Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):443-448
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700007
Purpose: to determine the main factors associated with the occurrence of surgical site infection in patients submitted to total abdominal hysterectomy at the Instituto Materno ¾ Infantil de Pernambuco (iMIP). Methods: a cross-sectional study was conducted, enrolling patients submitted to total abdominal hysterectomy at IMIP who returned to postsurgical consultation for infection control, between January, 1995 and December, 1998 (n = 414). The frequency of surgical site infection (defined according to the CDC criteria, 1998) was 10% (42 cases). Prevalence risk (PR) of infection (dependent variable) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated for independent variables: age, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, malignant pathology, type of incision, duration of surgery and antibiotic prophylaxis. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to determine adjusted risk of infection. Results: a significantly increased risk of infection was found for the following variables: age >60 years (PR = 2.39, 95% CI = 1.15-4.94), obesity (PR = 3.2, 95% CI = 1.83-5.59), duration of surgery >2 hours (PR = 2.35, 95% CI = 1.32-4.21) and diabetes (PR = 6.0, 95% CI = 3.41-10.57). On the other hand, risk of infection was significantly reduced when antibiotic prophylaxis was administered (PR = 0.38, 95% CI = 0.21-0.68). Type of incision, malignant disease and hypertension were not associated with infection. Conclusions: the factors associated with increased risk of surgical site infection after total abdominal hysterectomy at IMIP were: age >60 years, obesity, diabetes and surgical duration >2 hours. Antibiotic prophylaxis showed a protective effect with reduction of risk of infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):421-428
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700004
Purpose: to evaluate 24 cases of gastroschisis, in relation to the prognostic factors that interfered with postnatal outcome. Patients and Method: twenty-four pregnancies with fetal prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of gastroschisis, during an 8-year period, were analyzed. Gastroschisis was classified into isolated, when there were no other structural abnormalities, or associated, when other abnormalities were present. For both groups the following parameters were examined: ultrasound bowel dilatation (>18 mm), obstetric complications and postnatal outcome. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney and exact Fisher's tests were used for statistical analyses. Results: in 9 cases (37.5%) gastroschisis was associated with other abnormalities, and in 15 cases it was isolated (62.5%). All cases of associated gastroschisis had a letal prognosis, therefore the overall mortality rate was 60.8%. In the group of isolated gastroschisis, all were born alive and were submitted to surgery, but the survival rate after surgical correction was 60%. The median gestational age at birth was 35 weeks and birth weight 2,365 grams. Premature delivery was observed in 10 cases, mainly as a consequence of obstetric complication. Two newborns were small for gestational age, and only 3 had birth weight >2,500 grams. Oligohydramnios was found in 46.6% and it was more frequent in the group of postnatal death (66.7%). Ultrasound assessment of bowel showed bowel dilatation in 86.6%, however, without relation to the prognosis and postnatal bowel findings. There was no significant difference between gestational age at birth and birth weight comparing the survivor and postnatal death groups. Conclusions: isolated gastroschisis had a better prognosis when compared to associated, therefore this prenatal differentiation is important. Isolated gastroschisis was often associated with prematurity, small birth weight and obstetric complications. Prenatal diagnosis allows better monitoring of fetal and obstetric conditions. Delivery should be at term, unless presenting with obstetric complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):435-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700006
Purpose: to describe sociodemographic characteristics of a group of climacteric women in order to discover the frequency and the variables associated with obesity and android profile of body fat distribution. Methods: an observational study was carried out in 518 patients aged 45 to 65 years, in a climacterium outpatient clinic. Age, color, menopausal status, duration of menopause, physical activity, smoking status, diet, alcohol intake, personal and family antecedents of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia and obesity were considered. Body mass index and the waist/hip ratio were the dependent variables. For the statistical analysis Wilcoxon test, Pearson's correlation coefficient, with a 5% level of significance, and multivariate analysis using regression model were used. Results: more than two thirds of the participants were nonobese with an android profile and postmenopausal. One fourth had physical activity and were smokers; half reported an inadequate diet and one fifth were alcoholics. Patients with an android profile presented higher mean age than women with gynecoid pattern. Personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes and family history of diabetes were related to obesity and android pattern. Postmenopausal status was significantly associated with the android profile. Conclusions: the majority of the participants were nonobese with an android profile, white, postmenopausal, sedentary, neither smokers nor alcoholics. The main factors related to obesity and android pattern were personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes, family history of diabetes and particularly, postmenopausal status with android profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):359-364
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500009
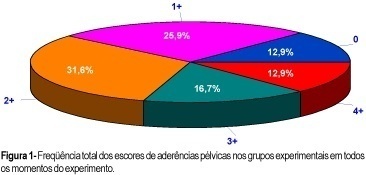
PURPOSE: to evaluate the degree of pelvic adhesions in function of time and the different substances used in its prophylaxis. MATERIAL AND METHODS: prospective study with 120 female, albino, virgin Wistar rats, 3 to 4 months of age, weighing approximately 250 g, randomly divided into 10 groups of 12 animals each: control, without lesion; lesions and without treatment; lesions + 0.9% physiologic saline, lesions + Ringer lactate; lesions + 32% dextran 70; lesions + Ringer lactate/heparin; lesions + Ringer lactate/dexamethasone; lesions + Ringer lactate/hydrocortisone/dexamethasone/ampicillin; lesions + Ringer lactate/albumin, and lesions + 1% carboxymethylcellulose. The animals were anesthetized and two types of lesions (scarification and electrocauterization) were performed in the uterine horns, followed by treatment with the solutions, intraperitoneally, to prevent pelvic adhesions. On the 7th, 14th and 28th postoperative days, moments M1, M2 and M3, respectively, the presence of adhesions was evaluated in 4 rats of each group. The methods applied to the quantification of the adhesions were based on Cohen's classification, with scores varying from 0 to 4+ according to the amount, characteristics and location of the adhesions. Statistical analysis was performed by parametric tests for analysis of variance and the Kruskal-Wallis test. RESULTS: the best treatments for prevention of pelvic adhesions in female rats were Ringer lactate/dexamethasone (score 1+ prevalence), 32% dextran 70 to (score 2+ prevalence) and Ringer lactate/hydrocortisone/dexamethasone/ampicillin (score 2+ prevalence). The postoperative period, represented by moment M3, and the surgical technique, predominantly with score 0, influenced adhesiolysis and maintenance of pelvic adhesions in female rats. CONCLUSIONS: the prevention of pelvic adhesions in female rats begins with the surgical process at a smaller extent of tissue damage. The use of prophylactic substances (solutions) had a varied effectiveness, since some were more efficient than others.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):149-154
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300002
PURPOSE: to describe the frequency of clinical and laboratorial findings in pregnant women with malaria. METHODS: a descriptive study was performed including 445 pregnant women with a positive diagnosis of malaria of the Maternity and women's Clinic Bárbara Heliodora (Rio Branco, Acre State), from January 1996 to December 2001. These cases were reviewed and the pregant women with malaria were selected. RESULTS: a total of 33,420 patients were hospitalized in that period. Of these, 445 pregnant women (1.4%) were included. Among these, the frequency of the infection with Plasmodium vivax was 52.8% (n=235), with P. falciparum, 43.8% (n=195), and 3.4% (n=15) with both plasmodia. The most frequent clinical and laboratorial alterations (p<0.05) were observed in the patients with P. falciparum: pale mucosa, jaundice hemoglobin and hematocrit decrease, hypoglycemia and increase in serum aminotransferase, urea, creatinine and in bilirubin levels. Only one patient (1/445), a pregnant woman infected with P. falciparum died. Abortions, premature birth and low birth weight were detected in 1.3, 1.1 and 1.1% of the cases, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: these findings reflect the repercussion of malaria during pregnancy, and justify the existence of qualified medical care in obstetric units for diagnosis and treatment of these cases, especially in the Amazon region.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):155-161
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300003
PURPOSE: the morbidity in HIV-positive patients due to puerperal fever was studied and correlated to the method and duration of labor, the duration of premature rupture of the membranes, CD4+ cell count and the viral load (VL) at peridelivery. METHODS: a total of 207 HIV-positive women with prenatal examinations and deliveries between May 1997 and December 2001 were enrolled. Of these, 32 had natural childbirth and 175 had a cesarean section. Of the total of enrolled patients, 62.8% were submitted to elective cesarean section. The average age of the group was 27.4 years, and 25.6% were nulliparous and 26% were primiparous. At the moment of the delivery the average gestational age was 37.8 weeks. At the end of pregnancy the average of the CD4+ cell count was approximately 481 cells/mm³ and the viral load 49,100 copies/mL. RESULTS: puerperal morbidity occurred in 34 patients, with 33 after cesarean section and one after natural childbirth. The most usual intercurrent post-cesarean infection was that of the surgical wound (13% of the infection cases). Analyzed factors, such as delivery duration, duration of rupture of the membranes, number of CD4+ cells or the viral load at peridelivery, did not interfere in puerperal morbidity. CONCLUSIONS: puerperal morbidity was 16.8% and occurred more frequently after cesarean sections (18.9%) than after vaginal deliveries (3.1%). The other factors did not present a significant effect on puerperal morbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):163-167
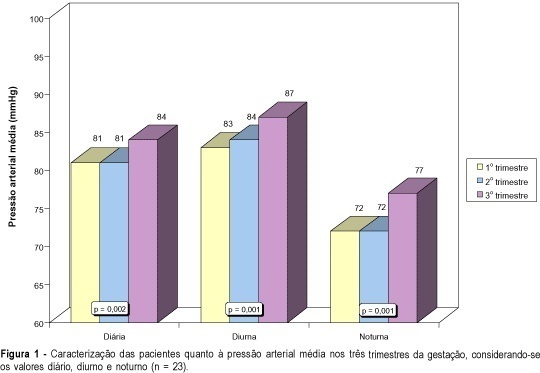
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300004
PURPOSE: to show longitudinally the profiles and parameters of pressure rhythm and heart rate in normotensive pregnant women during the three trimesters of pregnancy. PATIENTS AND METHODS: the longitudinal and random study involved 23 normotensive pregnant women, mean age 23.3 ± 3.9 years, recruited from the prenatal clinics of the "Maternidade-Escola Hilda Brandão - Santa Casa de Belo Horizonte/MG". Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was done every three months (up to 14 weeks, between 18 and 28 weeks and between 32 and 40 weeks, using the SpaceLabs monitor, model 90207. RESULTS: a significant increase (p<0.01) in the 24-h systolic (115 and 104 mmHg), diastolic (73 and 61 mmHg) and average diurnal and nocturnal blood pressures (87 and 77 mmHg respectively), was noticed in the third trimester of pregnancy. Mother's diurnal blood pressure and heart rate (83, 84 and 87 mmHg; 94, 95 and 93 bpm) were significantly higher than the nocturnal measurements (72, 72 and 77 mmHg; 74, 79 and 79 bpm), in the three trimesters. Mother's heart frequency did not change during progress of pregnancy. CONCLUSION: increase in blood pressure during the third trimester of pregnancy could be shown. Maternal daily and diurnal heart rate did not change when the three trimesters were compared. The nocturnal heart rate was significantly lower in the first trimester as compared to the other trimesters.