Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):147-155
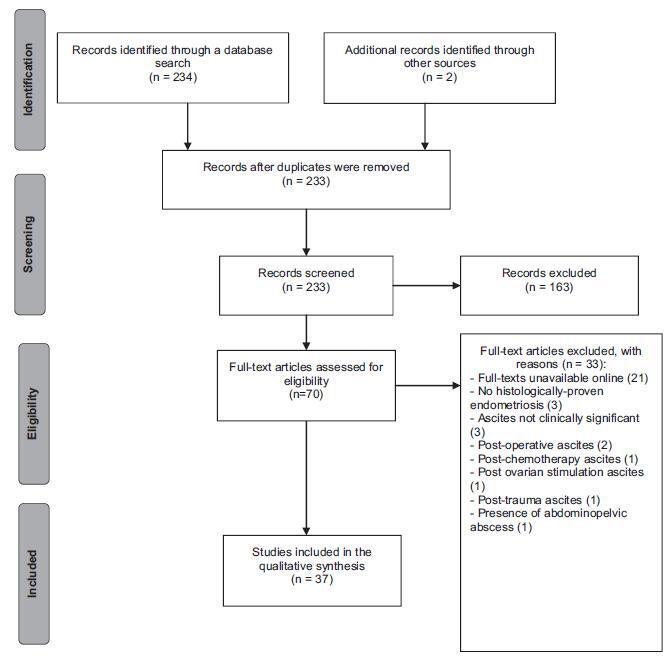
Endometriosis can have several different presentations, including overt ascites and peritonitis; increased awareness can improve diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. We aimto provide a systematic review and report a case of endometriosis with this unusual clinical presentation. The PubMed/MEDLINE database was systematically reviewed until October 2016. Women with histologically-proven endometriosis presenting with clinically significant ascites and/or frozen abdomen and/or encapsulating peritonitis were included; thosewith potentially confounding conditionswere excluded.Our search yielded 37 articles describing 42 women, all of reproductive age. Ascites was mostly hemorrhagic, recurrent and not predicted by cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) levels. In turn, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia and infertility were not consistently reported. The treatment choices and outcomes were different across the studies, and are described in detail. Endometriosis should be a differential diagnosis of massive hemorrhagic ascites in women of reproductive age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):156-162
Venous thromboembolism events are important causes of maternal death during pregnancyandthepostpartumperiodworldwide.Are view of the literature with the objective of evaluating venous thromboembolism events in the puerperium according to the route of delivery was performed through a bibliographic survey in the Medline, LILACS and Scielo databases. We observed that patients submitted to cesarean sections present a significantlyhigher riskofdeveloping venousthromboembolismwhencomparedwiththose who undergo spontaneous vaginal delivery. The pathophysiological bases for this difference were explored and described in this review, as well as the indications of prophylaxis and treatment. Doctors and health professionals must be continuously vigilant regarding this condition, since it is associated with high morbidity and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):96-102
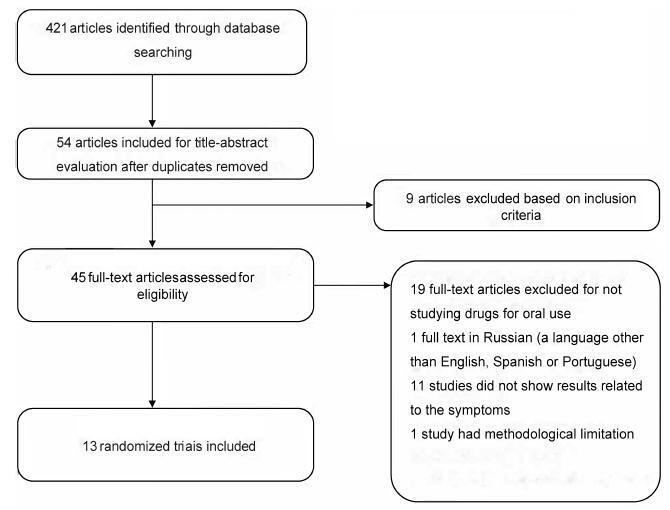
Interstitial cystitis (IC), including bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is a chronic and debilitating disease thatmainly affectswomen. It is characterized by pelvic pain associated with urinary urgency, frequency, nocturia and negative urine culture,with normal cytology. In 2009, the Society for Urodynamics and Female Urology (SUFU) defined the term IC/BPS as an unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, and discomfort) perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with lower urinary tract symptoms for more than 6 weeks duration, in the absence of infection or other identifiable causes. This is the definition used by the American Urological Association (AUA) in the most recent guidelines on IC/BPS. Interstitial cystitis may be sufficiently severe to have a devastating effect on the quality of life, but it may also be associated with moderate symptoms whose effects are less debilitating. Although there are several clinical trials to assess oral and intravesical therapies, the treatment for IC remains far from ideal. This systematic assessment evaluates published randomized clinical trials on oralmedications used totreat symptoms of BPS. This studywas performed according to the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaanalyses (PRISMA)method. Two independent reviewers screened the studies to determine their inclusion or exclusion and to perform the methodological analysis. The inclusion criteria included randomized studiespublishedbetween April of 1988and April of2016 that used oral medications to treat symptoms of BPS or IC. According to the systematic review performed,we should consider pentosan polysulfate as one of the bestoptions of oral drugs for the treatment of BPS symptoms. However, this drug is not an available option in Brazil. Orally administered amitriptyline is an efficacious medical treatment for BPS, and it should be the first treatment offered.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):32-42
Pregnancy is needed for the perpetuation of the human species, and it leads to physiological adaptations of the various maternal organs and systems. The eye, although a closed space, also undergoes some modifications, most of which are relatively innocuous, but they may occasionally become pathological. For women, pregnancy is a susceptibility period; however, for many obstetricians, their knowledge of the ocular changes that occur during pregnancy tends to be limited. For this reason, this is a important area of study as is necessary the development of guidelines to approach those changes. Of equal importance are the knowledge of the possible therapies for ophthalmological problems in this period and the evaluation of themode of delivery in particular conditions. For this article, an extensive review of the literature was performed, and a summary of the findings is presented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):676-685
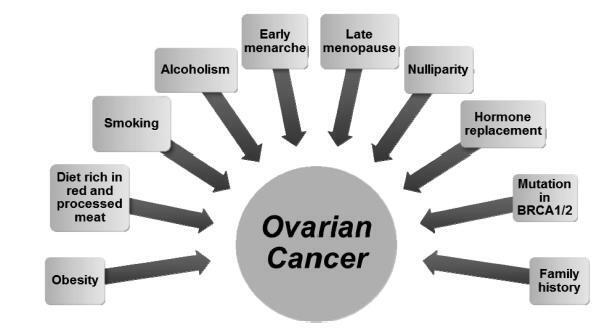
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among gynecologic tumors because in most of the cases (75%), the disease is diagnosed in advanced stages. Screening methods are not available since the disease is rare, and the tested methods, such as ultrasound and CA125, were not able to decrease the mortality rate for this type of cancer. This article discusses the main risk factors for ovarian cancer, and the potential clinical and surgical strategies for the prevention of this disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):560-568
To characterize the most common peripheral and central neurological disorders during pregnancy.
Original research and review of the literature on neurological complications during pregnancy. We searched for keywords related to the topic on different databases.
Pregnancy involves physiological changes that can trigger peripheral neurological and/or central nervous system pathologies, which can sometimes be associated with hypertensive disorders. A definitive diagnosis of neurological disorders can be made according to the trimester of pregnancy and the clinical findings. Carpal tunnel syndrome and peripheral facial palsy are common peripheral neurological disorders, more frequent in the second half of pregnancy. Central nervous disorders are more complex and a precise diagnosis must be made in order to improve perinatal outcomes, provide correct management and treatment and to prevent acute and long-term complications.
It is possible to achieve a precise diagnosis,management and treatment of neurological disorders during pregnancy, but these require a multidisciplinary approach, crucial to improve perinatal outcomes.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
The literature that supports and recommends the practice of exercise during pregnancy is extensive.However, although a more complete research on ways to evaluate the physical activity performedby pregnant women has been perfomed, it is found that there is no gold standard and that the articles in the area are inconclusive. Thus, the objective of the present article is to review relevant aspects, such as, technique and applicability of the different methods for the assessment of physical activity during pregnancy to providemore reliable and safe information for health professionals to encourage their pregnant patients to engage in the practice of physical activity. This review concluded that all tools for the analysis of physical activity have limitations. Thus, it is necessary to establish the objectives of evaluation in an appropriate manner, as well as to determine their viability and costeffectiveness for the population under study.