Summary
. 2016;38(11):564-575
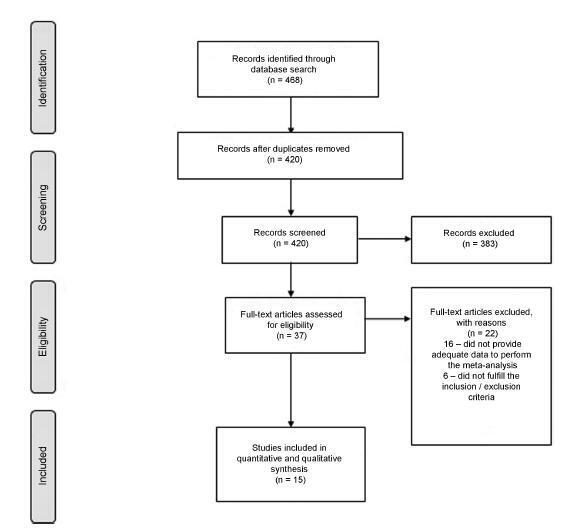
The overactive bladder (OAB) has a significant negative impact on the quality of life of patients. Antimuscarinics have become the pharmacological treatment of choice for this condition. The objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to examine the evidence from randomized clinical trials about the outcomes of the antimuscarinic drugs available in Brazil on OABs. We searched MEDLINE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials from the inception of these databases through to September 2015. The primary outcome measures were the mean decrease in urge urinary incontinence episodes and the mean decrease in the frequency of micturition. The results suggest that there is a moderate to high amount of evidence supporting the benefit of using anticholinergic drugs in alleviating OAB symptoms when compared with placebo. It is still not clear whether any of the specific drugs that are available in Brazil offer advantages over the others. These drugs are associated with adverse effects (dry mouth and constipation), although they are not related to an increase in the number of withdrawals.
Summary
. 2016;38(8):416-422
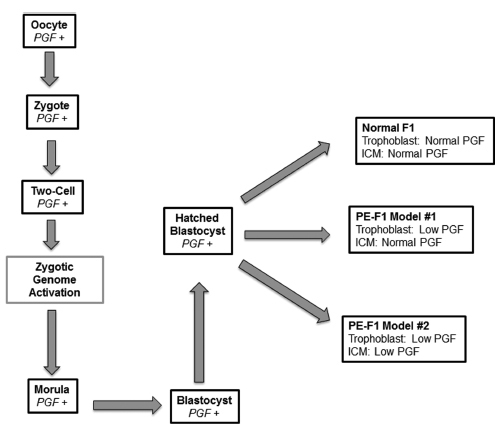
Preeclampsia (PE) is a significant gestational disorder that causes complications in 3- 5% of all human pregnancies. Apart from the immediate risks and complications for mother and fetus, both additionally carry elevated lifelong risks for specific complications. Offspring of PE pregnancies (PE-F1) have higher risks for hypertension, stroke and cognitive impairment compared with well-matched offspring (F1) fromuncomplicated pregnancies. Prior to the clinical onset of PE, placental angiokines secreted into the maternal plasma are deviated. In many PE patients this includes deficits in placental growth factor (PGF). Our laboratory found that mice genetically-deleted for PGF (PGF - / -) have altered cerebrovascular and brain neurological development detectable from midgestation to adulthood. We hypothesized that the PGF deficits seen in human PE, deviate fetal cerebrovascular and neurological development in a manner that impairs cognitive functions and elevates stroke risk. Here we summarize the initial analytical outcomes from a pilot study of 8-10 year old male and female PE-F1s and matched controls. Our studies were the first to report magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and functional brain region assessment by eyemovement control and clinical psychometric testing in PE-F1s. Further studies in larger cohorts are essential to define whether there are image-based biomarkers that describe unique anatomical features in PE-F1 brains.
Summary
. 2016;38(6):301-307
Episiotomy is a controversial procedure, especially because the discussion that surrounds it has gone beyond the field of scientific debate, being adopted as an indicator of the "humanization of childbirth". The scientific literature indicates that episiotomy should not be performed routinely, but selectively.
To review the literature in order to assess whether the implementation of selective episiotomy protects against severe perineal lacerations, the indications for the procedure, and the best technique to perform it.
A literature search was performed in PubMed using the terms episiotomy or perineal lacerations, and the filter clinical trial. The articles concerning the risk of severe perineal lacerations with or without episiotomy, perineal protection, or episiotomy techniques were selected.
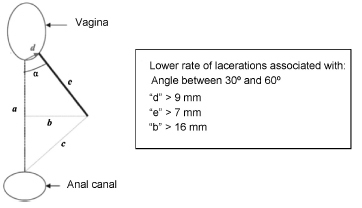
A total of 141 articles were identified, and 24 of them were included in the review. Out of the 13 studies that evaluated the risk of severe lacerations with and without episiotomy, 5 demonstrated a protective role of selective episiotomy, and 4 showed no significant differences between the groups. Three small studies confirmed the finding that episiotomy should be performed selectively and not routinely, and one study showed that midline episiotomy increased the risk of severe lacerations. The most cited indications were primiparity, fetal weight greater than 4 kg, prolonged second stage, operative delivery, and shoulder dystocia. As for the surgical technique, episiotomies performed with wider angles (> 40°) and earlier in the second stage (before "crowning ") appeared to be more protective.
Selective episiotomy decreases the risk of severe lacerations when compared with the non-performance or the performance of routine episiotomy. The use of a proper surgical technique is fundamental to obtain better results, especially in relation to the angle of incision, the distance from the vaginal introitus, and the correct timing for performing the procedure. Not performing the episiotomy when indicated or not applying the correct technique may increase the risk of severe perineal lacerations.
Summary
. 2016;38(5):253-262
Several authors have investigated the malignant transformation of endometriosis, which supports the hypothesis of the pre-neoplastic state of endometriotic lesions, but there are few data about the pathways and molecular events related to this phenomenon. This review provides current data about deregulated genes that may function as key factors in the malignant transition of endometriotic lesions. In order to do so, we first searched for studies that have screened differential gene expression between endometriotic tissues and normal endometrial tissue of women without endometriosis, and found only two articles with 139 deregulated genes. Further, using the PubMed database, we crossed the symbol of each gene with the terms related to malignancies, such as cancer and tumor, and obtained 9,619 articles, among which 444 were studies about gene expression associated with specific types of tumor. This revealed that more than 68% of the analyzed genes are also deregulated in cancer. We have also found genes functioning as tumor suppressors and an oncogene. In this study, we present a list of 95 informative genes in order to understand the genetic components that may be responsible for endometriosis' malignant transformation.
However, future studies should be conducted to confirm these findings.