Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2006;28(3):190-194
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300009
PURPOSE: to verify the viability of early diagnosis of fetal gender in maternal plasma by the real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) starting at the 5th week of pregnancy. METHODS: peripheral blood was collected from pregnant women with single fetus starting at the 5th week of gestation. After centrifugation, 0.4 mL plasma was separated for fetal DNA extraction. The DNA was analyzed in duplicate by real-time PCR for two genomic regions, one of the Y chromosome and the other common to both sexes, through the TaqMan® method, which uses a pair of primers and a fluorescent probe. Patients who aborted were excluded. RESULTS: a total of 79 determinations of fetal DNA in maternal plasma were performed in 52 pregnant women. The results of the determinations were compared to fetal gender after delivery. Accuracy according to gestational age was 92.6% (25 of 27 cases) at 5 weeks with 87% sensitivity, and 95.6% (22 of 23 cases) at 6 weeks with 92% sensitivity. Starting at the 7th week of pregnancy, accuracy was 100% (29 of 29 cases). Specificity was 100% regardless of gestational age. CONCLUSION: real-time PCR for the detection of fetal gender in maternal plasma starting at the 5th week of gestation has good sensitivity and excellent specificity. There was agreement of the results in 100% of the cases in which male gender was diagnosed, regardless of gestational age, and from the 7th week of gestation for female gender diagnosis.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(9):735-739
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000900010
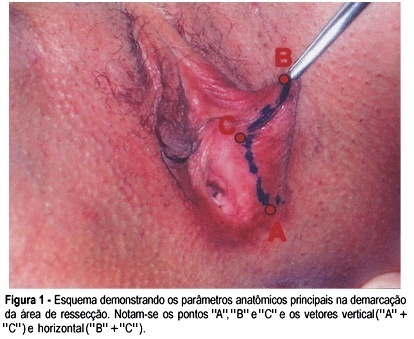
PURPOSE: to describe the use of a superior labial flap for the treatment of labia minora hypertrophy. METHODS: from May, 1998 to July, 2002 10 patients with labia minora hypertrophy were submitted to reduction of the labial excess through the resection of the inferior segment by an L-shaped incision. The transversal incision was done starting on the labial external border towards the hymenal caruncles, and the longitudinal incision, from that point until near the furcula. The border of the superior flap was then lowered to eliminate the defect caused by the inferior resection. RESULTS: within an average period of 45 days after surgery, the patients were satisfied with its esthetical and functional aspects. The local sensibility did not change. Only two cases presented complications: one case with perineal ecchymosis and the other with partial, early unilateral dehiscense. Infection, necrosis and late dehiscense were not observed. CONCLUSION: the utilization of the superior flap in the correction of labia minora hypertrophy produces a satisfactory esthetical and functional result with few complications and easy resolution.
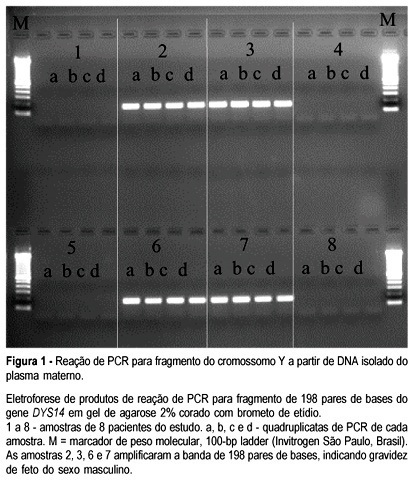
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2003;25(9):687-690
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900011
PURPOSE: to evaluate a new method of fetal sex determination through the analysis of DNA from maternal plasma. METHODS: peripheral blood (10 mL) was drawn from pregnant women in different gestational ages. Plasma was separated and isolated DNA was submitted to the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with primers from the Y-chromosome-specific gene DYS14. RESULTS: two hundred and twelve patients were enrolled. PCR results were compared to either confirmatory ultrasonography and/or birth. Agreement was observed in 209 samples. Discordant plasmas had a PCR result of female fetus and all of them were derived from mothers with less than 8 weeks of pregnancy. CONCLUSION: the PCR method developed for fetal sex determination has excellent sensitivity and specificity, permitting its use as a routine test. A PCR result of male fetus presents a higher confidence than a female one, specially in early gestational periods. New applications employing fetal DNA from maternal plasma are being developed and hopefully will allow noninvasive diagnosis of several conditions.