Summary
. 2021;43(10):749-758
To investigate whether patients with a previous recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (rFSH)-stimulated cycle would have improved outcomes with rFSH + recombinant luteinizing hormone (rLH) stimulation in the following cycle.
For the present retrospective case-control study, 228 cycles performed in 114 patients undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) between 2015 and 2018 in an in vitro fertilization (IVF) center were evaluated. Controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) was achieved with rFSH (Gonal-f, Serono, Geneva, Switzerland) in the first ICSI cycle (rFSH group), and with rFSH and rLH (Pergoveris, Merck Serono S.p.A, Bari, Italy) in the second cycle (rFSH + rLH group). The ICSI outcomes were compared among the groups.
Higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, day-3 high-quality embryos rate and implantation rate, and a lower miscarriage rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group compared with the rFSH group. In patients < 35 years old, the implantation rate was higher in the rFSH + rLH group compared with the rFSH group. In patients ≥ 35 years old, higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, day-3 high-quality embryos rate, and implantation rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group. In patients with ≤ 4 retrieved oocytes, oocyte yield, mature oocytes rate, normal cleavage speed, implantation rate, and miscarriage rate were improved in the rFSH + rLH group. In patients with ≥ 5 retrieved oocytes, higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, and implantation rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group.
Ovarian stimulation with luteinizing hormone (LH) supplementation results in higher implantation rates, independent of maternal age and response to COS when compared with previous cycles stimulated with rFSH only. Improvements were also observed for ICSI outcomes and miscarriage after stratification by age and retrieved oocytes.
Summary
. 2021;43(10):759-764
Breast surgery is considered a clean surgery; however, the rates of infection range between 3 and 15%. The objective of the present study was to intraoperatively investigate the presence of autochthonous microbiota in the breast.
Pieces of breast tissue collected from 49 patients who underwent elective breast surgery (reconstructive, diagnostic, or oncologic) were cultured. The pieces of breast tissue were approximately 1 cm in diameter and were removed from the retroareolar area, medial quadrant, and lateral quadrant. Each piece of tissue was incubated in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth for 7 days at 37°C, and in cases in which the medium became turbid due to microorganism growth, the samples were placed in Petri dishes for culturing and isolating strains and for identifying species using an automated counter.
Microorganism growth was observed in the samples of 10 of the 49 patients (20.4%) and in 11 of the 218 pieces of tissue (5%). The detected species were Staphylococcus lugdunensis, Staphylococcus hominis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Sphingomonas paucimobilis, and Aeromonas salmonicida. No patient with positive samples had clinical infection postoperatively.
The presence of these bacteria in breast tissue in approximately 20% of the patients in this series suggests that breast surgery should be considered a potential source of contamination that may have implications for adverse reactions to breast implants and should be studied in the near future for their oncological implications in breast implant-associated large-cell lymphoma etiology.
Summary
. 2021;43(10):765-774
To investigate depression and sexual function among pregnant and nonpregnant women throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
A total of 188 women, 96 pregnant and 92 non-pregnant were included. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX) were applied to the participants after obtaining sociodemographic data.
The depression scores of pregnant and non-pregnant women were similar (p = 0.846). We found that the depression scores were significantly higher among the group of participants who have lower economic status (p = 0.046). Moreover, the depression score was significantly higher among women who lost their income during the pandemic (p = 0.027). The score on the ASEX was significantly higher, and sexual dysfunction was more prevalent among women who have lower levels of schooling and income (p < 0.05). Likewise, the ASEX scores were significantly higher (p = 0.019) among the group who experienced greater income loss throughout the pandemic. Upon comparing the pregnant and non-pregnant groups, we detected that sexual dysfunction had a significantly higher rate among pregnant women (p < 0.001).
In times of global crisis, such as the current pandemic, low-income families have an increased risk of experiencing depression and sexual dysfunction. When we compared pregnant women with non-pregnant women, depression scores were similar, but pregnant women were at a 6.2 times higher risk of developing sexual dysfunction.
Summary
. 2021;43(9):648-654
To identify how health providers recognize postpartum hemorrhage early and the difficulties involved in it.
An exploratory, descriptive study using a qualitative approach through a semi-structured interview technique. In total, 27 health professionals (nursing tech nicians, nurses, medical residents in Gynecology and Obstetrics, hired medical doctors, and medicine professors) working in a tertiary-level hospital of reference in women’s health care in the State of São Paulo, Brazil, participated in the study through an invitation. After they accepted the invitation, they signed the free and informed consent form. All interviews were recorded and transcribed, and a thematic analysis was conducted. We found three analysis categories: a) perception of the severity: “there is something wrong with the women”; b) difficulties in the early diagnosis of postpartum hemorrhage; and c) the process to improve obstetrical care.
Caregivers believe teamwork and communication should be improved. Besides the visual estimation of blood loss, the nursing team is attentive to behavioral symptoms like irritability, while the medical staff follow protocols and look for objective signs, such as altered vital signs.
Besides the objective evaluations, the subjective perceptions of the providers are involved in the clinical judgement regarding the diagnosis of postpartum hemorrhage, and this should be included in a broader diagnosis strategy.
Summary
. 2021;43(9):655-661
To describe the clinical experience with the B-Lynch technique in the management of postpartum hemorrhage as well as the factors related to the indication of the technique and to present the success rates of the application of the B-Lynch technique.
Observational, retrospective, cross-sectional, and analytical study. Patient data was obtained through the study of medical records. The study population comprised of patients who underwent hemostatic suture using the B-Lynch technique, including 104 patients within the period from January 1, 2005, to December 31, 2019.
Of the total of 104 patients, 82.7% did not present any complications. Blood transfusion and intensive care unit admission were the most prevalent complications, with 13.5% and 15.4%, respectively. Only 1% of the patients had puerperal and surgical site infections. The factors most related to the application of the technique were the presence of previous cesarean section (30.8%), use of oxytocin (16.3%), and pre-eclampsia (11.6%). Puerperal hysterectomy was performed in 4.8% of the patients due to failure of the method.
The clinical experience with the B-Lynch technique was satisfactory since it presented few complications, with excellent results in hemorrhagic control. Previous cesarean section, the use of oxytocin, and preeclampsia stood out as factors related to the indication of the application of the technique, and the success rate in controlling postpartum hemorrhage was 95.2%.
Summary
. 2021;43(9):669-675
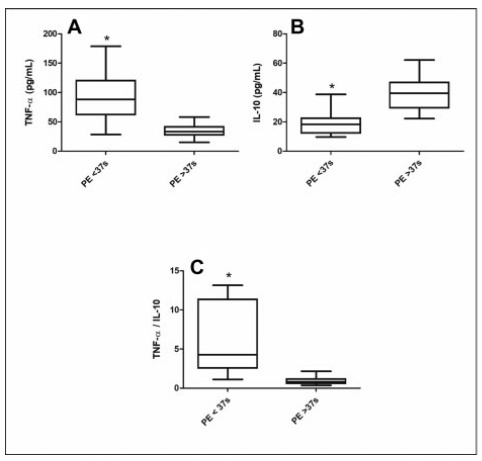
Preeclampsia (PE) is a pregnancy-specific syndrome characterized by abnormal levels of cytokines and angiogenic factors, playing a role in the disease development. The present study evaluated whether immunological markers are associated with the gestational age and with the disease severity in preeclamptic women.
Ninety-five women who developed PE were stratified for gestational age as preterm PE (< 37 weeks) and term PE (≥ 37 weeks of gestation) and compared for disease severity as well as plasma concentration of angiogenic factors and cytokines. The concentrations of placental growth factor (PlGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Fms-like soluble tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1) and soluble endoglin (sEng), as well as the cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin 10 (IL-10), were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
The comparison between preeclamptic groups showed a higher percentage of severe cases in preterm PE (82.1%) than in term PE (35.9%). Similarly, the concentrations of TNF-α, sFlt-1, and sEng, as well as TNF-α/IL-10 and sFlt-1/PlGF ratios were significantly higher in the preterm PE group. In contrast, concentrations of PlGF, VEGF, and IL-10 were significantly lower in women with preterm PE. Negative correlations between TNF-α and IL-10 (r = 0.5232) and between PlGF and sFlt1 (r = 0.4158) were detected in the preterm PE.
In pregnant women with preterm PE, there is an imbalance between immunological markers, with the predominance of anti-angiogenic factors and TNF-α, associated with adverse maternal clinical outcomes.
Summary
. 2021;43(9):676-681
To assess the most common psychological disturbances in women with deep endometriosis and bowel involvement who are waiting surgical treatment and to evaluate what forms of coping are used to solve the problem.
This was a cross-sectional observational study of 40 women diagnosed with deep endometriosis and intestinal symptoms. They completed two questionnaires: one for anxiety and depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [ HADS]) and the Scale of Mode of Confronting Problems (EMEP, in the Portuguese acronym).
We found that 77.1% of the patients had anxiety and depression, with anxiety being the most prevalent (87.5% of the patients); 90% of the patients used problem focused and religious introspection as their main modes of confronting problems.
In the use of the HADS questionary, two psychological aspects were the most present in women with deep endometriosis awaiting surgical treatment: anxiety and depression. The most used forms of coping to solve the problem were problem coping and religious practices.