Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):347-355
To review the literature and synthesize evidence on pathophysiological interactions attributed to the simultaneous occurrence of COVID-19 and preeclampsia.
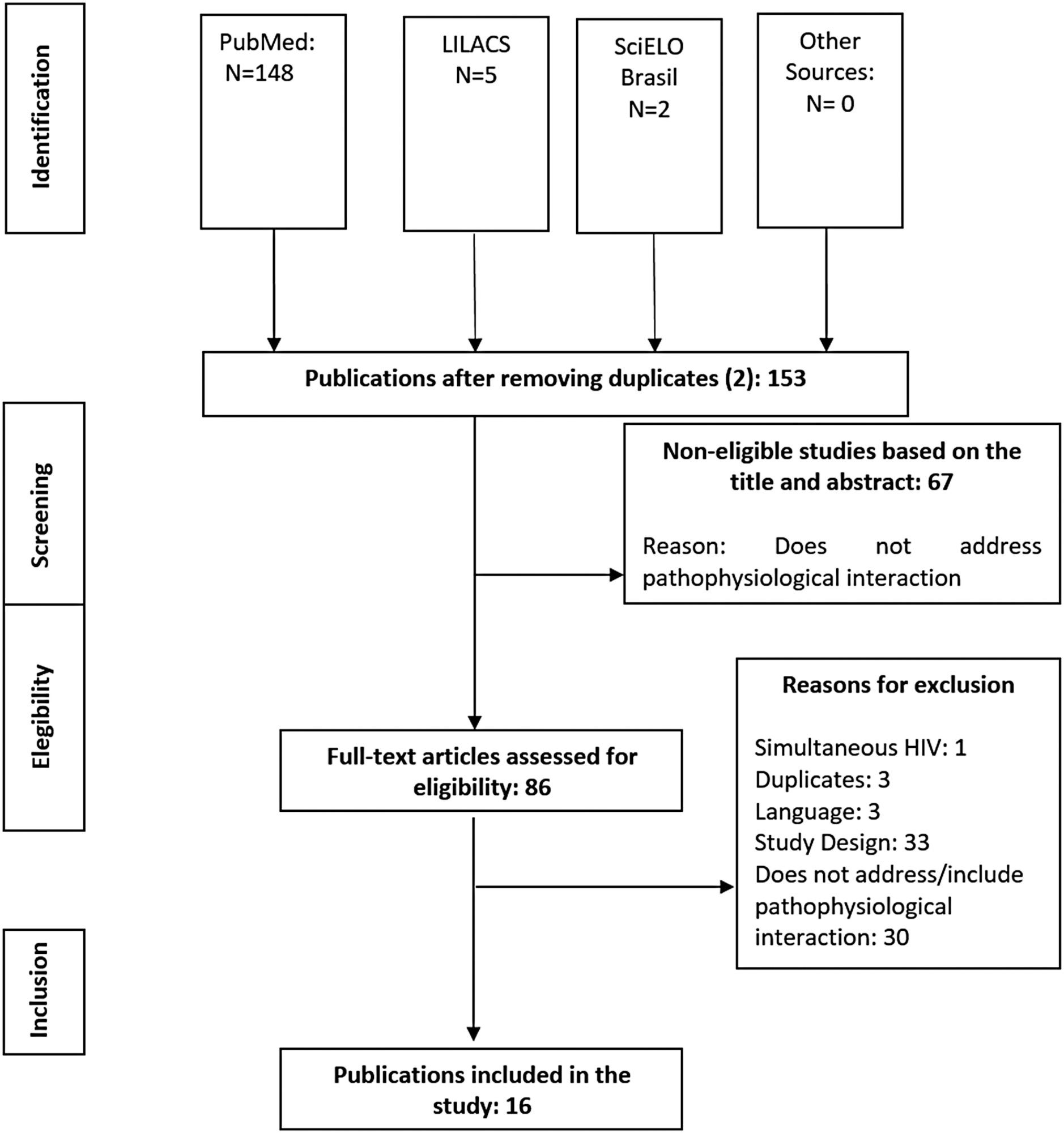
A systematic review was conducted from November (2021) to January (2022) to retrieve observational studies published on the PubMed, LILACS, SciELO Brazil and Google Scholar databases. The search was based on the descriptors [(eclampsia OR preeclampsia) AND (COVID-19)]. Quantitative studies that pointed to pathophysiological interactions were included. Literature reviews, studies with HIV participants, or with clinical approach only were excluded. The selection of studies was standardized and the evaluation was performed by pairs of researchers.
In this review, 155 publications were retrieved; 16 met the inclusion criteria. In summary, the physiological expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) receptors is physiologically increased in pregnant women, especially at the placental site. Studies suggest that the coronavirus binds to ACE-2 to enter the human cell, causing deregulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and in the ratio between angiotensin-II and angiotensin-1-7, inducing manifestations suggestive of preeclampsia. Furthermore, the cytokine storm leads to endothelial dysfunction, vasculopathy and thrombus formation, also present in preeclampsia.
The studies retrieved in this review suggest that there is a possible overlap of pathophysiological interactions between COVID-19 and preeclampsia, which mainly involve ACE-2 and endothelial dysfunction. Given that preeclampsia courses with progressive clinical and laboratory alterations, a highly quality prenatal care may be able to detect specific clinical and laboratory parameters to differentiate a true preeclampsia superimposed by covid-19, as well as cases with hypertensive manifestations resulting from viral infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):096-103
This comprehensive review compares clinical protocols of important entities regarding the management of fetal growth restriction (FGR), published since 2015. Five protocols were chosen for data extraction. There were no relevant differences regarding the diagnosis and classification of FGR between the protocols. In general, all protocols suggest that the assessment of fetal vitality must be performed in a multimodally, associating biophysical parameters (such as cardiotocography and fetal biophysical profile) with the Doppler velocimetry parameters of the umbilical artery, middle cerebral artery, and ductus venosus. All protocols reinforce that the more severe the fetal condition, the more frequent this assessment should be made. The timely gestational age and mode of delivery to terminate the pregnancy in these cases can vary much between the protocols. Therefore, this paper presents, in a didactic way, the particularities of different protocols for monitoring FGR, in order to help obstetricians to better manage the cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
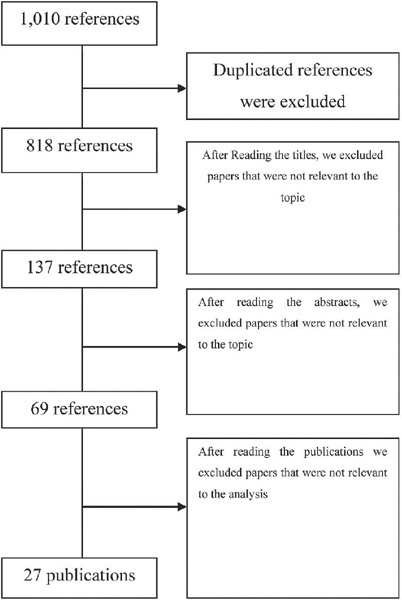
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(4):207-214
Supplementation with folic acid (FA) during gestation has been recommended by medical society all over the world, but some studies have shown that intake of high folic acid diet may unleash damages to the descendants. Objectives: Describing the effects of maternal supplementation with FA during gestation on offspring's kidney at late life stages. Data Source: It is a systematic review by which were consulted the following databases: Medline, through Pubmed, Lilacs, and SciELO. The research was performed using the keywords “Folic acid”, “Gestation” and “Kidney”. Study Selection: Eight studies were regarded for this systematic review. Data Collection: Only studies that evaluated folic acid consumption during gestation and its effects exclusively on descendants' kidney at several phases of life were regarded. Results: Gestational FA intake did not change the renal volume, glomerular filtration rate and the expression of some essential genes in the kidney of puppies whose dams were supplemented with FA. Maternal consumption of double FA plus selenium diet was effective in preserving antioxidant enzymes activity in the kidney of descendants from mothers exposed to alcohol. FA supplementation decreased some gross anomalies in the puppies caused by teratogenic drug despite of had not been effective in preventing some renal architectural damages. Conclusion: FA supplementation did not cause renal toxicity; it exerted an antioxidant protective effect and mitigated some renal disorders caused by severe aggressions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(1):43-48
Physical and emotional burdens during the journey of infertile people through assisted reproductive technologies are sufficient to justify the efforts in developing patient-friendly treatment strategies. Thus, shorter duration of ovarian stimulation protocols and the need for less injections may improve adherence, prevent mistakes, and reduce financial costs. Therefore, the sustained follicle-stimulating action of corifollitropin alfa may be the most differentiating pharmacokinetic characteristic among available gonadotropins. In this paper, we gather the evidence on its use, aiming to provide the information needed for considering it as a first choice when a patient-friendly strategy is desired.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1126-1133
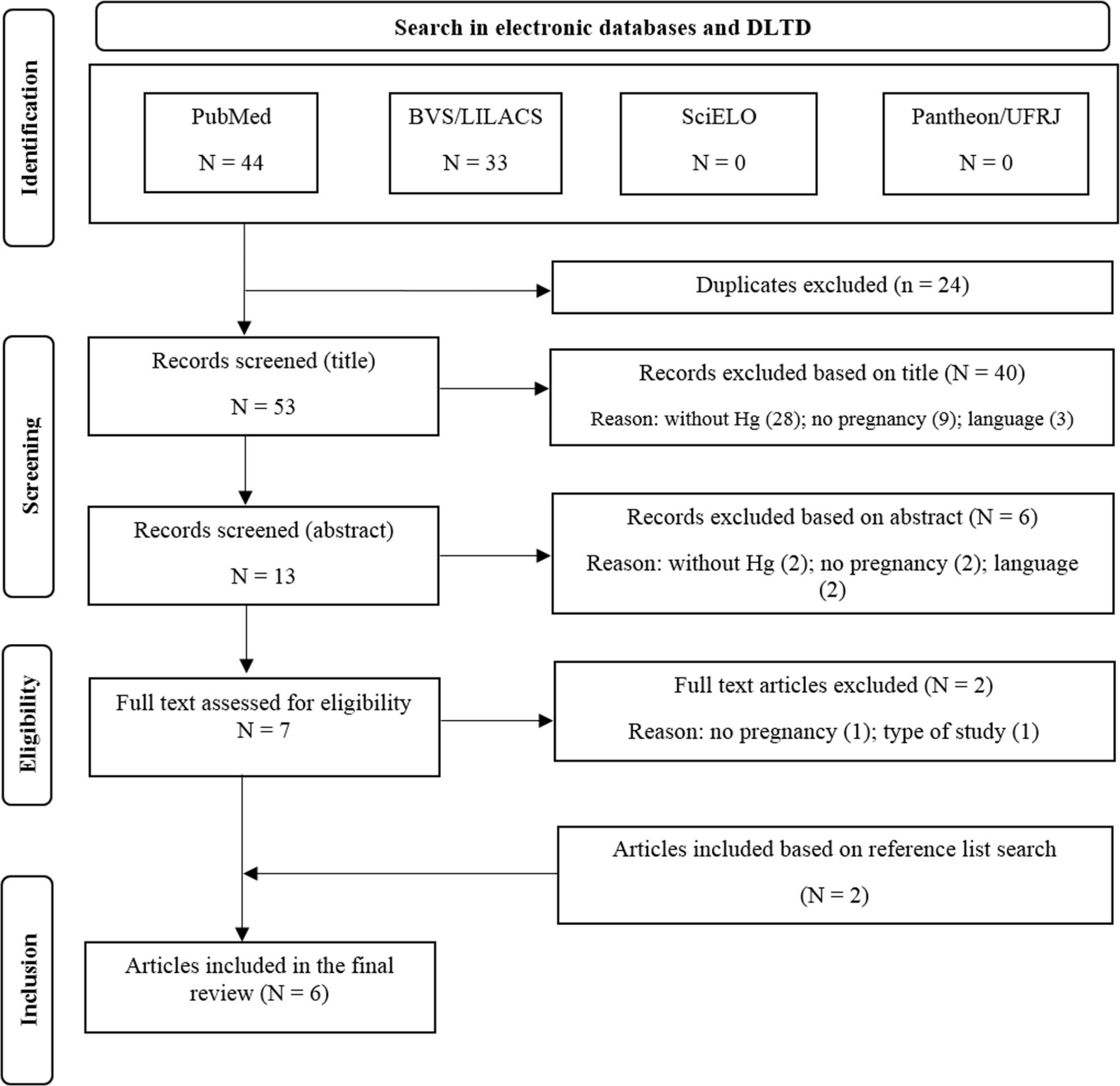
The present review aimed to synthesize the evidence regarding mercury (Hg) exposure and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP).
The PubMed, BVS/LILACS, SciELO and UFRJ's Pantheon Digital Library databases were systematically searched through June 2021.
Observational analytical articles, written in English, Spanish, or Portuguese, without time restriction.
We followed the PICOS strategy, and the methodological quality was assessed using the Downs and Black checklist.
We retrieved 77 articles, of which 6 met the review criteria. They comprised 4,848 participants, of which 809 (16.7%) had HDP and 4,724 (97.4%) were environmentally exposed to Hg (fish consumption and dental amalgam). Mercury biomarkers evaluated were blood (four studies) and urine (two studies). Two studies found a positive association between Hg and HDP in the group with more exposure, and the other four did not present it. The quality assessment revealed three satisfactory and three good-rated studies (mean: 19.3 ± 1.6 out 28 points). The absence or no proper adjustment for negative confounding factor, such as fish consumption, was observed in five studies.
We retrieved only six studies, although Hg is a widespread toxic metal and pregnancy is a period of heightened susceptibility to environmental threats and cardiovascular risk. Overall, our review showed mixed results, with two studies reporting a positive association in the group with more exposure. However, due to the importance of the subject, additional studies are needed to elucidate the effects of Hg on HDP, with particular attention to adjusting negative confounding.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1134-1140
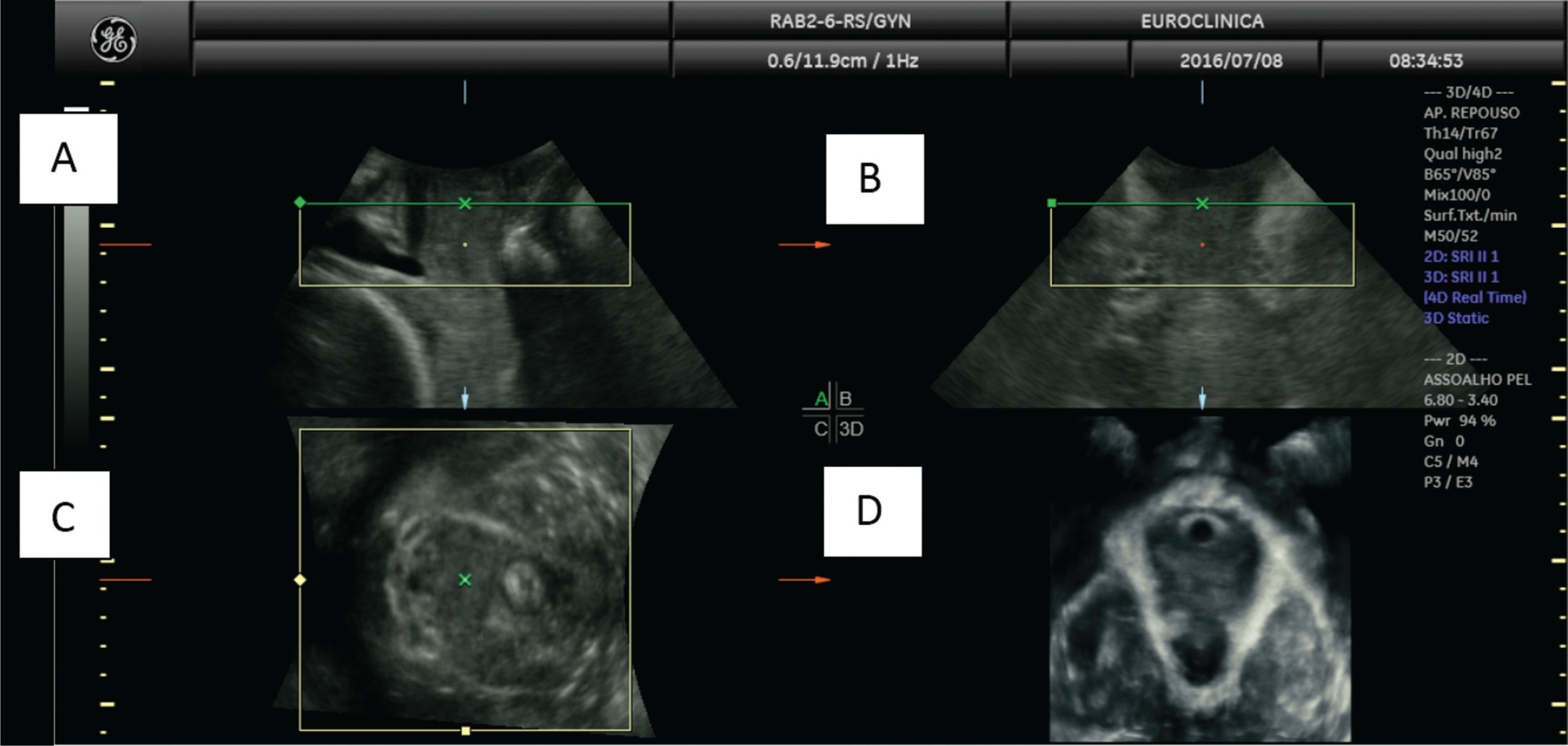
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM)is an entity with evolving conceptual nuances that deserve full consideration. Gestational diabetes leads to complications and adverse effects on the mother's and infants' health during and after pregnancy. Women also have a higher prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) related to the hyperglycemic status during pregnancy. However, the exact pathophysiological mechanism is still uncertain. We conducted a narrative review discussing the impact of GDM on the women's pelvic floor and performed image assessment using three-dimensional ultrasonography to evaluate and predict future UI.