Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo60
To analyze marital outcomes, divorce or separation, and its association with demographic, socioeconomic, and clinicopathological factors among breast cancer (BC) survivors after 2-years of diagnosis.
We performed a retrospective analysis of marital status at baseline and at years 1 and 2 of follow-up of women aged ≥ 18 years diagnosed with invasive BC participating in the AMAZONA III (GBECAM0115) study. The BC diagnosis occurred between January 2016 and March 2018 at 23 institutions in Brazil.
Of the 2974 women enrolled in AMAZONA III, 599 were married or living under common law at baseline. Divorce or separation occurred in 35 (5.8%) patients at 2 years of follow-up. In the multivariate analysis, public health insurance coverage was associated with a higher risk of marital status change (8.25% vs. 2.79%, RR 3.09, 95% CI 1.39 - 7.03, p = 0.007). Women who underwent mastectomy, adenomastectomy or skin-sparing mastectomy were associated with a higher risk of divorce or separation (8.1% vs. 4.49%, RR 1.97, 95 CI 1.04 – 3.72, p = 0.0366) than those who underwent breast-conserving surgery.
Women covered by the public health system and those who underwent mastectomy, adenomastectomy or skin-sparing mastectomy were associated with a higher risk of divorce or separation. This evidence further supports the idea that long-term marital stability is associated with a complex interplay between socioeconomic conditions and stressors, such as BC diagnosis and treatment. ClinicalTrials Registration: NCT02663973.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo40
To evaluate and compare the sexual function and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) function of women with endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain (CPP) with and without Myofascial Pelvic Pain Syndrome (MPPS).
Cross-sectional study conducted between January 2018 and December 2020. Women with deep endometriosis underwent assessments for trigger points (TP) and PFM function using the PERFECT scale. Electromyographic activity (EMG) and sexual function through Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) were assessed. Statistical analyses included chi-square and Mann-Whitney tests.
There were 46 women. 47% had increased muscle tone and 67% related TP in levator ani muscle (LAM). Weakness in PFM, with P≤2 was noted in 82% and P≥3 in only 17%. Incomplete relaxation of PFM presented in 30%. EMG results were resting 6.0, maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) 61.9 and Endurance 14.2; FSFI mean total score 24.7. We observed an association between increased muscle tone (P<.001), difficulty in relaxation (P=.019), and lower Endurance on EMG (P=.04) in women with TP in LAM. Participants with TP presented lower total FSFI score (P=.02). TP in the right OIM presented increased muscle tone (P=.01). TP in the left OIM presented lower values to function of PFM by PERFECT (P=.005), and in MVIC (P=.03) on EMG.
Trigger points (TP) in pelvic floor muscles (PFM) and obturator internus muscle (OIM) correlates with poorer PFM and sexual function, particularly in left OIM TP cases. Endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain raise muscle tone, weaken muscles, hinder relaxation, elevate resting electrical activity, lower maximum voluntary isometric contraction, and reduce PFM endurance.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
To describe Top-hat results and their association with margin status and disease relapse in a referral facility in Brazil.
A retrospective study of 440 women submitted to LEEP to treat HSIL, in which 80 cases were complemented immediately by the top hat procedure (Top-hat Group - TH). TH Group was compared to women not submitted to Top-hat (NTH). The sample by convenience included all women that underwent LEEP from January 2017 to July 2020. The main outcome was the histological result. Other variables were margins, age, transformation zone (TZ), depth, and relapse. The analysis used the Chi-square test and logistic regression.
The TH Group was predominantly 40 and older (NTH 23.1% vs. TH 65.0%, p<0.001). No difference was found in having CIN2/CIN3 as the final diagnosis (NTH 17.0% vs. TH 21.3%, p=0.362), or in the prevalence of relapse (NTH 12.0% vs. TH 9.0%, p=0.482). Of the 80 patients submitted to top hat, the histological result was CIN2/CIN3 in eight. A negative top hat result was related to a negative endocervical margin of 83.3%. A CIN2/CIN3 Top-hat result was related to CIN2/CIN3 margin in 62.5% (p=0.009). The chance of obtaining a top hat negative result was 22.4 times higher (2.4-211.0) when the endocervical margin was negative and 14.5 times higher (1.5-140.7) when the ectocervical margin was negative.
The top hat procedure did not alter the final diagnosis of LEEP. No impact on relapse was observed. The procedure should be avoided in women of reproductive age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo45
To explore women's experiences with postpartum intrauterine device (PPIUD) insertion and the decision-making process in the postpartum period.
A qualitative design was employed with face-to-face interviews using a semi-structured script of open questions. The sample was intentionally selected using the concept of theoretical information saturation.
Interviews were conducted (1) in the immediate postpartum period, and (2) in the postpartum appointment. 25 women (N = 25) over 18 years old who had a birth followed by PPIUD insertion were interviewed between October 2021 and June 2022. Three categories were constructed: (1) Choice process, (2) Relationship with the health team at the time of birth and the postpartum period, and (3) To know or not to know about contraception, that is the question.
Professionals’ communication management, popular knowledge, advantages of the PPIUD and the moment PPIUD is offered play a fundamental role in the construction of knowledge about the IUD. Choice process did not end in the insertion.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo64
To evaluate whether there were differences in the presentation of patients with tubal ectopic pregnancy (EP) during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic.
We performed a retrospective cohort study of all cases of tubal EP between March 2019 and March 2020 (pre-pandemic) and between March 2020 and March 2021 (pandemic). We compared between these two groups the risk factors, clinical characteristics, laboratory data, sonographic aspects, treatment applied and complications.
We had 150 EP diagnoses during the two years studied, of which 135 were tubal EP. Of these, 65 were included in the pre-pandemic and 70 in the pandemic period. The prevalence of lower abdominal pain was significantly higher in the pandemic compared to the pre-pandemic period (91.4% vs. 78.1%, p=0.031). There was no significant difference in shock index, initial beta-hCG level, hemoglobin level at diagnosis, days of menstrual delay, aspect of the adnexal mass, amount of free fluid on ultrasound, and intact or ruptured presentation between the groups. Expectant management was significantly higher during the pandemic period (40.0% vs. 18.5%, p=0.008), surgical management was lower during the pandemic period (47.1% vs. 67.7%, p=0.023), and number of days hospitalized was lower in the pandemic period (1.3 vs. 2.0 days, p=0.003).
We did not observe a significant difference in patient history, laboratory and ultrasound characteristics. Abdominal pain was more common during the pandemic period. Regarding treatment, we observed a significant increase in expectant and a decrease in surgical cases during the pandemic period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo23
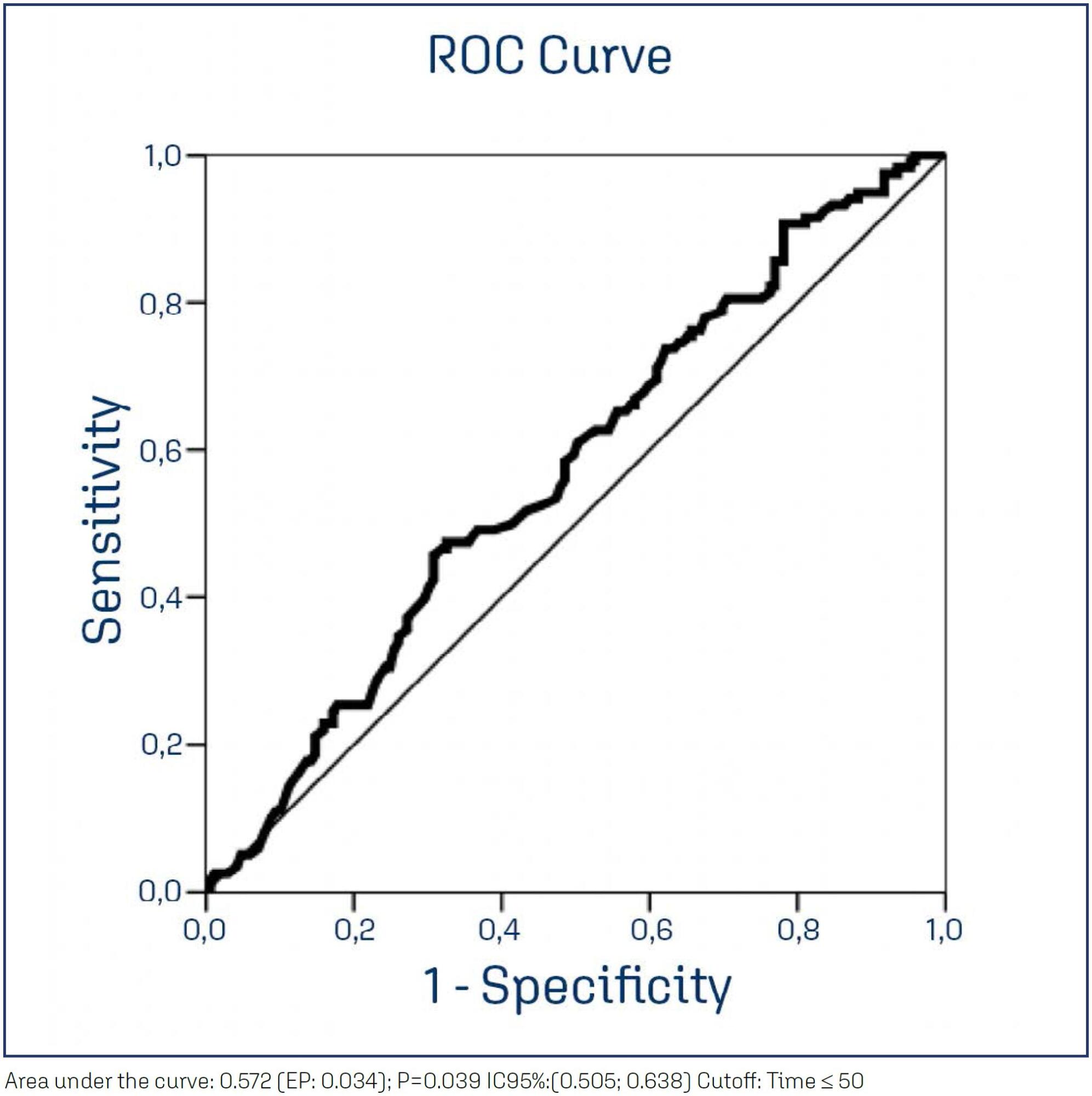
To assess the rate of missed postpartum appointments at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy and compare puerperal women who did and did not attend these appointments to identify related factors.
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study with all women scheduled for postpartum consultations at a high-risk obstetrics service in 2018. The variables selected to compare women were personal, obstetric, and perinatal. The variables of interest were obtained from the hospital's electronic medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using the Chi-square, Fisher's exact, or Mann–Whitney tests. For the variable of the interbirth interval, a receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to best discriminate whether or not patients attended the postpartum consultation. The significance level for the statistical tests was 5%.
A total of 1,629 women scheduled for postpartum consultations in 2018 were included. The rate of missing the postpartum consultation was 34.8%. A shorter interbirth interval (p = 0.039), previous use of psychoactive substances (p = 0.027), current or former smoking (p = 0.003), and multiparity (p < 0.001) were associated with non-attendance.
This study showed a high rate of postpartum appointment non-attendance. This is particularly relevant because it was demonstrated in a high-risk obstetric service linked to clinical severity or social vulnerability cases. This highlights the need for new approaches to puerperal women before hospital discharge and new tools to increase adherence to postpartum consultations, especially for multiparous women.
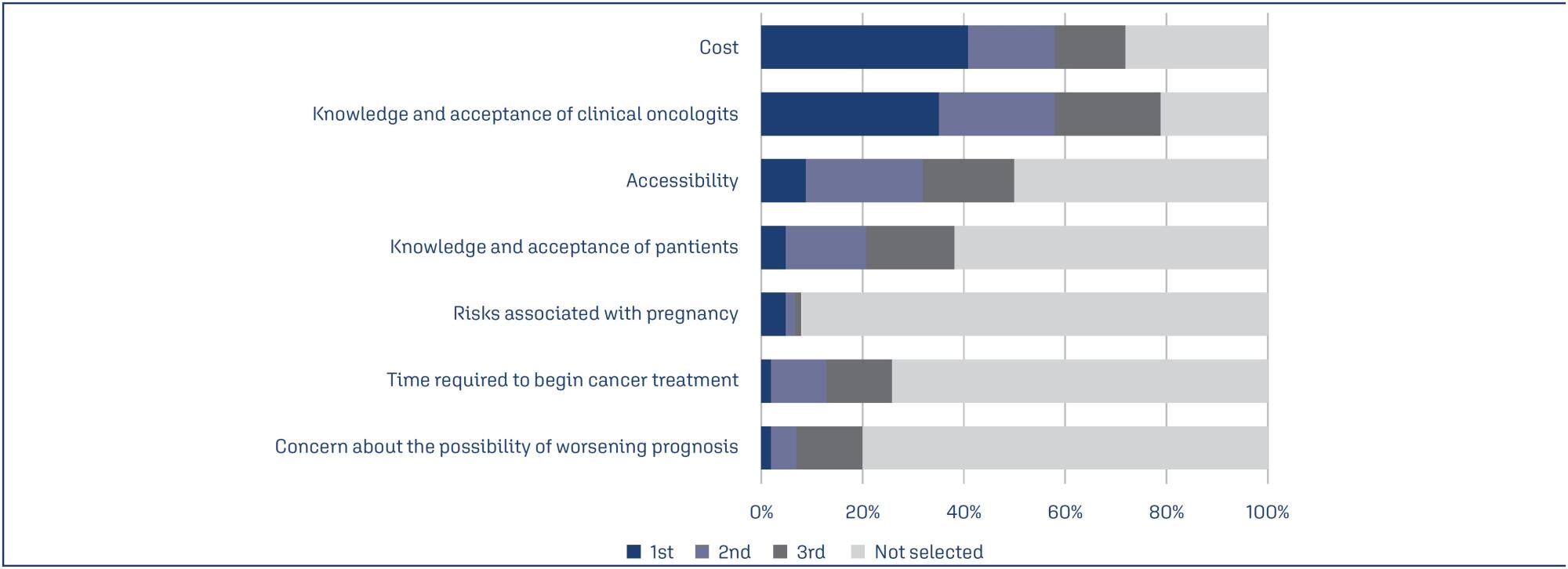
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo25
Fertility preservation is a priority in oncology for female cancer patients. However, there is a lack of communication between infertility specialists and oncologists. This study aimed to evaluate infertility specialists’ perceptions and experiences regarding fertility preservation.
Conduct an online survey to profile infertility specialists. Participants were infertility affiliated with the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO). The specialists received an online survey, which response rate were 30.9%, most of whom were in southern and southeastern. The survey consisted on 14 questions about the infertility specialists’ location, techniques in clinical practice, treatment successful rate, patients idea, etc.
The average experience in human reproduction were 15.5 ± 10.2 years (mean ± standard deviation, range 1-40). Among reproductive-aged female cancer patients recommended for fertility preservation, 60.3 ± 28.8% (range 10-100%) underwent preservation procedures. Main barriers were cost (41%), oncologists’ knowledge or acceptance (35%) and accessibility (9%). Most infertility specialists (58%) considered 40 years the limit for fertility preservation. Leukemia, lymphoma, breast and ovarian cancers were prioritized for fertility preservation, while lung, thyroid, gastric, and brain cancers were less relevant.
This is the first Brazilian study about infertility specialists’ perceptions on oncology patients access to fertility preservation. These patients primarily receive treatment in the public health system, while infertility specialists mainly work in the private healthcare. This healthcare mode is currently fragmented, but integrating these experts is enhancing patient access to fertility preservation. Studies on this topic are still warranted.
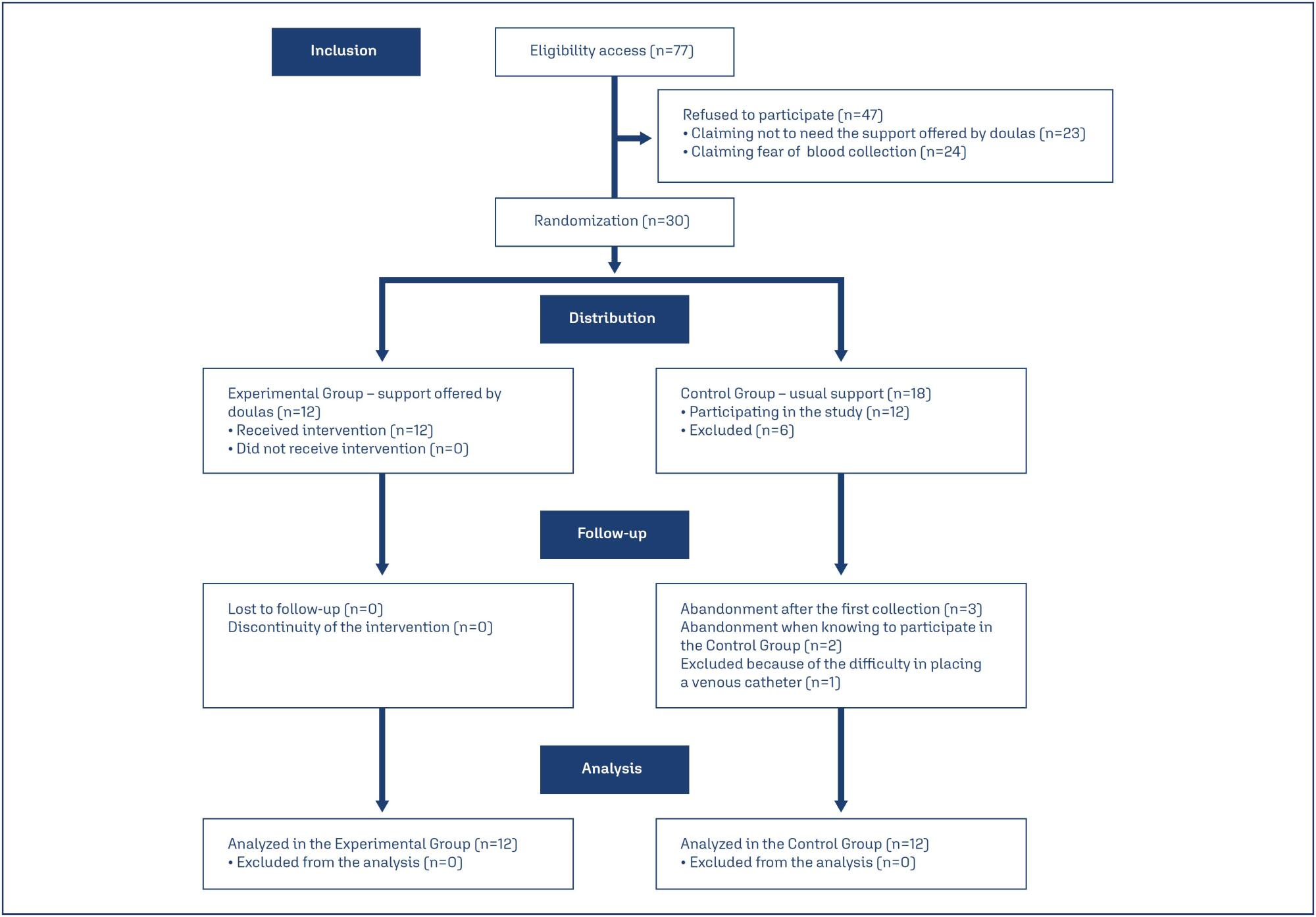
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo27
To evaluate whether the continuous support provided by doulas influences the endogenous release of serotonin in parturients.
This pilot study included 24 primigravidae at term. Of these, 12 women received continuous doula support (Experimental Group), whereas the other 12 received the usual assistance without doula support (Control Group). Blood samples were collected from all the women at the active and expulsion stages of labor and at the fourth period of labor (Greenberg period) for evaluation of their serotonin levels using high-performance liquid chromatography.
The average serotonin concentrations in the control and experimental groups were respectively 159.33 and 150.02 ng/mL at the active stage, 179.13 and 162.65 ng/mL at the expulsion stage, and 198.94 and 221.21 ng/mL at the Greenberg period. There were no statistically significant differences in serotonin concentrations between the two groups at the active and expulsion stages of labor. By contrast, within the experimental group, a significant increase in serotonin concentration was observed in the Greenberg period compared with the levels in the active and expulsion stages (p < 0.05).
The novelty of this study relies on the ability to correlate the influence of the continuous support offered by doulas with the release of serotonin in parturients, with the results suggesting that the assistance received during labor can modulate the levels of hormone release in the Greenberg period.
RBR-4zjjm4h