Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):683-690
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100009
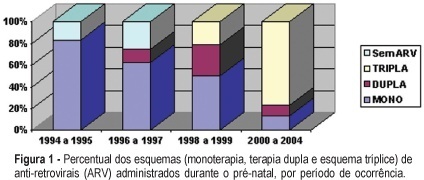
PURPOSE: to evaluate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vertical transmission and risk factors related to perinatal infection. METHODS: descriptive study of 170 HIV-infected pregnant women and their 188 neonates, admitted from June 1994 to September 2004 at the "Maternidade do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG". Demographic characteristics, mother's serologic state, mode of delivery and perinatal results were analyzed. Children were followed for 18 months after birth. Data were stored and analyzed by Epi-Info, version 6.0. Confidence interval was established at 95% (p<0.05). RESULTS: HIV infection was confirmed in 84 (45.4%) patients during gestation. Viral load was below 1,000 copies/mL in 60.4% patients. Highly active antiretroviral therapy was the predominant antiretroviral regimen (65.5%). C-section rate was high: 79.5%. Prematurity rate was 18.2%. There were 184 (97.8%) live births and four (2.2%) perinatal deaths among 188 neonates. Among live neonates 97.8% received zidovudine after birth. Global mother-to-child transmission rate was 3.8%. Virus vertical transmission rates for each period were: 60%, until 1996; 28% between 1996 and 1998; 0.68%, between 1999 and 2004. Significant risk factors were not found related to perinatal HIV-infection because there was a small number of infected neonates (n=6). CONCLUSION: there was a great reduction of HIV vertical transmission during the analyzed period. Current transmission rate is zero. This confirms that by adopting adequate measures perinatal virus transmission can be prevented.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):691-697
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100010
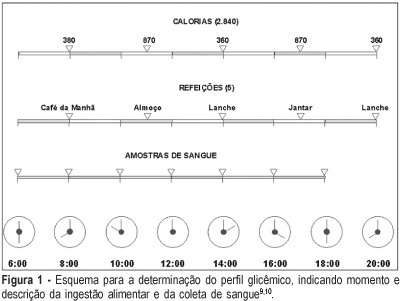
This is both a synthesis and a review of the major research findings, with the aim of validating Rudge's group IB. In this group of pregnants, screening for gestational diabetes was positive while the diagnosis was negative (normal 100 g-oral glucose tolerance test 100 g-OGTT). Nonetheless, the variations in glucose levels observed throughout the day, and confirmed by the glycemic profile (GP), characterized diurnal hyperglycemia, which accounts for maternal risk and adverse perinatal outcome. The description of this group is unique for both the establishment of the diagnosis during gestation and the follow-up of both the mother and the infant. These pregnancies have been erroneously classified as "low risk" and have not been diagnosed or treated. The IB group corresponds to 13.8% of the pregnant women screened in our service. This rate, added to the 7% of pregnancies complicated by diabetes, increase the occurrence of hyperglycemic disorders during gestation to up to 20.0%. In Rudge's group IB: a) perinatal mortality rate is 41‰, which is similar to that observed among diabetic pregnant women and 10 times higher than that found among non-diabetics; b) the observed placental abnormalities (both morphological and functional) differed from those seen in non-diabetic and diabetic pregnant women, indicating an adjustment to maintain functional activities that facilitated the passage of glucose to the fetus and explained fetal macrosomia (53.8% in non-treated pregnancies); c) maternal risk for hypertension, obesity and hyperglycemia was high and seemed to reproduce a model of metabolic syndrome, favoring the potential risk for future diabetes; d) 10 years after the index-pregnancy, type 2 diabetes was confirmed in 16.7% of the women in group IB. The authors suggest the development of multicentric studies in order to identify biomarkers specific for Rudge's group IB and establish protocols for the diagnosis of gestational hyperglycemic disorders using the combination GP + 100g-GTT as a standard. This procedure may cause an impact on the morbidity/mortality rate among pregnancies complicated by diurnal hyperglycemia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):698-705
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100011
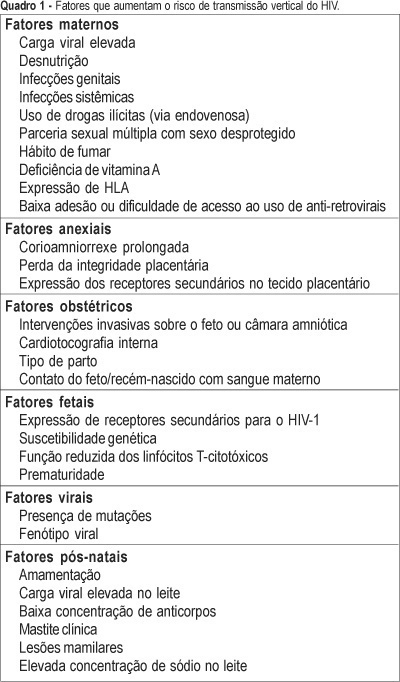
One of the most important advances in the control of the spread of infection with type 1 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) occurred within the context of vertical transmission (VT), with a reduction from levels of more than 40% to levels of less than 3%. Technological progress together with a better physiopathological understanding of this infection has permitted the determination of the situations and factors that increase the rates of perinatal transmission of the virus, indicating which interventions are most adequate for its control. The situations of higher risk for VT of HIV involve maternal, adnexal, obstetrical, fetal, viral, and postnatal factors. Among maternal factors, particularly important is viral load, the major indicator of the risk of this form of transmission. However, despite its relevance, viral load is not the only variable in this equation, with the following factors also playing important roles: use of illicit drugs, multiple sex partners and unprotected sex, malnutrition, smoking habit, advanced maternal disease, and lack af access or compliance with antiretroviral drugs. Among the adnexal factors are prolonged chorion-amniorrhexis, loss of placental integrity, and the expression of secondary receptors in placental tissue. Among the obstetrical factors, it should be remembered that invasive interventions in the fetus or amniotic chamber, internal cardiotocography, type of delivery, and contact of the fetus/newborn infant with maternal blood are also important elements to be controlled. Among the fetal factors are the expression of secondary HIV-1 receptors, genetic susceptibility, reduced cytotoxic T-lymphocyte function, and prematurity. Among the viral factors, mutations and syncytium-inducing strains are believed to be risk factors for VT. Finally, there are postnatal factors represented by an elevated viral load in maternal milk, a low antibody concentration in this fluid, clinical mastitis and nipple lesions, which can be grouped within the context of breast-feeding.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):706-706
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):707-707
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(11):707-707