Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-28-2022;44(5):540-547
The present systematic review (PROSPERO: CRD42020148630) hypothesizes the association of excessive weight gain during pregnancywith dietary patterns composed of ultraprocessed foods. Thus, the objective was to investigate the association between dietary patterns after analysis and weight gain during pregnancy. The search for articles was performed in nine databases. Two reviewers selected the articles in the databases and extracted from them the data used in the review. Two scales were used to evaluate the quality of the selected studies: New Castle-Ottawa Quality Assessment for cohort-based studies and Appraisal tool for Cross-Sectional Studies (AXIS) for cross-sectional-based studies. In total, 11 studies were identified with sample size variation (n=173-5,733). Women presenting more adherence to healthy and traditional patterns (fruits, vegetables, salads, nuts, and dairy) recorded less excessive gestational weight gain (GWG). Higher intake ofmixed patterns and western patterns rich in ultraprocessed foods were associated with a higher prevalence of excessive GWG (24.48- 55.20%). Gestational dietary patterns a posteriori-derived that have presented ultraprocessed components rich in fat and sugars presented association with high GWG; healthy and traditional dietary patterns were related to better mother-child health conditions, such as adequate GWG.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-11-2022;44(5):519-531
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 02-18-2022;44(5):511-518
The Burch procedure (1961) was considered the gold standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) before the midurethral slings (MUSs) were introduced, in 2001.
This historical perspective of the Burch’s timeline can encourage urogynecological surgeons to master the Burch technique as one of the options for surgical treatment of SUI.
Criteria A bibliographic search was performed in the PubMed and National Library of Medicine (NIH) databases with the terms Burch colposuspension AND history AND stress urinary incontinence in the last 20 years. The original article by Burch (1961) was included. The references were read by three authors. The exclusion criterion was studies in non-English languages. Biomedical Library Special Collections were included as historical relevant search.
Some modifications of the technique have been made since the Burch procedure was first described. The interest in this technique has been increasing due to the negative publicity associated with vaginal synthetic mesh products. Twenty-nine relevant articles were included in the present review article, and numerous trials have compared Burch colposuspension with MUS.
This historical perspective enables the scientific community to review a standardized technique for SUI. Burch colposuspension should be considered an appropriate surgical treatment for women with SUI, and an option in urogynecological training programs worldwide.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 02-17-2022;44(5):503-510
To evaluate the impact of surgical treatment of deep infiltrative endometriosis (DIE) on pelvic floor dysfunction (urinary incontinence [UI], pelvic organ prolapse [POP], fecal incontinence [FI)] or constipation, and sexual function [dyspareunia]).
The present systematic review was performed in the PubMed database. For the selection of studies, articles should be published by January 5, 2021, without language restriction.
Six randomized controlled studies that evaluated surgical treatment for DIE and the comparison of different surgical techniques were included.
The studies were selected independently by title and abstract by two authors. Disagreements were resolved by a third author. All included studies were also evaluated according to the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the quality of the evidence was analyzed using the GRADE criteria. Subgroup analysis by different treatments and follow-up periods was also performed.
Six studies were included in the quantitative analysis. The risk of bias between studies showed an uncertain risk of bias for most studies, with concealment of allocation being the least reported category. The quality of the evidence was considered low. High heterogeneity was found between the studies. No study has evaluated UI or POP comparatively before and after surgery.
Dyspareunia and FI have improved after the surgical procedure, but it was not possible to demonstratewhich surgical technique was related to these outcomes as there was surgical heterogeneity. This diversity was found across data, with the recommendation of future prospective studies addressing pelvic floor disorders withDIE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 02-09-2022;44(5):532-539
The present article seeks to consolidate existing knowledge on breastfeeding during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
Articles from 2020 and 2021 collected from the PubMed, CAPES, Virtual Health Library, Google Scholar, SciELO, and UpToDate databases were analyzed. Books and government documents published in the last decade (2010-2020) were also consulted.
Sixteen works were used in the present study. The date of publication and discussion of SARS-CoV-2 transmission through breastmilk were the inclusion criteria. Thus, articles containing repeated information or with no relevance to add to the production were excluded. Data collection comprised critical reading and synthesis of the main information obtained on the subject, which were performed for the preparation of the present study. The research took place in the period from March 27 to April 2, 2021.
Breast milk has diverse benefits for both the nursing mother and the infant. The presence of viral RNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) in milk from disease-positive mothers has been detected in a few cases, and infant infections in these conditions suggest oral transmission of maternal or third-party origin. The virulence of the novel coronavirus in human milk is not confirmed, while significant amounts of exclusive antibodies are.
Lactation in the context of COVID-19 has shown greater benefits than risks of vertical transmission. Therefore, it should be encouraged when possible.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-01-2017;39(6):294-308
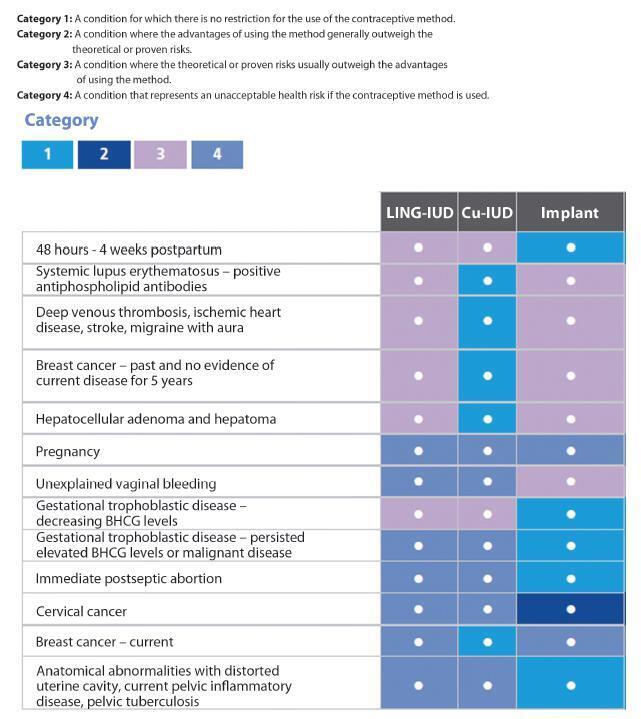
Unwanted pregnancy is a major public health problem both in developed and developing countries. Although the reduction in the rates of these pregnancies requires multifactorial approaches, increasing access to long-acting contraceptive methods can contribute significantly to change this scenario. In Brazil, gynecologists and obstetricians play a key role in contraceptive counseling, being decisive in the choice of long-acting reversible methods, characterized by intrauterine devices (IUDs) and the contraceptive implant. The vast scope due to the reduced number of situations to indicate long-acting methods should be emphasized in routine contraceptive counseling. On the other hand, gynecologists and obstetricians should adapt the techniques of insertion of long-acting methods, and engage in facilitating conditions to access these contraceptives through public and private health systems in Brazil. This study is part of a project called Diretrizes e Recomendações FEBRASGO (Guidelines and Recommendations of the FEBRASGO - Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations from the Portuguese acronym). It aims to review the main characteristics of long-acting contraceptives and critically consider the current situation and future prospects to improve access to these methods, proposing practical recommendations of interest in the routine of gynecologists and obstetricians.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 01-01-2015;37(1):42-51
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005198
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) is the term to describe a set of malignant placental diseases, including invasive mole, choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor. Both invasive mole and choriocarcinoma respond well to chemotherapy, and cure rates are greater than 90%. Since the advent of chemotherapy, low-risk GTN has been treated with a single agent, usually methotrexate or actinomycin D. Cases of high-risk GTN, however, should be treated with multiagent chemotherapy, and the regimen usually selected is EMA-CO, which combines etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide and vincristine. This study reviews the literature about GTN to discuss current knowledge about its diagnosis and treatment.