Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):343-346
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000500009
Aplastic anemia is characterized by a circulating pancytopenia, hypocellularity, and fatty replacement of cellular marrow elements, without evidence of malignant transformation or myeloproliferative disease. It usually affects young and senior adults, without any sexual preference. Most cases of aplastic anemia are acquired, but the disease may also be inherited due to a molecular disorder (Fanconi's anemia). Aplastic anemia in pregnancy is an extremely rare condition with high maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality rates. The authors describe a case of a patient with previously diagnosed aplastic anemia, whose pregnancy was complicated with urinary tract infection, preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction, with elective preterm birth. In spite of the adverse conditions in pregnancy and delivery, mother and newborn had a satisfactory clinical evolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(4):271-276
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000400009
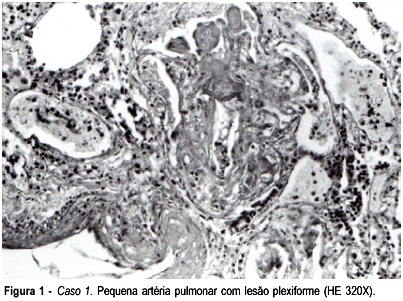
The severity of the association of pulmonary hypertension with pregnancy is well known. Pulmonary arterial hypertension constitutes one of the highest risk conditions for maternal mortality in late pregnancy and postpartum. Patients with portal hypertension of varying etiology may develop pulmonary arterial hypertension (portopulmonary hypertension) and most cases present cirrhosis as the underlying disease; however, a few cases of noncirrhotic etiology have been described. Clinical and pathological findings in two cases of portopulmonary hypertension and pregnancy are presented here. The two patients (30 and 24 years old) developed severe right heart failure and shock just after the delivery and the disease progressed rapidly to death. Autopsy demonstrated fibrosis in hepatic portal tracts, as has been described in cases of idiopathic portal hypertension. Also, pulmonary hypertension classified as plexogenic was reported.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(3):201-204
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000300009
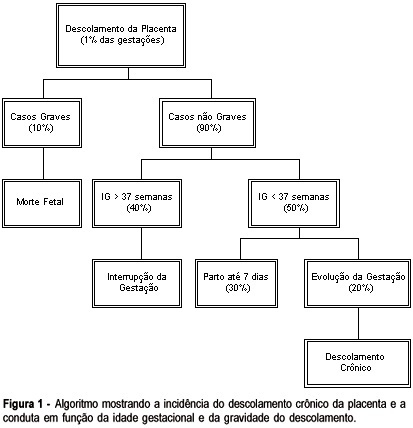
Chronic placental abruption is a rare condition that can be early detected by ultrasound. Vaginal bleeding and uterine excitability can be present in an infrequent way. Chronic placental abruption physiopathology is unknown and there are no consistent medical risks that predispose to this condition. The perinatal outcome is poor and is often associated with prematurity and fetal or perinatal death. The obstetric treatment depends on the gestational age, fetal conditions and the size of the clot. We present a case of a chronic placental abruption diagnosed in a 14-week gestation complicated by intrauterine growth retardation, oligohydramnios and perinatal death.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(2):129-132
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000200009
Hepatic rupture is one of the most serious and catastrophic complications of pregnancy, with an estimated incidence of 1:45000 to 1:225000 deliveries. It is usually associated with preeclampsia. Maternal mortality is about 60-86% and fetal mortality can reach 56-75%. Diagnosis is difficult, but commonly relies on the presence of severe bleeding and hypovolemic shock. We present the case of a patient with a 32-week gestation complicated by spontaneous preeclampsia-associated hepatic hemorrhage, which was submitted to surgical treatment with good outcome.