Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):47-52
Patient autonomy has great importance for a valid informed consent in clinical practice. Our objectives were to quantify thedomains of patient autonomy and to evaluate the variables that can affect patient autonomy in women with chronic pelvic pain.
This study is a cross sectional survey performed in a tertiary care University Hospital. Fifty-two consecutive women scheduled for laparoscopic management of chronic pelvic were included. Three major components of autonomy (competence, information or freedom) were evaluated using a Likert scale with 24 validated affirmatives.
Competence scores (0.85 vs 0.92; p = 0.006) and information scores (0.90 vs 0.93; p = 0.02) were low for women with less than eight years of school attendance. Information scores were low in the presence of anxiety (0.91 vs 0.93; p = 0.05) or depression (0.90 vs 0.93; p = 0.01).
Our data show that systematic evaluation of patient autonomy can provide clinical relevant information in gynecology. Low educational level, anxiety and depression might reduce the patient autonomy in women with chronic pelvic pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):9-19
To present and validate a multifunctional electronic medical record (EMR) for outpatient care to women with endocrine disorders in pregnancy and to compare health information data fill rate to conventional medical records.
We developed an EMR named Ambulatory of Endocrine Diseases in Pregnancy (AMBEG) for systematic registration of health information The AMBEG was used for obstetric and endocrine care in a sample of pregnant women admitted to the maternity reference in high-risk pregnancies in Bahia from January 2010 to December 2013. We randomly selected 100 patients accompanied with AMBEG and 100 patients monitored with conventional consultation and compared the health information data fill rate of the electronic consultation to that performed using conventional medical records.
1461 consultations were held, of which 253, 963 and 245 were first, follow-up and puerperium consultations, respectively. Most patients were pregnant women with diabetes (77.2%) and 60.1% were women with pre-gestational diabetes. The AMBEG satisfactorily replaced the conventional medical record. The percentage of registered information was significantly higher in the AMBEG: clinical symptoms (87% versus 100, p < 0.01), uterine height (89 versus 75%, p = 0.01), total weight gain (91 versus 40%, p < 0.01) and specific diabetes data (diet, insulin regimen, glycemic control and management of hypoglycemia) revealed a significant difference (p < 0.01). The ability to export data to worksheets greatly facilitated and accelerated the statistical analysis of the data.
AMBEG is a useful tool in clinical care for women with endocrine diseases during pregnancy. The fill rate of clinical information was superior to that registered in conventional medical records.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):552-558
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320155443
To compare differences in the occurrence and changed domains of sexual dysfunction in obese and non-obese Brazilian women.
Female Sexual Function Index, based on six domains, to investigate 31 sexual dysfunction incidence for obese compared to 32 non-obese women, was used. Statistical analysis using ANOVA and MANOVA were performed to compare total scores of Female Sexual Function Index among groups and to identify the differences among domains, Student t -test was used. Statistical significant level was established for all tests for p<0.05.
No difference in female sexual dysfunction frequency between obese (25.8%) and non-obese women (22.5%) was found. However, an important distinction in which aspects of sexual life were affected was found. While the obese group was impaired in three domains of sexual life (desire, orgasm, and arousal), in the control group five aspects were dysfunctional (desire, orgasm, arousal, pain and lubrication). Future research exploring psychological outcomes in obese females, such as body image and measures of positive and negative effect, might better characterize the female sexual dysfunction in this group.
Obesity does not appear to be an independent factor for allow quality of female sexual life. However, disturbance associated to obesity indicates a low frequency of disorder in physical domains, suggesting that psychological factors seem to be mainly involved in the sexual dysfunction in obese women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):559-564
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005462
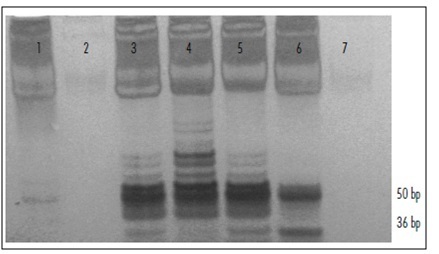
To analyze the relation between the cytological findings and telomerase activity (TA).
Cervical samples were evaluated and classified according to the Bethesda System. Telomerase activity was measured total product generated values (TPG) using the TRAP assay (telomeric repeat amplification protocol); data were analyzed statistically using the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
The study was conducted on 102 patients. Of these, 3.9% showed normal cytological findings, 8.8% showed cervicitis; 2% showed Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS); 67.6% showed Low Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (LSIL); 11.8% showed High Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (H-SIL) and 5.9% showed Squamous Carcinoma. Among telomerase-positive samples, the TPG values were cervicitis Results show increased telomerase activity with increasing severity of lesion, supporting the association between TA and type of lesion.CONCLUSION
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):578-584
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005445
To estimate the future pregnancy success rate in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
A retrospective cohort study including 103 women seen at a clinic for recurrent pregnancy loss (loss group) between January 2006 and December 2010 and a control group including 204 pregnant women seen at a low-risk prenatal care unit between May 2007 and April 2008. Both groups were seen in the university teaching hospital the Maternidade Climério de Oliveira, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Reproductive success rate was defined as an alive-birth, independent of gestational age at birth and survival after the neonatal period. Continuous variables Means and standard deviations (SD) were compared using Student's t-test and nominal variables proportions by Pearson χ2test.
Out of 90 who conceived, 83 (91.2%) had reproductive success rate. There were more full-term pregnancies in the control than in the loss group (174/187; 92.1 versus 51/90; 56.7%; p<0.01). The prenatal visits number was satisfactory for 76 (85.4%) women in the loss group and 125 (61.3%) in the control (p<0.01). In this, the beginning of prenatal care was earlier (13.3; 4.2 versus 19.6; 6.9 weeks). During pregnancy, the loss group women increased the weight more than those in the control group (58.1 versus 46.6%; p=0.04). Although cervix cerclage was performed in 32/90 women in the loss group, the pregnancy duration mean was smaller (34.8 weeks; SD=5.6 versus 39.3 weeks; SD=1.6; p<0.01) than in the control group. Due to gestational complications, cesarean delivery predominated in the loss group (55/83; 64.7 versus 73/183; 39.5%; p<0.01).
A very good reproductive success rate can be attributed to greater availability of healthcare services to receive pregnant women, through prenatal visits (scheduled or not), cervical cerclage performed on time, and available hospital care for the mother and newborn.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):411-416
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005397
The aim of this study was to evaluate serum levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (INOS), myeloperoxidase (MPO), total antioxidant status (TAS), and total oxidative status (TOS) in women with primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) and to compare them with healthy fertile women. We also examined the possible risk factors associated with POI.
This cross-sectional case control study was conducted in Zekai Tahir Burak Women's Health Education and Research Hospital. The study population consisted of 44 women with POI (study group) and 36 healthy fertile women (control group). In all patients, serum levels of INOS, MPO, TAS, and TOS were determined. INOS and MPO levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay whereas colorimetric method was used for evaluating TAS and TOS levels. Age, body mass index (BMI), obstetric history, smoking status, family history, comorbidities, sonographic findings, complete blood count values, C-reactive protein and baseline hormone levels were also analyzed. Student's t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables between the groups; categorical data were evaluated by using Pearson χ2 or Fisher exact test, when appropriate. Binary logistic regression method was used to identify risk factors for POI.
We found significantly elevated levels of INOS (234.1±749.5 versus133.8±143.0; p=0.005), MPO (3,438.7±1,228.6 versus 2,481.9±1,230.1; p=0.001), and TOS (4.3±1.4 versus 3.6±1.4; p=0.02) in the sera of the study group when compared to the BMI-age matched control group. However, difference in serum levels of TAS were not significant between the 2 groups (1.7±0.2 versus 1.6±0.2; p=0.15). Logistic regression method demonstrated that BMI <25 kg/m2, nulliparity, family history of POI, smoking, and elevated serum levels of INOS, MPO, and TOS were independent risk factors for POI.
We found an increase in INOS, MPO, and TOS in women with POI. These serum markers may be promising in early diagnosis of POI. Further large-scale studies are required to determine whether oxidative stress markers have a role in diagnosing POI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):258-265
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005366
To compare two single-agent chemotherapy (ChT) regimens evaluating, in first-line treatment, response and side effects and, in final single-agent treatment, the outcomes, among Brazilian patients with low-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN), according to International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) 2002.
Retrospective analysis of two concurrent cohorts with 194 low-risk GTN patients: from 1992 to 2012, as first-line treatment, 115 patients received 4 intramuscular doses of methotrexate alternated with 4 oral doses of folinic acid (MTX/FA) repetead every 14 days and, since 1996, 79 patients received an endovenous bolus-dose of actinomycin D (Act-D), biweekly. At GTN diagnosis, patient opinion was taken into consideration when defining the initial single-agent ChT regimen, and when there was resistance or toxicity to one regimen, the other drug was used preferentially. This study was approved by the Irmandade da Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre Ethical Committee.
Both groups were clinically similar (p>0.05). In first-line treatments, frequency of complete response was similar (75.7% with MTX/FA and 67.1% with bolus Act-D); the number of ChT courses -median 3 (range: 1-10) with MTX/FA and 2 (range: 1-6) with bolus Act-D - and the time to remission -median 9 weeks (range: 2-16) with MTX/FA and 10 weeks (range: 2-16) with bolus Act-D) - were not different between the groups. In both groups, first-line side effects frequency were high but intensity was low; stomatitis was higher with MTX/FA (p<0.01) and nausea and vomit with Act-D (p<0.01). Final single-agent ChT responses were high in both groups (94.8% with MTX/FA and 83.5% with bolus Act-D; p<0.01) and 13% higher in the group initially treated with MTX/FA. Rates of hysterectomy and of GTN recurrence were low and similar. No patient died due to GTN.
The two regimens had similar first-line ChT response. Final single-agent response rates were high and similar in both groups but the final single-agent remission rate was higher in the MTX/FA group.