-
Review Article04-08-2022
Transcutaneous Nerve Electrostimulation (TENS) in Pain Relief During Labor: A Scope Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):187-193
Abstract
Review ArticleTranscutaneous Nerve Electrostimulation (TENS) in Pain Relief During Labor: A Scope Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):187-193
Views268See moreAbstract
Objective
To map health evidence on the effectiveness of transcutaneous nerve electrostimulation (TENS) therapy in pain relief during delivery.
Methods
This is a scoping review in the PubMed, LILACS, Cochrane, VHL, PEDRO, and SciELO databases, through the descriptors electric stimulation, transcutaneous and labor, obstetric and their synonyms.
Results
A total of 263 studies were identified, of which 54 duplicates were excluded. After sorting by titles and abstracts, there were 24 articles for reading, remaining 6. The six studies evaluated the reduction of pain through the visual analogue scale (VAS).
Conclusion
The findings indicate that the use of TENS as a nonpharmacological strategy for pain relief in labor has positive results.
-
Review Article04-08-2022
Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Gynecological Health: An Integrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):194-200
Abstract
Review ArticleEffects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Gynecological Health: An Integrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):194-200
Views209Abstract
Objective
To analyze the existing scientific literature to find out if the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has an effect on gynecological health.
Search Strategy
We performed an integrative review of articles published between April 2020 and April 2021 on the PubMed, SciELO, and LILACS databases, using COVID-19 and the following relevant terms: Menstrual change; Ovarian function; Violence against women; Contraception; HPV; Mental health; and Urogynecology.
Selection Criteria
Among the eligible studies found, editorials and primary research articles, which describe the dynamics between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection (the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic) and gynecological health, were included.
Data Collection and Analysis
Through qualitative synthesis, data were extracted from the included publications and from guidelines of national and international societies of gynecology.
Main Results
The 34 publications included in the present study showed that some factors of the SARS-CoV-2 infection, and, consequently, the COVID-19 pandemic, might be associated with menstrual abnormalities, effects on contraception, alterations in steroid hormones, changes in urogynecological care, effects on women’s mental health, and negative impact on violence against women.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the health of women. The scientific community encourages the development of recommendations for specialized care for women and strategies to prevent and respond to violence during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Key-words ContraceptionCOVID-19 pandemicmenstrual changeovarian functionSARS-CoV-2urogynecologyViolence against womenSee more -
Review Article02-28-2022
Perinatal Outcomes after Fetal Endoscopic Tracheal Occlusion for Isolated Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Rapid Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
Abstract
Review ArticlePerinatal Outcomes after Fetal Endoscopic Tracheal Occlusion for Isolated Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Rapid Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):74-82
Views169Abstract
Objective
To compare the perinatal outcomes of fetuses with isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia after fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion (FETO) and antenatal expectant management.
Data sources
In this rapid review, searches were conducted in the MEDLINE, PMC, EMBASE and CENTRAL databases between August 10th and September 4th, 2020. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-RCTs or cluster-RCTs published in English in the past ten years were included.
Study selection
We retrieved 203 publications; 180 studies were screened by abstract. Full-text selection was performed for eight studies, and 1 single center RCTmet the inclusion criteria (41 randomized women; 20 in the FETO group, and 21 in the control group).
Data collection
Data collection was performed independently, by both authors, in two steps (title and abstract and full-text reading).
Data synthesis
There were no cases of maternal mortality. The mean gestational age at delivery was of 35.6±2.4 weeks in the intervention group, and of 37.4±1.9 weeks among the controls (p<0.01). Survival until 6 months of age was reported in 50% of the intervention group, and in 5.8% of the controls (p<0.01; relative risk: 10.5; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.5-74.7). Severe postnatal pulmonary hypertension was found in 50% of the infants in the intervention group, and in 85.7% of controls (p=0.02; relative risk: 0.6; 95%CI: 0.4-0.9). An analysis of the study indicated some concerns of risk of bias. The quality of evidence was considered moderate to low.
Conclusion
Current evidence is limited but suggests that FETO may be an effective intervention to improve perinatal outcomes.
Key-words congenital diaphragmatic herniasPrenatal ultrasonographyPrognosissystematic reviewultrasound diagnosisSee more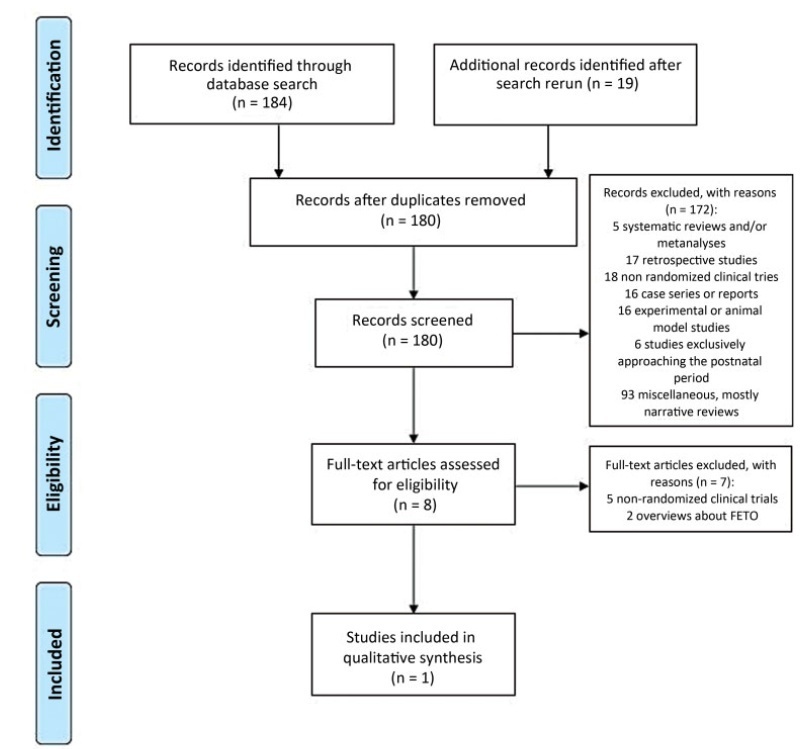
-
Review Article02-28-2022
Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
Views383Abstract
Objective
To summarize the available evidence of TAP Block in efficacy in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy.
Data Sources
We searched databases and gray literature for randomized controlled trials in which transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block was compared with placebo or with no treatment in patients who underwent laparoscopic or robot-assisted hysterectomy.
Method of Study
Selection Two researchers independently evaluated the eligibility of the selected articles. Tabulation, Integration, and Results Seven studies were selected, involving 518 patients. Early postoperative pain showed a difference in the mean mean difference (MD): - 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI]: - 1.87-0.46) in pain scale scores (I2=68%), which was statistically significant in favor of using TAP block, but without clinical relevance; late postoperative pain: DM 0.001 (95%CI: - 0.43-0.44; I2=69%); opioid requirement: DM 0.36 (95%CI: - 0.94-1.68; I2=80%); and incidence of nausea and vomiting with a difference of 95%CI=- 0.11 (- 0.215-0.006) in favor of TAP.
Conclusion
With moderate strength of evidence, due to the high heterogeneity and imbalance in baseline characteristics among studies, the results indicate that TAP block should not be considered as a clinically relevant analgesic technique to improve postoperative pain in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy, despite statistical significance in early postoperative pain scale scores.
Key-words laparoscopic hysterectomyOpioidPainrobotic-assisted hysterectomytransversus abdominis plane blockSee more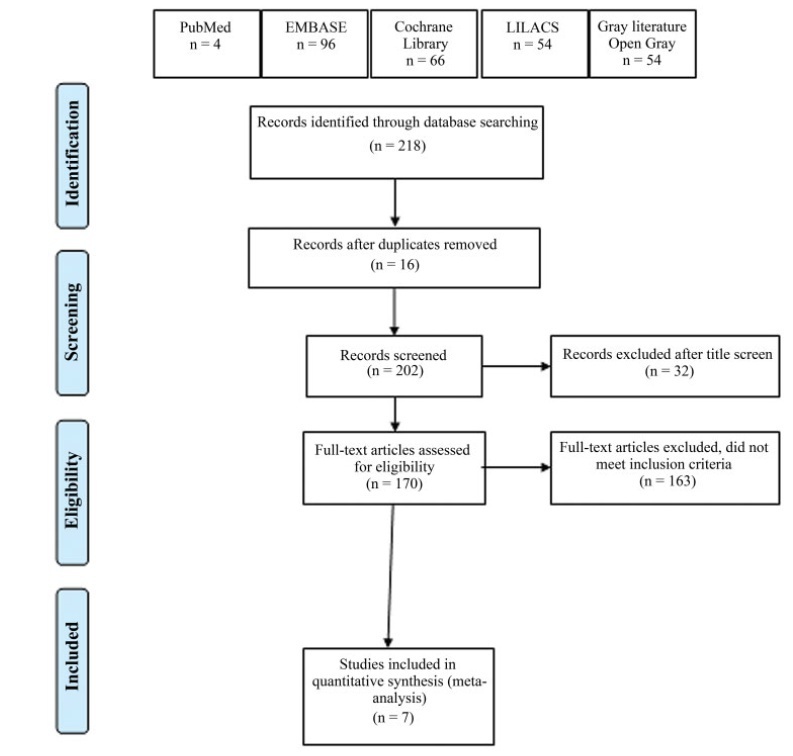
-
Review Article02-28-2022
Underestimation Rate in the Percutaneous Diagnosis of Radial Scar/Complex Sclerosing Lesion of the Breast: Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):67-73
Abstract
Review ArticleUnderestimation Rate in the Percutaneous Diagnosis of Radial Scar/Complex Sclerosing Lesion of the Breast: Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):67-73
Views140See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the underestimation rate in breast surgical biopsy after the diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion through percutaneous biopsy.
Data Sources
A systematic review was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations. The PubMed, SciELO, Cochrane, and Embase databases were consulted, with searches conducted through November 2020, using specific keywords (radial scar OR complex sclerosing lesion, breast cancer, anatomopathological percutaneous biopsy AND/OR surgical biopsy).
Data collection
Study selection was conducted by two researchers experienced in preparing systematic reviews. The eight selected articles were fully read, and a comparative analysis was performed.
Study selection
A total of 584 studies was extracted, 8 of which were selected. One of them included women who had undergone a percutaneous biopsy with a histological diagnosis of radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion and subsequently underwent surgical excision; the results were used to assess the underestimation rate of atypical and malignant lesions.
Data synthesis
The overall underestimation rate in the 8 studies ranged from 1.3 to 40% and the invasive lesion underestimation rate varied from 0 to 10.5%.
Conclusion
The histopathological diagnosis of a radial scar/complex sclerosing lesion on the breast is not definitive, and it may underestimate atypical andmalignant lesions, which require a different treatment, making surgical excision an important step in diagnostic evaluation.
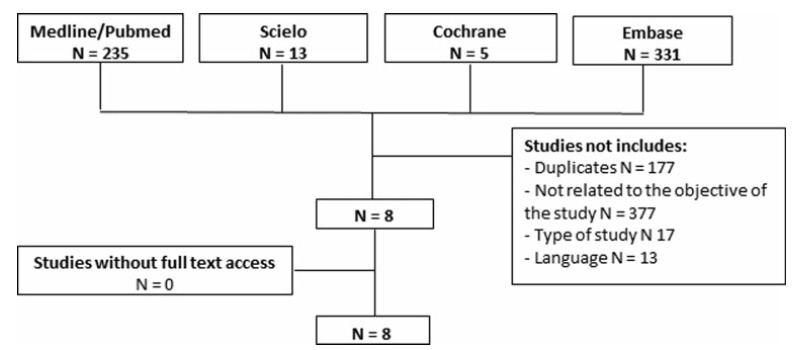
-
Review Article02-24-2022
Deficiency and Insufficiency of Vitamin D in Women of Childbearing Age: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):409-424
Abstract
Review ArticleDeficiency and Insufficiency of Vitamin D in Women of Childbearing Age: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):409-424
Views288Abstract
Objective
To estimate the prevalence of inadequate vitamin D level and its associated factors for women of childbearing age in Brazil.
Methods
A systematic reviewwas conducted (last updatedMay 2020).Meta-analyses were performed using the inverse-variance for fixed models with summary proportion calculation by Freeman-Tukey double arcsine. Reporting and methodological quality were assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute tool for prevalence studies.
Results
Our review identified 31 studies, comprising 4,006 participants. All the studies had at least one weakness, mainly due to the use of convenience sampling and small sample size. The overall prevalence of vitamin D deficiency, insufficiency, and both deficiency and insufficiency were 35% (confidence interval, 95%CI: 34-37%), 42% (95%CI: 41-44%), and 72% (95%CI: 71-74%), respectively.
Conclusion
Although the magnitude of the prevalence of inadequate levels of vitamin D is uncertain, the evidence suggests that presence of vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency in women of reproductive age can cause moderate to severe problems.
Key-words cholecalciferolMaternal nutritionnutritional epidemiologyvitamin D deficiencyWomen's healthSee more -
Review Article02-18-2022
Burch Procedure: A Historical Perspective
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):511-518
Abstract
Review ArticleBurch Procedure: A Historical Perspective
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):511-518
Views145See moreAbstract
Introduction
The Burch procedure (1961) was considered the gold standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) before the midurethral slings (MUSs) were introduced, in 2001.
Objective
This historical perspective of the Burch’s timeline can encourage urogynecological surgeons to master the Burch technique as one of the options for surgical treatment of SUI.
Search Strategy and Selection
Criteria A bibliographic search was performed in the PubMed and National Library of Medicine (NIH) databases with the terms Burch colposuspension AND history AND stress urinary incontinence in the last 20 years. The original article by Burch (1961) was included. The references were read by three authors. The exclusion criterion was studies in non-English languages. Biomedical Library Special Collections were included as historical relevant search.
Data Collection, Analysis and Main Results
Some modifications of the technique have been made since the Burch procedure was first described. The interest in this technique has been increasing due to the negative publicity associated with vaginal synthetic mesh products. Twenty-nine relevant articles were included in the present review article, and numerous trials have compared Burch colposuspension with MUS.
Conclusion
This historical perspective enables the scientific community to review a standardized technique for SUI. Burch colposuspension should be considered an appropriate surgical treatment for women with SUI, and an option in urogynecological training programs worldwide.
-
Review Article02-17-2022
Effect of Surgical Treatment for Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis on Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):503-510
Abstract
Review ArticleEffect of Surgical Treatment for Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis on Pelvic Floor Disorders: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):503-510
Views220See moreAbstract
Objectives
To evaluate the impact of surgical treatment of deep infiltrative endometriosis (DIE) on pelvic floor dysfunction (urinary incontinence [UI], pelvic organ prolapse [POP], fecal incontinence [FI)] or constipation, and sexual function [dyspareunia]).
Data Source
The present systematic review was performed in the PubMed database. For the selection of studies, articles should be published by January 5, 2021, without language restriction.
Study Selection
Six randomized controlled studies that evaluated surgical treatment for DIE and the comparison of different surgical techniques were included.
Data Collection
The studies were selected independently by title and abstract by two authors. Disagreements were resolved by a third author. All included studies were also evaluated according to the Cochrane risk of bias tool and the quality of the evidence was analyzed using the GRADE criteria. Subgroup analysis by different treatments and follow-up periods was also performed.
Results
Six studies were included in the quantitative analysis. The risk of bias between studies showed an uncertain risk of bias for most studies, with concealment of allocation being the least reported category. The quality of the evidence was considered low. High heterogeneity was found between the studies. No study has evaluated UI or POP comparatively before and after surgery.
Conclusion
Dyspareunia and FI have improved after the surgical procedure, but it was not possible to demonstratewhich surgical technique was related to these outcomes as there was surgical heterogeneity. This diversity was found across data, with the recommendation of future prospective studies addressing pelvic floor disorders withDIE.


