-
Original Article09-01-2018
Risk Assessment for Preterm Delivery using the Fetal Fibronectin Test Associated with the Measurement of Uterine Cervix Length in Symptomatic Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):507-512
Abstract
Original ArticleRisk Assessment for Preterm Delivery using the Fetal Fibronectin Test Associated with the Measurement of Uterine Cervix Length in Symptomatic Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):507-512
Views117See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the use of the measurement of uterine cervix length (MUCL) and the fetal fibronectin (fFN) rapid test as predictors of preterm delivery (PTD) in symptomatic pregnant women assisted at the Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Sobral Maternity Hospital.
Methods
This was a prospective and analytic study involving 53 parturients assisted between September of 2015 and July of 2016; the participants were between 24 and 34 weeks of gestational age (GA) and presented complaints related to preterm labor (PTL) prodromes. Vaginal secretion was collected for fFN testing, and the MUCL was obtained via transvaginal ultrasonography.
Results
A total of 58.49% of the subjects showed MUCL < 25 mm, and 41.51% were positive in the fFNrapid test.Atotal of 48 patients were followed-up until their delivery date, and 54.17% resulted in PTL. The relative risk (RR) for PTD in patients with MUCL < 25 mm was 1.83 (p = 0.09, 0.99-3.36, 95% confidence interval [CI]), with a mean time before delivery of 2.98 weeks. Based on fFN positive results, the RR was 3.50 (p = 0.002, 1.39- 8.79, 95%CI) and themean time until delivery was 1.94weeks. The RRwas 2.70 (p = 0.002, 1.08-6.72, 95%CI) when both tests were used. The RR of PTD within 48 hours, and 7 and 14 days were, respectively, 1.30 (p = 0.11, 95% CI 1.02-1.67), 1.43 (p = 0.12, 95% CI % 0.99-2.06), and 2.03 (p = 0.008, 95% CI 1.26-3.27), when based on the MUCL, and 1.75 (p = 0.0006, 95% CI 1.20-2.53), 2.88 (p = 0.0001, 95% CI, 1.57-5.31), and 3.57 (p = 0.0002, 95% CI 1.63-7.81) when based on positive fFN results. The RR at 48 hours and 7 and 14 days considering both tests was 1.74 (p = 0.0001, 95% CI 1.14-2.64), 2.22 (p = 0.0001, 95% CI 1.22-4.04), and 2.76 (p = 0.0002, 95% CI 1.27-5.96), respectively.
Conclusion
In symptomatic pregnant women, we concluded that the MUCL < 25 mm associated with positive fFN rapid test indicate increased the risk for PTD. Further studies with larger sample sizes could contribute in supporting the results presented in the current study.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Robson Classification System Applied to Induction of Labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):513-517
Abstract
Original ArticleRobson Classification System Applied to Induction of Labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):513-517
Views110See moreAbstract
Objective
Induction of labor (IL) is a common obstetric procedure, but it is questionable whether or not it results in higher cesarean section (CS) rates. The present study aims to evaluate the impact of IL in the overall CS rates and to analyze these rates according to the method of IL employed and to the Robson group in which it was applied.
Methods
We have conducted a retrospective study including pregnant women whose labor was induced at a tertiary hospital in 2015 and 2016. All women were classified according to the Robson Classification System (RCS). The CS rates were analyzed and compared regarding the method of IL employed.
Results
A total of 1,166 cases were included. The CS rate after IL was 20.9%, which represented 23.1% of the total of CSs performed in 2015 and 2016. The highest CS rates were recorded in RCS groups 5 (65.2%) and 8 (32.3%). Group 2 was the highest contributor to the overall CS rate, since it represented 56.7% of the population. The intravaginal prostaglandins method was the most used (77%). Transcervical Foley catheter was the preferredmethod in group 5 and intravaginal prostaglandins in all the other groups. The CS rate was higher when transcervical Foley catheter was used (34.1%).
Conclusion
Transcervical Foley catheter induction was associated with a higher rate of CS, probably because it was the preferred method used in group 5.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Drug Use during Pregnancy and its Consequences: A Nested Case Control Study on Severe Maternal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):518-526
Abstract
Original ArticleDrug Use during Pregnancy and its Consequences: A Nested Case Control Study on Severe Maternal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):518-526
Views250See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the relationship between the use of psychoactive substances during pregnancy and the occurrence of severe maternal morbidity (SMM), perinatal outcomes and repercussions on the neuropsychomotor development of exposed children.
Methods
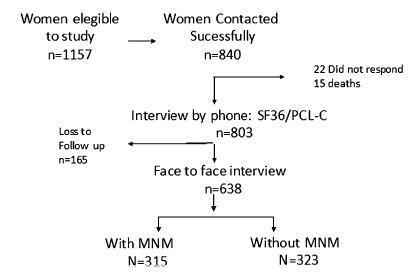
A case-control study nested within a cohort of severe maternal morbidity (COMMAG) was performed. Women with SMM were considered cases. Controls were thosewith low-risk pregnancy,without SMMand admitted during the same time period as the cases. Cohort data were collected retrospectively in hospital records for childbirth. A face-to-face interview was also performed with 638 women (323 without SMM and 315 with SMM) and their children of the index pregnancy between 6 months and 5 years after childbirth. During the interview, substance abuse during pregnancy was assessed by a modified question from the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test 2.0 (ASSIST) and the neuropsychomotor development in the children was assessed by the Denver Developmental Screening Test, 2nd edition.
Results
The prevalence of licit or illicit drug use during pregnancy was ~ 17%. Among drug users, 63.9% used alcohol, 58.3% used tobacco, 9.2% used cocaine/crack and 4.6% used marijuana. There was no association between drug use during pregnancy and SMM, although tobacco use during pregnancy was associated with bleeding, presence of near-miss clinical criteria (NMCC) and alteration in infant development; alcohol use was associated with neonatal asphyxia; and cocaine/crack use was associated with the occurrence of some clinical complications during pregnancy.
Conclusion
The use of psychoactive substances during pregnancy is frequent and associated with worse maternal, perinatal and child development outcomes.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Shared Oocyte Donation: Ideas and Expectations in a Bioethical Context Based on a Qualitative Survey of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):527-533
Abstract
Original ArticleShared Oocyte Donation: Ideas and Expectations in a Bioethical Context Based on a Qualitative Survey of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):527-533
Views149See moreAbstract
Objective
Assisted reproduction combines innovative technologies and new forms of procreation through gamete donation; however, it also leads to moral and ethical issues and to the wide application of referential bioethics. The objective of the present study was to understand the bioethical context of shared oocyte donation.
Methods
The present qualitative study used the Collective Subject Discourse methodology to interview donors and recipients in Brazil.
Results
Donors suffer from infertility, and in vitro fertilization opens the possibility of having a child; however, the cost is high, and helping the recipient is more important than the financial cost. The recipients regret delaying motherhood; adopting a child is their last option, and they desire to feel the physical stages of pregnancy. The recipients find the rules unfair regarding the lack of an oocyte bank and the fact that the treatment must be performed in shared cycles; however, oocyte donation makes it possible to realize the common dream of motherhood.
Conclusion
The obtained data showed that the patients are suffering and frustrated due to infertility, and they realize that in vitro fertilization may be the treatment they need. These women believe that children are essential in the constitution of the family, and scientific advances bring about innovative technologies and new forms of family constitution, with repercussions in the social, economic, political, and family contexts that lead to bioethical questions in Postmodernity.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Quality Information about Uterine Fibroids on the Internet
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):547-553
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality Information about Uterine Fibroids on the Internet
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):547-553
Views133See moreAbstract
Objective
There are no published studies analyzing the quality of the information for lay women on the Internet regarding uterine fibroids. The accuracy of the provided material is also unknown. Thus, we have performed a cross-sectional study with 381 websites in the English and Brazilian Portuguese languages between May and December 2017.
Methods
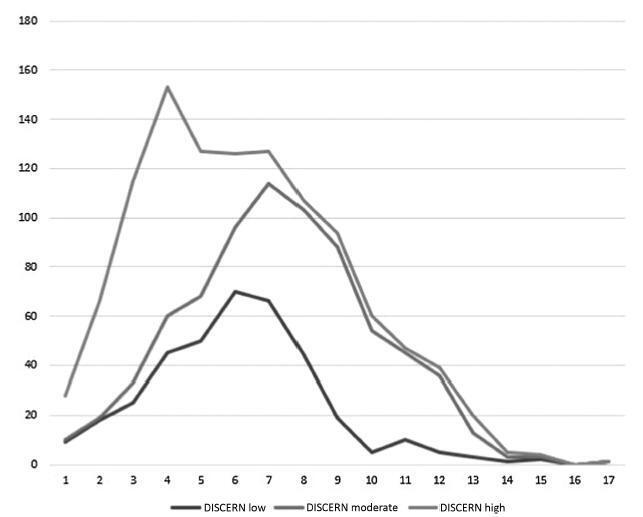
Two investigators performed the analysis, and the Cohen kappa coefficient was calculated to analyze the agreement between them. Search terms (uterine fibroids and derivatives) in the English and Brazilian Portuguese languages were used. The accuracywas analyzed by a 10-itemchecklist created based on the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), National Institutes of Health (NIH) and European Menopause and Andropause Society (EMAS) consensuses about uterine fibroids. The item-test correlation and the intraclass coefficient were performed in the 16 questions from the DISCERN instrument, which was designed to measure the quality of health information on the Internet. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) measurements were performed for the independent variables and the DISCERN/accuracy scores.
Results
Google was the most used search engine, and uterine fibroid was the search term that generatedmost of the analyzed material. The median score for accuracy in all websites was 5 out of 10, and the median score of the DISCERN instrument was 38 out of 80. The top-scoring sites in the English language were derived from scientific organizations and federal governments, and they regarded the DISCERN score (The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [ACOG], the Food and Drug Administration [FDA]) and the accuracy criteria (NIH, and FDA). On the other hand, in the Brazilian Portuguese language, the highest scores in both instruments were from magazines or physician’s blogs. The Cronbach α test showed a higher correlation (0.77-0.79) between the sites and DISCERN; however, the item-test correlation varied from 0.39 to 0.56.
Conclusion
There is a need to improve the quality of the information regarding uterine fibroids for lay women.
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Sexually Transmitted Infections Detected by Multiplex Real Time PCR in Asymptomatic Women and Association with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):540-546
Abstract
Original ArticleSexually Transmitted Infections Detected by Multiplex Real Time PCR in Asymptomatic Women and Association with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):540-546
Views228Abstract
Objective
To determine the frequency of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in asymptomatic women and the association of STIs with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
Methods
A cross-sectional studywas performed, enrollingwomen examined in a general gynecology clinic and in a colposcopy referral center fromOctober 2014 to October 2015. The colposcopy groupconsisted of 71women, and the general gynecologygroupconsisted of 55 women. Cervical samples were collected for cervical cytology and a multiplex realtime polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed to detect human papillomavirus (HPV) and the STIs caused by the following microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A multivariate analysis was performed by logistic regression, considering the significance level of 0.05.
Results
The general frequency of STIs was: 46.8% (HPV); 27.8% (C. trachomatis); 28.6% (M. genitalium); 0.8% (M. hominis); 4.8% (U. urealyticum); and 4.8% (N. gonorrhoeae). The significant risk factors for CIN were: HPV infection (odds ratio [OR] = 2.53; p = 0.024); C. trachomatis (OR = 3.04; p = 0.009); M. genitalium (OR = 2.37; p = 0.04); and HPV and C. trachomatis coinfection (OR = 3.11; p = 0.023). After the multivariate analysis, a significant associationwas found betweenHPVand CIN(OR = 2.48; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.04-5.92; p = 0.04); and between C. trachomatis and CIN (OR = 2.69; 95%CI: 1.11-6.53; p = 0.028).
Conclusion
The frequency of STIs was high in asymptomatic patients. Infections by HPV and C. trachomatis were independently associated with the presence of CIN. The high frequency of STIs in asymptomatic women suggests the need for routine screening of these infections.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaChlamydiaPapillomavirus infectionsPolymerase chain reactionSexually transmitted diseasesSee more -
Original Article08-01-2018
Hazards of Repeat Pregnancy during Adolescence: A Case-control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):437-443
Abstract
Original ArticleHazards of Repeat Pregnancy during Adolescence: A Case-control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):437-443
Views163See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the social, obstetric and psychological risk factors related to repeat pregnancy in teenagers.
Methods
A case control study conducted at Centro de Atenção à Saúde Integral da Mulher (Caism, in the Portuguese acronym), in Campinas, Brazil, from 2015 to 2017. Three groups were selected: a case-group of adolescents who had repeat pregnancy and two control-groups, one consisting of adolescents who had delivered at first time and another one of adult women with more than one deliveries. Participants were asked about habits, socio-demographics characteristics, reproductive and obstetric history and assessed psychological issues.
Results
Ninety women were enrolled, 30 in each study group. Adolescents with repeat pregnancy have lower self-esteem scores and more ineffective contraceptive use. When compared with teens at first delivery, they had less schooling level (odds ratio [OR] 4.03 [1.37-11.8]), more school abandon (OR 8.16 [2.36-28.2]) and drugs use (OR 4.97[1.39-17.8]). Non-white skin color (OR 6.2 [1.15-41.0]), drugs use (OR 17.5 [2.62-116.6]) and first sexual intercourse under 15y (OR 18.0[2.82-115.0]) were found as higher risk factors for repeat pregnancy when comparing adolescents and adults.Moreover, adolescents withmore than one gestation had lower self-esteem and greater susceptibility to unplanned pregnancy.
Conclusion
There was an association between repeat pregnancy among adolescents and lower education, early onset of sexual activity, non-white skin color, low use of contraception and increased use of drugs.


