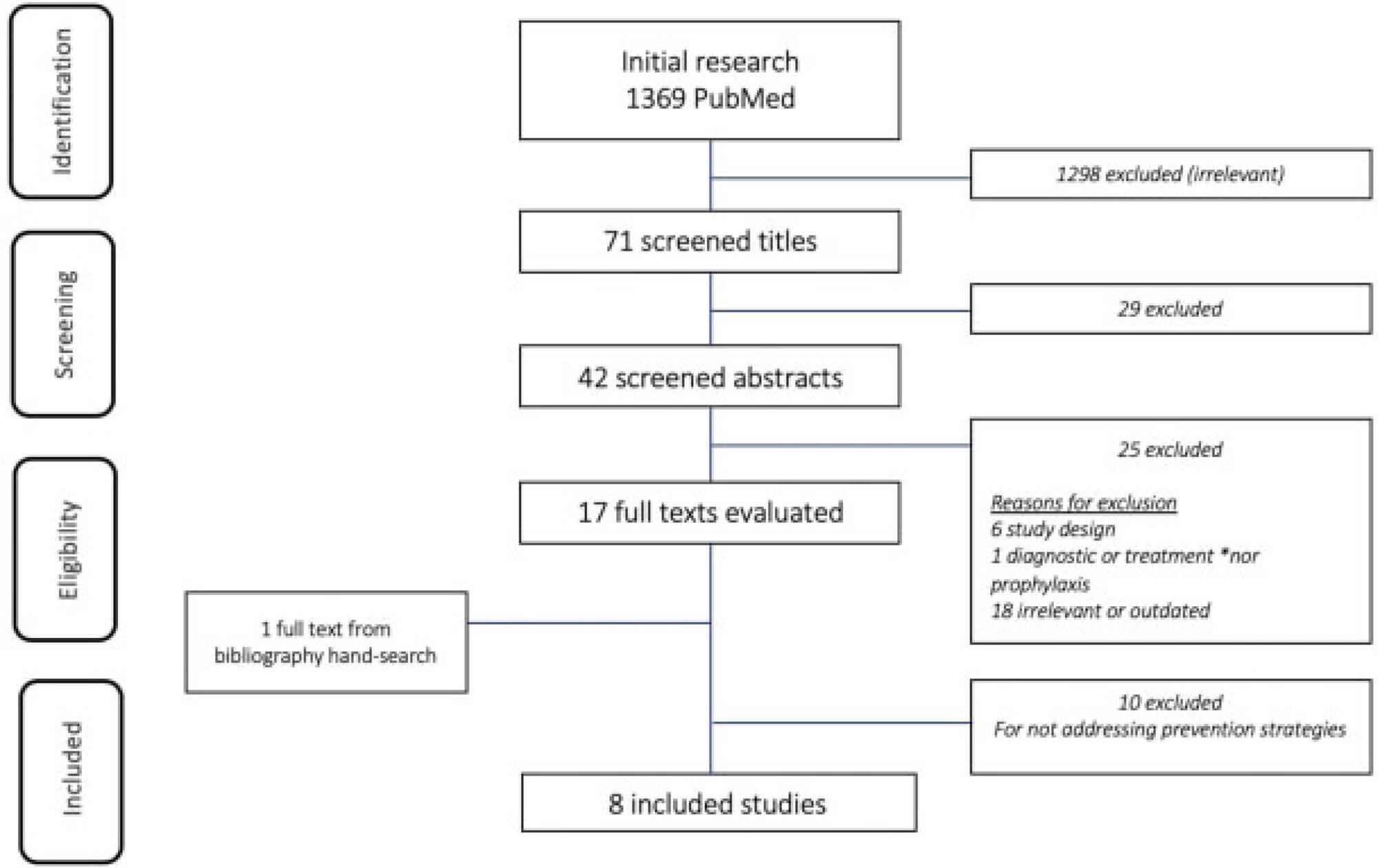
To identify current strategies and recommendations for venous thromboembolism prophylaxis associated with the pregnancy-puerperal cycle, a condition of high morbidity and mortality among women.
The literature search was performed between May and October 2019, using the PubMed database, including papers published in Portuguese, English and Spanish. The terms thromboembolism (Mesh) AND pregnancy (Mesh) OR postpartum (Mesh) were used as descriptors, including randomized controlled trials, meta-analyses, systematic reviews and guidelines published from 2009 to 2019, presenting strategies for prevention of thromboembolism during pregnancy and the postpartum.
Eight articles met the inclusion criteria. Many studies evaluated were excluded because they did not address prevention strategies. We compiled the recommendations from the American Society of Hematologists, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada, the American College of Chest Physicians and the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
There are some gaps in the research, and clinical studies with appropriate methodology are needed to support decisions made regarding the risk of thromboembolism in the perigestational period. Thus, the attention of the professionals involved in the care of pregnant and postpartum women is crucial, as it is a condition associated with high morbidity and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):218-218
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(10):218-218