Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):962-971
To explore the main sexuality complaints of gynecologic cancer survivors after treatment and to identify the care strategies provided.
Searches were conducted in six electronic databases: Scopus, Web of Science, LILACS, MEDLINE, PsychINFO, and EMBASE.
Articles published between 2010 and 2020 were selected and the following descriptors were used in the English language: female genital neoplasms and gynaecological cancer. The methodological quality of the studies used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT).
The primary data extracted were: names of the authors, year of publication, country of origin, objective and type of study, data collection instrument, sample size and age range, types of cancer, and symptoms affected with the strategies adopted.
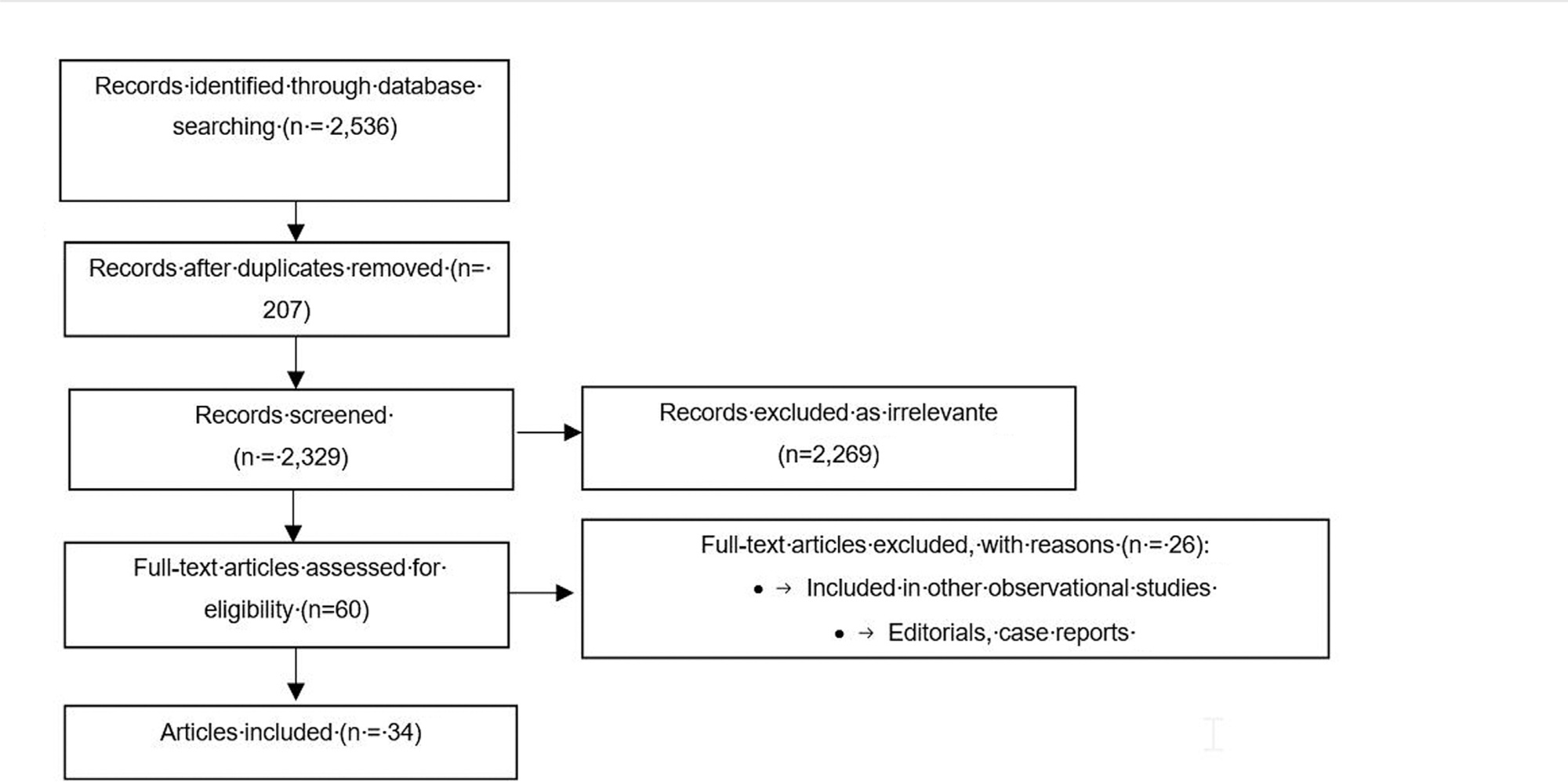
A total of 34 out of 2,536 screened articles were included. The main strategies found for patient care were patient-clinician communication, practices for sexuality care, individualized care plan, multiprofessional team support, and development of rehabilitation programs. For sexuality care, the most common practices are pelvic physiotherapy sessions and the use of vaginal gels and moisturizers.
The main complaints identified in the scientific literature were low libido and lack of interest in sexual activity, vaginal dryness, pain during sexual intercourse, and stenosis. Different care strategies may be adopted, such as follow-up with a multidisciplinary health team and sexual health rehabilitation programs, which could minimize these symptoms and ensure the quality of life of patients.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):972-985
Different drugs are used to treat mastalgia, such as danazol and bromocriptine, and both are associated with side effects, due to which most of women and healthcare providers are interested in herbal medicines. Therefore we aim to study the effectiveness of phytoestrogens on the severity of cyclic mastalgia.
To carry out the present study, English electronic resources such as the Cochrane Library, ISI Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed were used systematically and with no time limitation up to February 10, 2020.
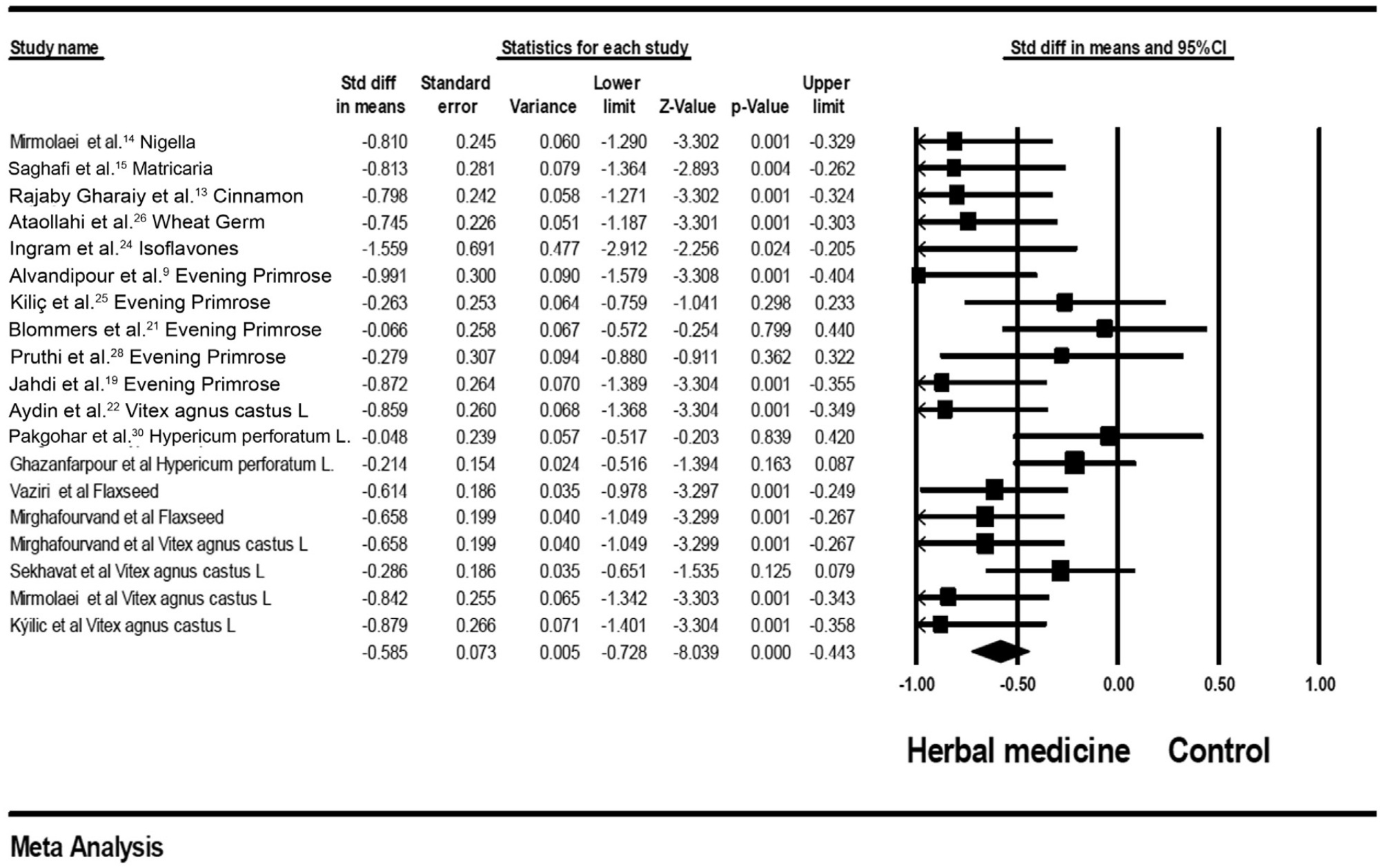
In total, 20 studies were included in the present meta-analysis. The results of the meta-analysis showed that herbal medicines versus the control group (standard mean difference [SMD] = - 0.585; 95% confidence interval [CI]: - 0.728–- 0.44; heterogeneity; p = 0.02; I2 = 42%), herbal medicines versus the B group (SMD = - 0.59; 95%CI: - 0.75–- 0.44; heterogeneity; p = 0.03; I2 = 42%), and its subgroups, such as phytoestrogen (SMD = - 0.691; 95%CI: - 0.82–- 0.55; heterogeneity; p = 0.669; I2 = 0%), Vitex-agnus-castus (SMD = - 0.642; 95%CI: - 0.84–- 0.44; p < 0.001; p = 203; I2 = 32%), flaxseed (SMD = - 0.63; 95%CI: - 0.901–- 0.367; p = 0.871; I2 = 0%), and evening primrose (SMD= - 0.485; 95%CI:- 0.84–- 0.12; p = 0.008; heterogeneity; p = 0.06; I2 = 56%] may have effective and helpful effects on improving cyclic breast mastalgia. Also, chamomile, isoflavone, cinnamon, and nigella sativa significantly reduced mastalgia symptoms.
Herbal medicines and their subgroups may have effective and helpful effects on improving cyclic breast mastalgia. The findings of our meta-analysis must be done cautiously because low methodological quality in some evaluated studies of this systematic review.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):986-994
To evaluate the efficacy of the hormonal and nonhormonal approaches to symptoms of sexual dysfunction and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women.
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, SciELO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) databases, as well as on clinical trial databases. We analyzed studies published between 1996 and May 30, 2020. No language restrictions were applied.
We selected randomized clinical trials that evaluated the treatment of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women.
Three authors (ACAS, APFC, and JL) reviewed each article based on its title and abstract. Relevant data were subsequently taken from the full-text article. Any discrepancies during the review were resolved by consensus between all the listed authors.
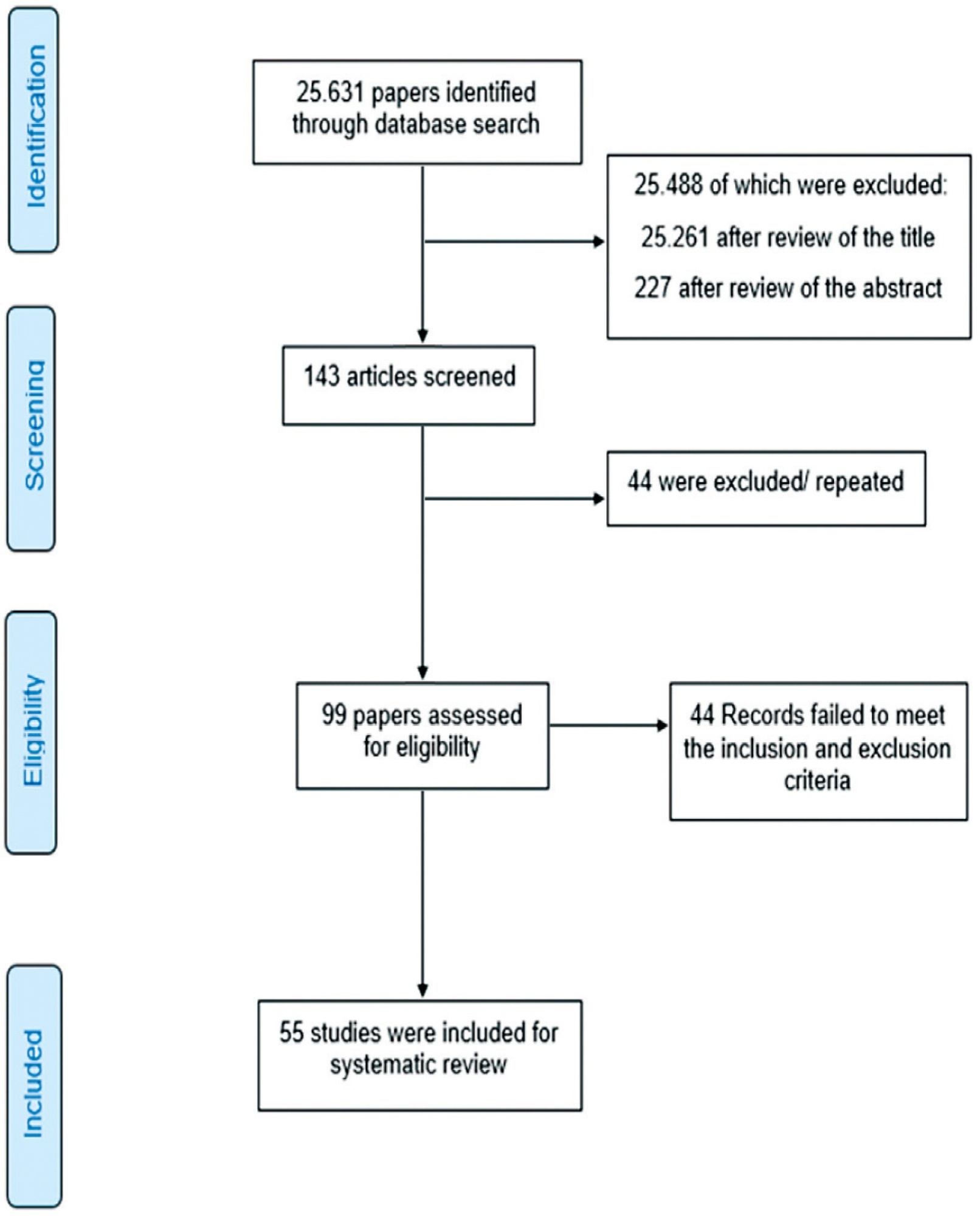
A total of 55 studies were included in the systematic review. The approaches tested to treat sexual dysfunction were as follows: lubricants and moisturizers (18 studies); phytoestrogens (14 studies); dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; 8 studies); ospemifene (5 studies); vaginal testosterone (4 studies); pelvic floor muscle exercises (2 studies); oxytocin (2 studies); vaginal CO2 laser (2 studies); lidocaine (1 study); and vitamin E vaginal suppository (1 study).
We identified literature that lacks coherence in terms of the proposed treatments and selected outcome measures. Despite the great diversity in treatment modalities and outcome measures, the present systematic review can shed light on potential targets for the treatment, which is deemed necessary for sexual dysfunction, assuming that most randomized trials were evaluated with a low risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. The present review is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42018100488).
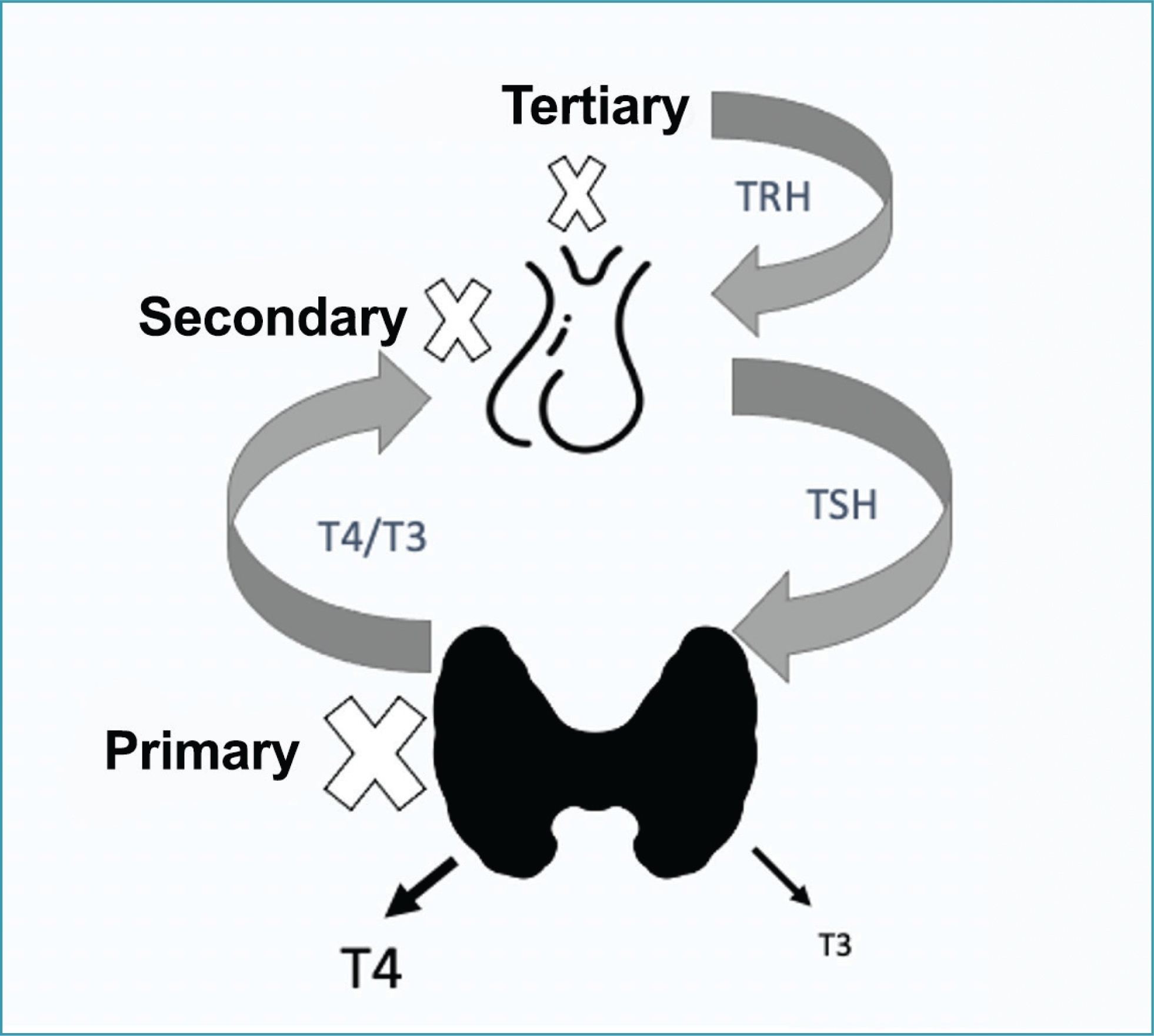
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):995-998
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):999-1009