Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):357-360
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600009
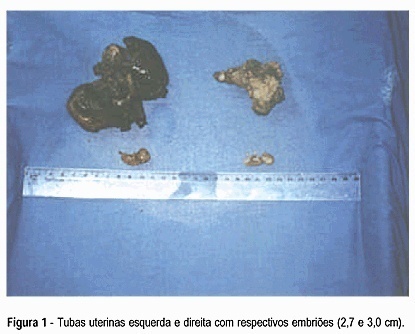
Bilateral ectopic pregnancy is the most unusual twin gestation considering that less than 250 cases have been reported in the literature. Our case fulfills the diagnostic criterion determined by Norris9 which requires demonstration of chorionic villi in each fallopian tube. We report the case of a 36-year-old multiparous woman who had an hemorrhagic acute abdomen. A laparotomy performed under general anesthesia revealed hemoperitoneum of 1.8 liters and both swelled tubes with laceration of their walls, besides two embryos with 2,7 and 3,0 cm in length free in the intra-abdominal blood. A literature review on bilateral ectopic pregnancy is presented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700007
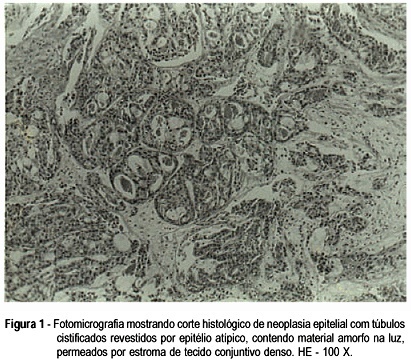
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix is a rare disease associated commonly with the use of diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy. The most commom complaint is irregular vaginal bleeding, which could be confused with vaginitis in children and abnormalities in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in adolescents. We report a case of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the endocervix in a 7-year-old child who was attended at the Children and Adolescent Gynecology Sector, and we call attention to the diagnosis of genital cancer which, in spite of its rarity at this age, must be considered in children with genital bleeding.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):415-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700008
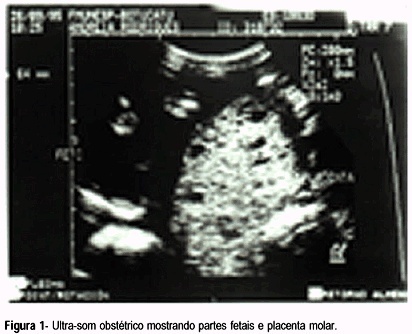
Twin pregnancy in which a normal fetus and a complete mole develop at the same time is a rare event. Clinical complications and malignancy are frequent in this type of disease.This report is about a case of a late diagnosis due to the presence of the fetus. The diagnosis was made when the pregnancy was interrupted and then confirmed by histopathological study and flow cytometry. The pregnancy was terminated transpelvically due to massive uterine hemorrhage. The post-molar follow-up showed the persistence of high levels of bhCG. The patient's complete recovery was achieved after the administration of methotrexate. The diagnosis, natural history, and procedures for this rare disease are discussed in view of this case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):109-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200009
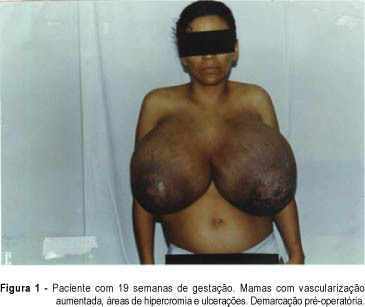
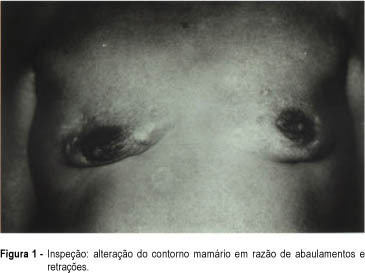
A rare case of bilateral benign phyllode tumor of the breast with fast growth during pregnancy and reaching great dimensions is presented. The patient was submitted to bilateral mastectomy on the 20th week of pregnancy. She had a good postoperative evolution and vaginal delivery occurred on the 40th week, when a healthy boy was born. The clinical and surgical features, the pathologic findings and the evolution of pregnancy are discussed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(2):113-115
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000200010
The authors report a rare case of dermatomyositis diagnosed at the Mastology Sector of the Division of Gynecology of the Federal University of São Paulo - Escola Paulista de Medicina, which caused breast deformity due to formation of bilateral dystrophic calcifications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):235-238
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400009
We report a case of nonmolar fetal triploidy detected by fetal blood sampling at 20 weeks of gestation, performed as an investigation of intrauterine growth retardation and severe oligohydramnios found by ultrasound scan. At 19 weeks of gestation very low levels of maternal free serum beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin and unconjugated estriol, and normal levels of alpha-fetoprotein were found, which were interpreted as a high risk of fetal Edwards syndrome. Fetal death supervened the day after fetal blood sampling, and the pregnancy was terminated by vaginal delivery induced by misoprostol and oxytocin, under epidural anesthesia. Chromosome study of the fetal blood cells showed a 69,XXX karyotype. The severe intrauterine growth retardation and macrocephaly noted on pathological review plus the very low levels of hCG and unconjugated estriol suggest a fetal gynoid triploidy case, caused by the fertilization of a diploid egg by a haploid sperm.