Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(7):529-532
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000700011
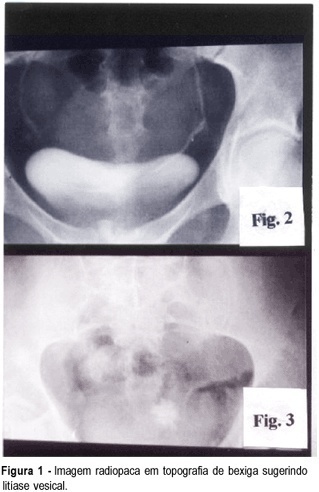
The fistulas caused by mechanical trauma are rare, mainly the intrinsic type caused by vesical lithiasis. The treatment of these fistulas is controversial, concerning the ideal surgical technique. Several techniques have been developed, including the transvaginal and the transabdominal surgical approaches. The authors report the case of a patient with urinary loss for six months. Physical and radiological examination showed the occurrence of a vesicovaginal fistula caused by vesical lithiasis. The treatment was in two stages: first the extraction of the vesical stone by transabdominal approach and second, the correction of the fistula by transvaginal approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(6):381-384
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000600009
Parkinson's disease is characterized by tremor, stiffness of the musculature, bradykinesia, and postural and march abnormalities. It attacks all ethnic groups, with no sex preference, frequently in the 45-50-year range. The diagnosis is essentially clinical. The association with pregnancy is rare. The experience with that association is scarse, some questions remaining without answer. The authors describe a case of Parkinson's disease and gestation with satisfactory evolution, in spite of the clinical worsening during pregnancy. The mother presented elevation of blood pressure levels, alterations of the hepatic enzymes, and oligohydramnios. She used, independently, selegiline until the third month, and, later on, amantadine. The newborn presented low weight, respiratory distress and jaundice, being discharged from the hospital, with no other complications, on the fourth day of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):445-448
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600010
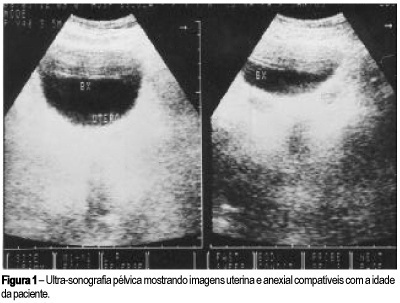
Development of preeclampsia/eclampsia prior to 20 weeks of pregnancy should raise the suspicion of hydatidiform mole. We report a case of complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) concurrent with eclampsia in a 20-year-old patient with vaginal bleeding, anemia, large uterine size, and ovary cysts associated with hypertension and proteinuria. Plasmatic b-hCG levels were high and there was abnormal thyroid function. The ultrasonographic findings were compatible with CHM. After uterine evacuation, the patient had headache and visual alterations, followed by tonic-clonic seizures, which ceased with the administration of 50% magnesium sulfate. At post-molar follow-up, a gestational trophoblastic tumor (GTT) was diagnosed and promptly treated with chemotherapy. Association between CHM and eclampsia requires immediate uterine evacuation and strict post-molar follow-up, due to increased risk of GTT development.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):455-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700009
Primary angiosarcoma of the breast is a rare tumor, which appears between 14 and 82 years, with an average of 35 years of age. Its predominant clinical aspect is a painful mass with diffuse increase in the breast and violet or blackened color. Equally to other cases of sarcoma, the medium size of the lesion is approximately 5 cm at the diagnosis. Histologically, it is characterized by the proliferation of endothelial cells that form vascular channels linked to each other infiltrating glandular structures and fatty tissue. Its histological diagnosis is difficult and not always the right diagnosis is immediately established, mainly in the cases of a low malignancy degree, due to limited biopsy material. Because of the difficult diagnosis and aggressivity, it is a neoplasia with ominous prognosis, due to frequent metastasis. In our service, a 18-year-old patient presented with a painful lump which grew quickly. It was biopsied and a hemangioma was diagnosed, a wide excision being indicated. Three months later, she suffered a tumoral relapse, that was biopsied again and mastectomy was indicated, because it was an angiosarcoma with low degree of malignancy. After other relapses, chemotherapy was indicated and later, radiotherapy. During radiotherapy she developed new metastases, and died of pulmonary metastasis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):207-210
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300010
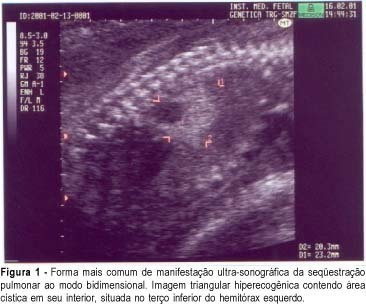
Bronchopulmonary sequestration is a mass of anomalous lung tissue, which in general does not communicate with the tracheobronchial tree and receives systemic arterial blood supply more often originating from the aorta. This is such a rare malformation, that is not always thought of as a diagnostic possibility. We present a case of bronchopulmonary sequestration and emphasize the significant role of color Doppler in its diagnosis, as it identifies the artery originating from the descending aorta irrigating the sequestration. We also present its three-dimensional ultrasound features.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):211-214
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300011
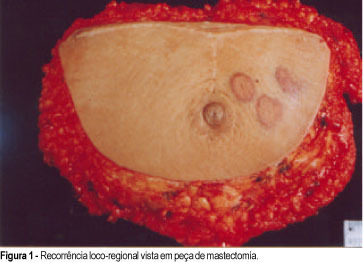
The authors present a case of lymphangiosarcoma in the upper left limb of a 52-year-old patient previously submitted to a left-sided modified radical mastectomy followed by radiotherapy due to breast cancer six years earlier. This rare syndrome is associated with chronic lymphedema as a consequence of radical mastectomy followed by radiotherapy. Approximately 400 cases have been reported in the literature. The infrequent occurrence of this disease and the rather innocuous appearance of the tumor often lead to late diagnosis and treatment. In the present case, the diagnosis was based on an incision biopsy of the lesion and confirmed immunohistochemically using endothelial markers, antibodies (anti-CD31), vimentin and muscle actin. The patient's limb was amputated and no local or distant recurrence has so far been observed during 18 months of follow-up.
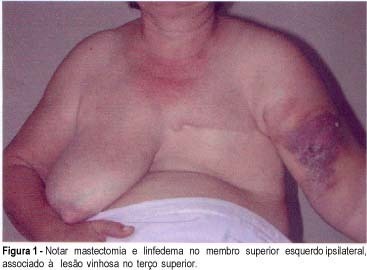
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(10):653-656
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000001000009
Chronic appendicitis might simulate several diseases, making clinical management difficult. We report the case of a 9-year-old girl with an abdominal pain for 13 months. Ultrasound and tomography showed an expansive mass in the lower abdomen. It was extremely difficult to establish the diagnosis because the symptoms, laboratory results and images were inconclusive. The definitive diagnosis occurred only after laparotomy. We discuss in the present article several differential diagnoses for chronic appendicitis, mainly gynecological malformations, endometriosis, neoplasias and pseudotumors.