Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(4):207-214
Supplementation with folic acid (FA) during gestation has been recommended by medical society all over the world, but some studies have shown that intake of high folic acid diet may unleash damages to the descendants. Objectives: Describing the effects of maternal supplementation with FA during gestation on offspring's kidney at late life stages. Data Source: It is a systematic review by which were consulted the following databases: Medline, through Pubmed, Lilacs, and SciELO. The research was performed using the keywords “Folic acid”, “Gestation” and “Kidney”. Study Selection: Eight studies were regarded for this systematic review. Data Collection: Only studies that evaluated folic acid consumption during gestation and its effects exclusively on descendants' kidney at several phases of life were regarded. Results: Gestational FA intake did not change the renal volume, glomerular filtration rate and the expression of some essential genes in the kidney of puppies whose dams were supplemented with FA. Maternal consumption of double FA plus selenium diet was effective in preserving antioxidant enzymes activity in the kidney of descendants from mothers exposed to alcohol. FA supplementation decreased some gross anomalies in the puppies caused by teratogenic drug despite of had not been effective in preventing some renal architectural damages. Conclusion: FA supplementation did not cause renal toxicity; it exerted an antioxidant protective effect and mitigated some renal disorders caused by severe aggressions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(1):43-48
Physical and emotional burdens during the journey of infertile people through assisted reproductive technologies are sufficient to justify the efforts in developing patient-friendly treatment strategies. Thus, shorter duration of ovarian stimulation protocols and the need for less injections may improve adherence, prevent mistakes, and reduce financial costs. Therefore, the sustained follicle-stimulating action of corifollitropin alfa may be the most differentiating pharmacokinetic characteristic among available gonadotropins. In this paper, we gather the evidence on its use, aiming to provide the information needed for considering it as a first choice when a patient-friendly strategy is desired.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1134-1140
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)is an entity with evolving conceptual nuances that deserve full consideration. Gestational diabetes leads to complications and adverse effects on the mother's and infants' health during and after pregnancy. Women also have a higher prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) related to the hyperglycemic status during pregnancy. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is still uncertain. We conducted a narrative review discussing the impact of GDM on the women's pelvic floor and performed image assessment using three-dimensional ultrasonography to evaluate and predict future UI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1126-1133
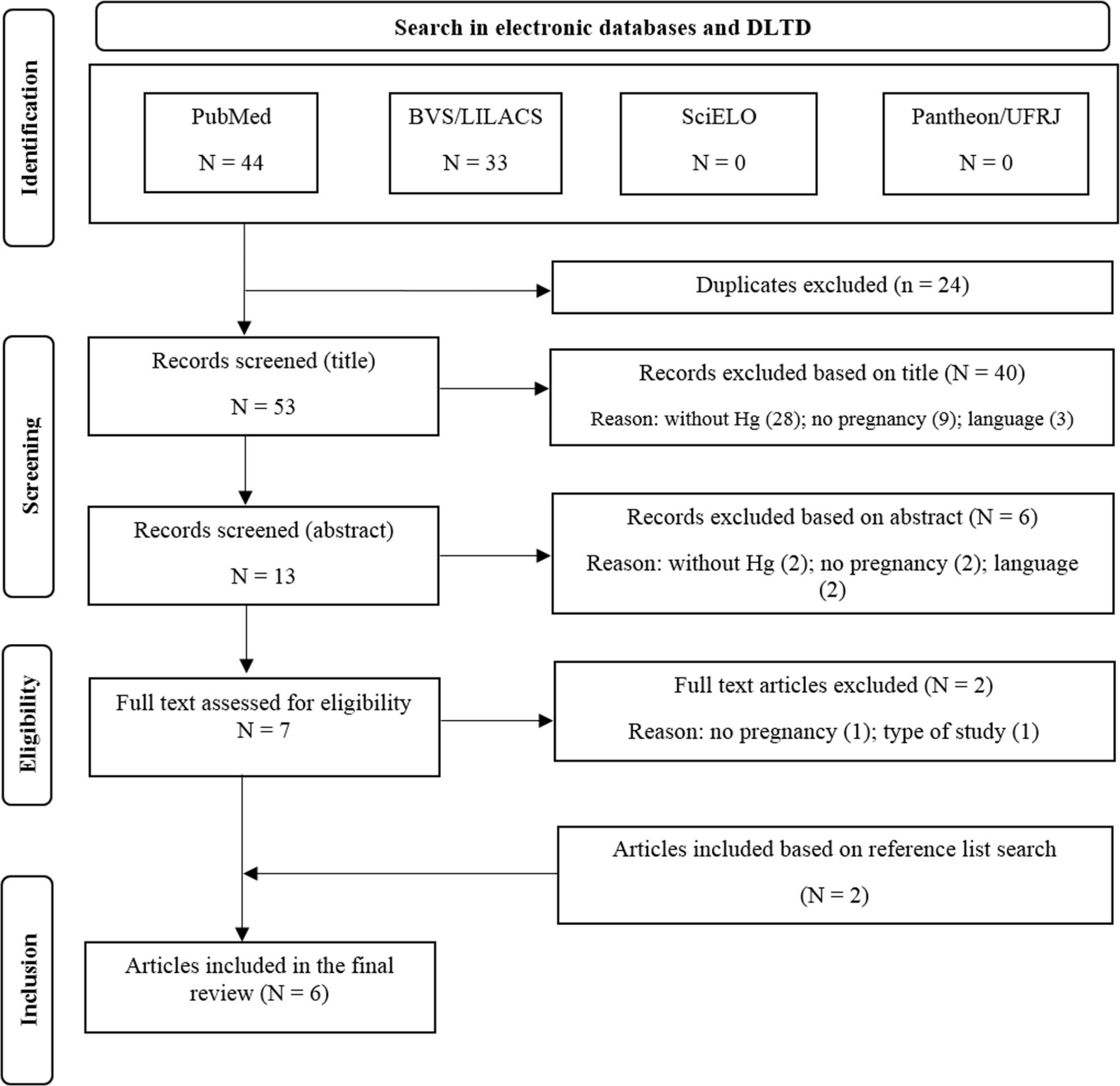
The present review aimed to synthesize the evidence regarding mercury (Hg) exposure and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP).
The PubMed, BVS/LILACS, SciELO and UFRJ's Pantheon Digital Library databases were systematically searched through June 2021.
Observational analytical articles, written in English, Spanish, or Portuguese, without time restriction.
We followed the PICOS strategy, and the methodological quality was assessed using the Downs and Black checklist.
We retrieved 77 articles, of which 6 met the review criteria. They comprised 4,848 participants, of which 809 (16.7%) had HDP and 4,724 (97.4%) were environmentally exposed to Hg (fish consumption and dental amalgam). Mercury biomarkers evaluated were blood (four studies) and urine (two studies). Two studies found a positive association between Hg and HDP in the group with more exposure, and the other four did not present it. The quality assessment revealed three satisfactory and three good-rated studies (mean: 19.3 ± 1.6 out 28 points). The absence or no proper adjustment for negative confounding factor, such as fish consumption, was observed in five studies.
We retrieved only six studies, although Hg is a widespread toxic metal and pregnancy is a period of heightened susceptibility to environmental threats and cardiovascular risk. Overall, our review showed mixed results, with two studies reporting a positive association in the group with more exposure. However, due to the importance of the subject, additional studies are needed to elucidate the effects of Hg on HDP, with particular attention to adjusting negative confounding.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Surrogacy is the process in which a woman carries and delivers a baby to other person or couple, known as intended parents. When carriers are paid for surrogacy, this is known as commercial surrogacy. The objective of the present work is to review the legal, ethical, social, and cultural aspects of commercial surrogacy, as well as the current panorama worldwide.
This is a review of the literature published in the 21st century on commercial surrogacy.
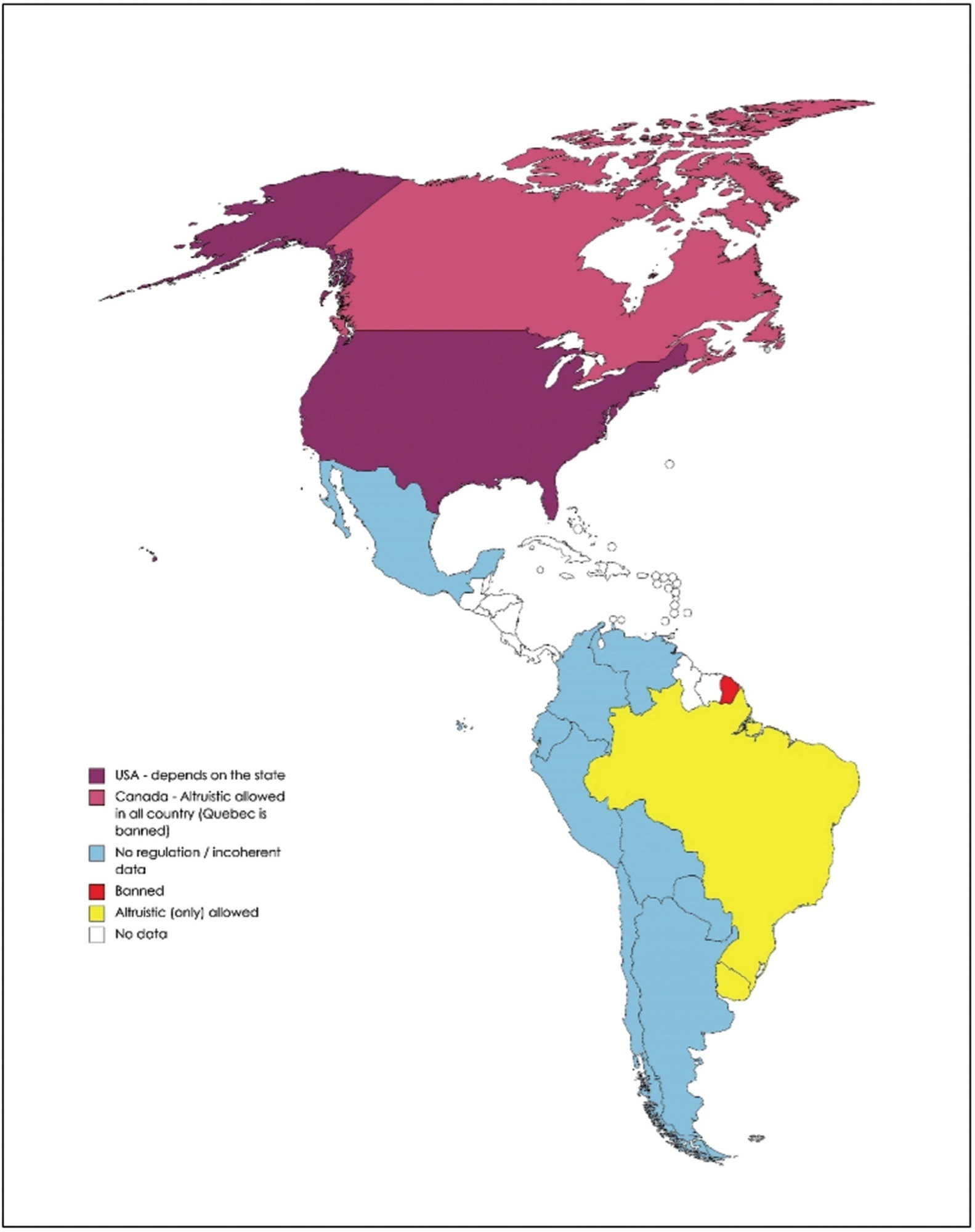
A total of 248 articles were included as the core of the present review. The demand for surrogate treatments by women without uterus or with important uterine disorders, single men and same-sex male couples is constantly increasing worldwide. This reproductive treatment has important ethical dilemmas. In addition, legislation defers widely worldwide and is in constant change. Therefore, patients look more and more for treatments abroad, which can lead to important legal problems between countries with different laws. Commercial surrogacy is practiced in several countries, in most of which there is no specific legislation. Some countries have taken restrictive measures against this technique because of reports of exploitation of carriers.
Commercial surrogacy is a common practice, despite important ethical and legal dilemmas. As a consequence of diverse national legislations, patients frequently resort to international commercial surrogacy programs. As of today, there is no standard international legal context, and this practice remains largely unregulated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1070-1077
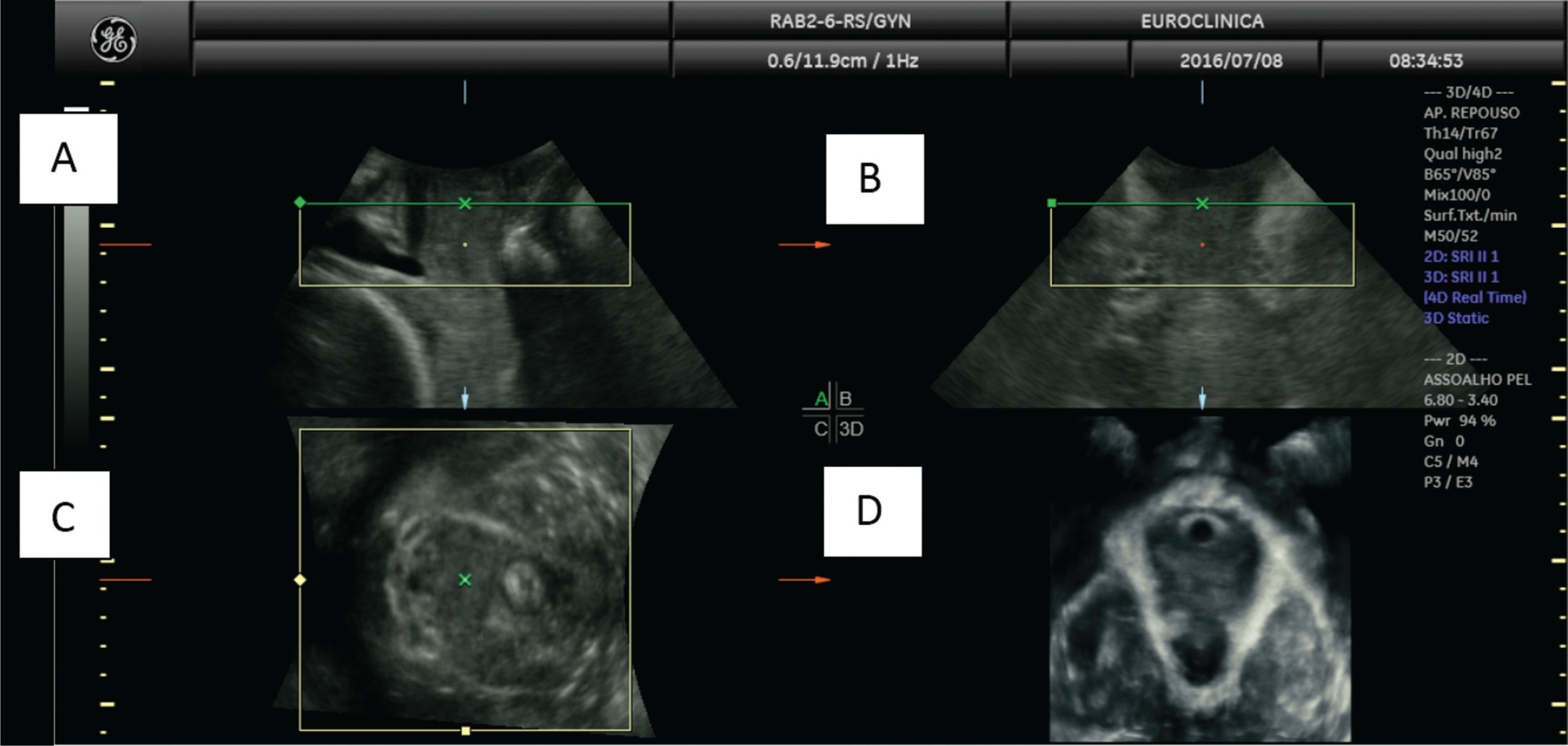
Ultrasonography is an instrument that is present in the maternal-fetal assessment throughout pregnancy and with widely documented benefits, but its use in intrapartum is becoming increasingly relevant. From the assessment of labor progression to the assessment of placental disorders, ultrasound can be used to correlate with physiological findings and physical examination, as its benefit in the delivery room cannot yet be proven. There are still few professionals with adequate training for its use in the delivery room and for the correct interpretation of data. Thus, this article aims to present a review of the entire applicability of ultrasound in the delivery room, considering the main stages of labor. There is still limited research in evidence-based medicine of its various possible uses in intrapartum, but it is expected that further studies can bring improvements in the quality of maternal and neonatal health during labor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(11):1059-1069
The aim of this study was to systematically review literature on the use of iron supplements (not including iron derived from diet), increased levels of hemoglobin and/or ferritin, and the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
The following databases were searched, from the study's inception to April 2021: PUBMED, Cochrane, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, Cinahl and Lilacs.
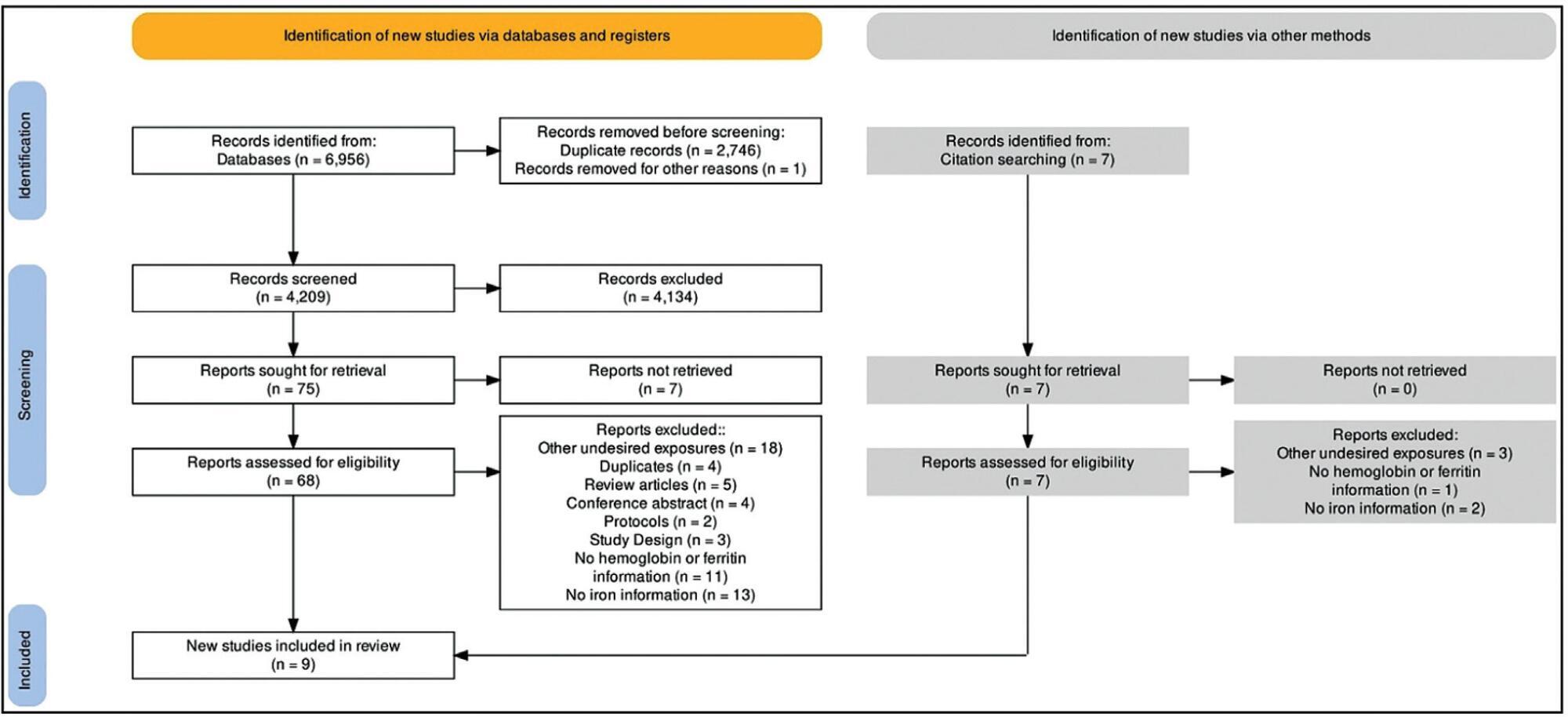
A total of 6,956 titles and abstracts were reviewed, 9 of which met the final inclusion criteria, with 7,560 women in total.
Data extraction was performed by two independent reviewers and disagreements were resolved by a third researcher.
Methodological quality in controlled trials were assessed according to the Cochrane Collaboration tools (ROB-2 and ROBINS-1) and for the observational studies, the National Institutes of Health's (NIH) quality assessment tool was used. Among the 5 observational studies, women with a higher hemoglobin or ferritin level were more likely to develop GDM when compared with those with lower levels of these parameters. Among the 3 randomized clinical trials, none found a significant difference in the incidence of GDM among women in the intervention and control groups. However, we identified many risks of bias and great methodological differences among them.
Based on the studies included in this review, and due to the important methodological problems pointed out, more studies of good methodological quality are needed to better establish the association between iron supplementation and GDM.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):986-994
To evaluate the efficacy of the hormonal and nonhormonal approaches to symptoms of sexual dysfunction and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women.
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, SciELO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) databases, as well as on clinical trial databases. We analyzed studies published between 1996 and May 30, 2020. No language restrictions were applied.
We selected randomized clinical trials that evaluated the treatment of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women.
Three authors (ACAS, APFC, and JL) reviewed each article based on its title and abstract. Relevant data were subsequently taken from the full-text article. Any discrepancies during the review were resolved by consensus between all the listed authors.
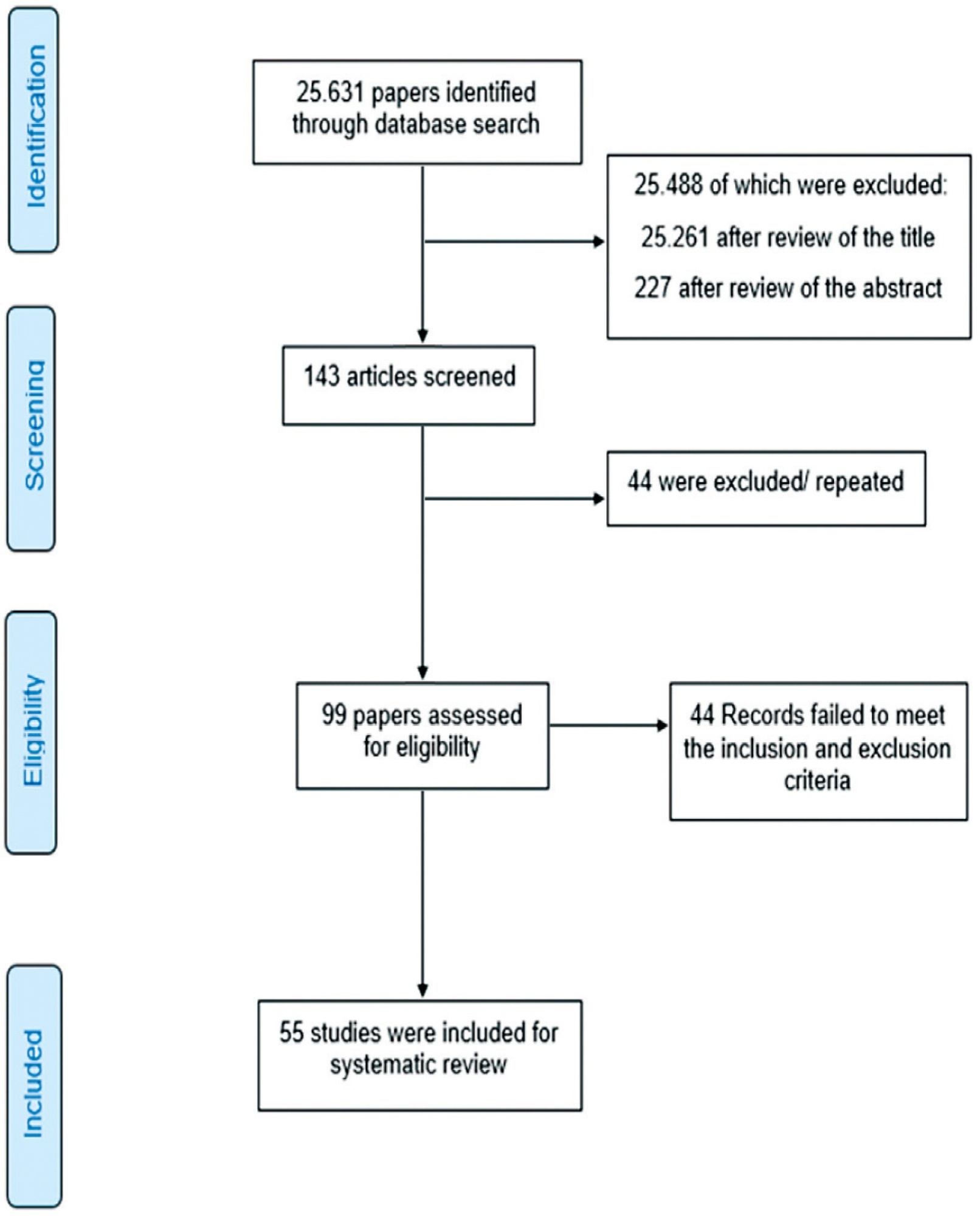
A total of 55 studies were included in the systematic review. The approaches tested to treat sexual dysfunction were as follows: lubricants and moisturizers (18 studies); phytoestrogens (14 studies); dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; 8 studies); ospemifene (5 studies); vaginal testosterone (4 studies); pelvic floor muscle exercises (2 studies); oxytocin (2 studies); vaginal CO2 laser (2 studies); lidocaine (1 study); and vitamin E vaginal suppository (1 study).
We identified literature that lacks coherence in terms of the proposed treatments and selected outcome measures. Despite the great diversity in treatment modalities and outcome measures, the present systematic review can shed light on potential targets for the treatment, which is deemed necessary for sexual dysfunction, assuming that most randomized trials were evaluated with a low risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. The present review is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42018100488).