Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):272-279
To evaluate whether colposcopy-directed biopsy is necessary to increase the accuracy of diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions in relation to colposcopy.
We performed a retrospective, observational study by analyzing medical records obtained fromHospital de Clínicas do Paraná fromFebruary 2008 to February 2018. Patients with results of Pap tests, colposcopy, colposcopy-directed biopsy, and surgical procedures (high-frequency surgery or cold conization) were included. Data such as quadrants involved during colposcopy and age differences were also analyzed.
A total of 299 women were included. Colposcopy was found to have an accuracy rate of 76.25% (95% confidence interval [CI], 71.4-81.1). Among the highest-grade lesions, the accuracy rate was 80.5% (95% CI, 75.7-85.3). The accuracy rates for biopsy were 79.6% (95% CI, 75-84.2) and 84.6% (95% CI, 80-89.1) for the highest-grade lesions. High-grade lesions were accurately confirmed in 76.9% and 85% of patients with 1 and 2 or more affected quadrants, respectively. For women younger than 40 years, the accuracy rates were 77.6% and 80.8% for colposcopy and biopsy, respectively. For women 40 years or older, the accuracy rates were 72.5% and 76.3% for colposcopy and biopsy, respectively.
There is no difference between the accuracy of colposcopy and that of biopsy in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions in relation with the result of conization. The patients who received the greatest benefit when biopsy was not performed were those with high-grade lesions at colposcopy, a lesion involving 2 or more quadrants, and those younger than 40 years.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):755-760
To evaluate the acceptance of telemedicine and determine its associated factors in an urogynecology outpatient clinic of a public hospital in Brazil.
The present was a cross-sectional study performed between June and November 2020. The included patients had their elective appointments postponed due to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The variables considered regarding the acceptance of telemedicine were: urogynecologic diagnosis, age, level of schooling, place of residence, access to the internet, type of device used, frequency of internet use, and use of social media platforms. The categorical variables were described by their absolute and relative frequencies. The association among variables was evaluated through the Fisher exact test, and univariate and multivariate analyses, considering the acceptance of telemedicine as the dependent variable.
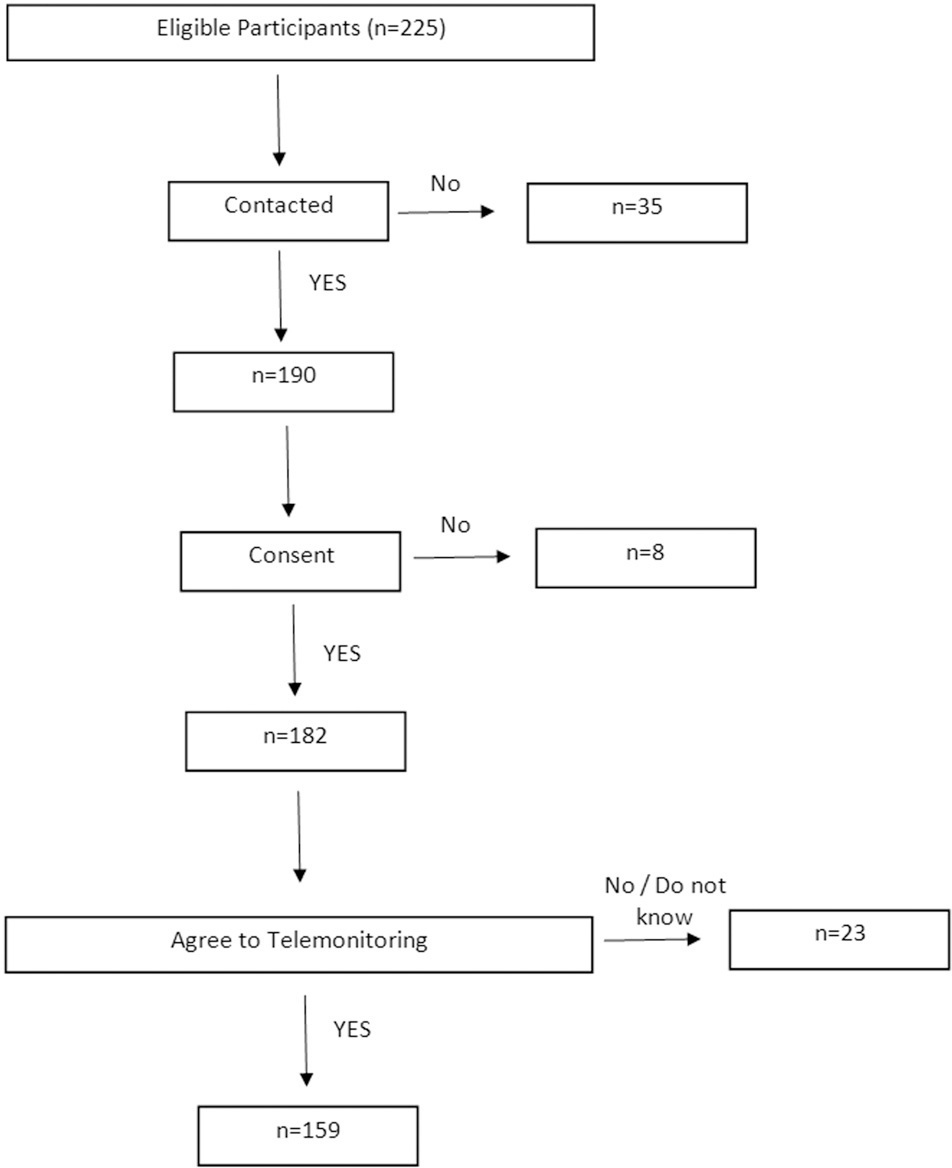
A total of 225 patients were listed, and 182 agreed to participate. The mean age was 59 years old, 81.3% of the patients had access to the internet, and 87.3% of them accepted telemedicine. There were statistically significant associations regarding the acceptance of telemedicine and high levels of schooling (p< 0.01), internet access (p< 0.01), daily use of the internet (p< 0.01), access through personal mobile phone (p< 0.01), and access through the participant's own residence (p< 0.01). In the univariate and multivariate analyses, only high levels of schooling were associated with the acceptance of telemedicine (Adjusted odds ratio: 4.82; 95% confidence interval = 1.59–14.65).
Most of the urogynecology patients of a public hospital in a developing country accepted telemedicine. Internet access and level of schooling were the factors associated with the acceptance of telemedicine in urogynecology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):327-335
Determine the predictive criteria for success in inducing labor for live fetuses using misoprostol in pregnant women. Secondarily, the objective is to determine the rates of vaginal or cesarean delivery, duration of induction, interval of administration of misoprostol, the main causes of induction of labor and indication for operative delivery.
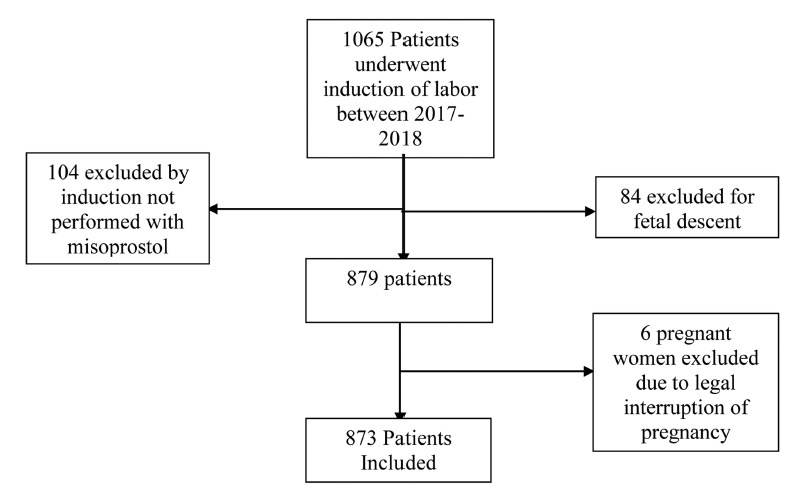
Medical records of 873 pregnant women admitted for cervical maturation from January 2017 to December 2018 were reviewed in a descriptive observational study of retrospective analysis, considering the following response variables: age, parity, Bishop Index, doses of misoprostol, labor induction time. Logistic regression models were used to predict success with misoprostol in non-operative deliveries.
Of the 873 patients evaluated, 72% evolved with vaginal delivery, 23% of the cases were cesarean, 5% forceps or vacuum-extractor. For non-operative delivery the predictive variables at admission were age, parity, gestational age and dilation. During hospitalization, fewer vaginal touches,amniotomy or amniorrhexis with clear fluid lead to a shorter induction time and a greater chance of non-operative delivery. False positives and false negatives of the model were always below 50% and correct answers above 65%.
At admission, age less than 24 years, previous normal births, lower the gestational age and greater the dilation, were predictive of greater probability of nonoperative delivery. During hospitalization, the less vaginal touches and occurrence of amniotomy/amniorrhexis with clear liquid indicate shorter induction time. Future studies with a prospective design and analysis of other factors are necessary to assess the replicability, generalization of these findings.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):391-397
To determine knowledge, attitude, and preventive (KAP) practices towards the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic among women in reproductive age seeking to use copper or hormonal intrauterine devices (IUD/LNG-IUS).
We conducted a cross-sectional study in which we applied a questionnaire on 400 women about KAP practices on COVID-19 at the University of Campinas, Campinas, SP, Brazil, from May to August 2020.
The mean (±SD) age of the women was 30.8±7.9 years, and 72.8% of them reported being pregnant at least once. Most women (95%) had heard or read about COVID-19, and their main sources of information were television (91%) and government websites (53%). However, 53% of the women had doubts about the veracity of the information accessed.
Women without a partner and with>12 years of schooling had more information about COVID-19 and on its impact on new pregnancy, and those from high socioeconomic status had a higher chance of maintaining physical distance. Safety, effectiveness, comfort, and absence of hormone in the contraceptive method (in the case of TCu380A IUD) were the main reasons for the participants to seek the service during the pandemic, and the possibility to stop menstrual bleeding was the main reason to choose the LNG-IUS.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):369-375
To compare the oocyte maturation rate in the treatment of in vitro fertilization (IVF) in terms of the use of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), agonist gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and dual trigger and to evaluate the associated risk factors for sub-optimal maturation rates.
A retrospective cohort study with 856 women who underwent IVF. They performed oocyte retrieval and were classified into 3 groups (1 - hCG, 2 - GnRHagonist, 3 - dual trigger). The primary outcome was maturation rate per trigger, and the secondary outcomes were the pregnancy rate per oocyte retrieval and the correlations between low maturation rate as well as the clinical and treatment characteristics of women.
The maturation rate was 77% in group 1; 76% in group 2, and 83% in group 3 (p=0.003). Group 2 showed women with better ovarian reserve, greater number of oocytes collected, and more mature oocytes and embryos compared with the other groups (p<0.001). The cumulative clinical pregnancy rate was no different between the groups (p=0.755). Low ovarian reserve and low doses of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) administered during the stimulus were associated with a higher chance of null maturation rate.
The oocyte maturation rates and IVF results were similar in all groups. Low ovarian reserve is associated with the worst treatment results.