You searched for:"Tiago Elias Rosito"
We found (3) results for your search.-
Original Article
Gender affirming hormone therapy and transgender women fertility: Histologic predictors of germ cell presence
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo33
Summary
Original ArticleGender affirming hormone therapy and transgender women fertility: Histologic predictors of germ cell presence
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo33
Views173Abstract
Objective:
Evaluate histological changes in testicular parameters after hormone treatment in transgender women.
Methods:
Cross-section study with patients who underwent gonadectomy at Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre from 2011 to 2019. Hormone treatment type, route of administration, age at initiation and duration were recorded. Atrophy parameters were observed: testicular volume, tubular diameter, basal membrane length, presence of spermatogonia and spermatids (diploid and haploid spermatozoid precursors).
Results:
Eighty-six patients were included. Duration of hormone treatment is associated with testicular atrophy and spermatogenesis arrest. Other characteristics of hormone treatment such as age of initiation, route of administration and type of treatment were not associated with testicular histological changes. Testicular volume may predict spermatogenesis arrest. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio is an interesting predictor of germ cell presence.
Conclusion:
Cross-sex hormone treatment affects testicular germ cell presence. Basal membrane length and tubular diameter ratio reduces inter variability of measurements and better exemplify how atrophic seminiferous tubules are. Fertility preservation should be addressed by healthcare providers in order to recognize gender affirming treatment impact on transgender health.
Key-words fertilityfertility preservationGonadal steroid hormonesHormone treatmentSpermatogenesisTransgender personsTransgender womenSee more -
Outcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo20
Summary
Outcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo20
Views151Abstract
Objective:
To present a series of cases with our initial experience and short-term outcomes of a modified vaginal mucosal flap urethroplasty.
Methods:
Patients diagnosed with urethral stricture and operated by the same operative technique between January 2012 and January 2018 were followed for at least 6 months. Uroflowmetry and clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Results:
Nineteen patients were included with an average age of 56.4 years, mean preoperative Qmax of 5.3 ml/s, and PVR of 101.4 mL. After 6 months of the procedure, the mean Qmax improved to 14.7 mL/s (p<0.05), PVR decreased to 47.3 mL (p<0.05), and 84.2% of all patients reported improvement in clinical self-reported symptoms. There was an improvement in symptoms such as voiding effort in 84.2% of patients, weak stream (89.5%), and recurrent urinary tract infection (85.7%). The success rate (absence of symptoms and normal Qmax with no significant PVR) of the procedure was 84.2%.
Conclusion:
The described technique was considered effective for the treatment of female urethra stricture, with a high clinical success rate and an objective improvement of Qmax and decrease in PVR after 6 months of the procedure.
Key-words Urethral strictureUrethroplastyUrinary bladder neck obstructionUrological surgical proceduresSee more -
Original Article
Sexuality of Female Spina Bifida Patients: Predictors of a Satisfactory Sexual Function
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(6):467-473
Summary
Original ArticleSexuality of Female Spina Bifida Patients: Predictors of a Satisfactory Sexual Function
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(6):467-473
Views1See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the sexual function of women with spina bifida (SB), and to verify the factors that influence their sexual function.
Methods
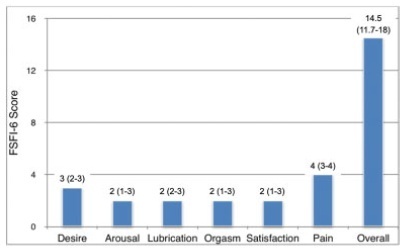
A cross-sectional study in which a validated female-specific questionnaire was applied to 140 SB female patients from four different cities (Porto Alegre, Brazil; and Barcelona, Madrid, and Málaga, Spain) between 2019 and 2020. The questionnaires collected data on the clinical characteristics of SB, and female sexual function was assessed using the 6-item version of the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6) validated to Portuguese and Spanish.
Results
Half of the patients had had sexual activity at least once in the life, but most (57.1%) did not use any contraception method. Sexual dysfunction was present in most (84.3%) patients, and all sexual function domains were impaired compared those of non-neurogenic women. The presence of urinary and fecal incontinence significantly affected the quality of their sexual activity based on the FSFI-6.
Conclusion
The specific clinical aspects of the SB patients, such as urinary and fecal incontinence, should be properly addressed by their doctors, since they are associated with reduced sexual activity and lower FSFI-6 scores in the overall or specific domains. There is also a need to improve gynecological care among sexually-active SB patients, since most do not use any contraceptive methods and are at risk of inadvertent pregnancy.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)