Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):196-200
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400007
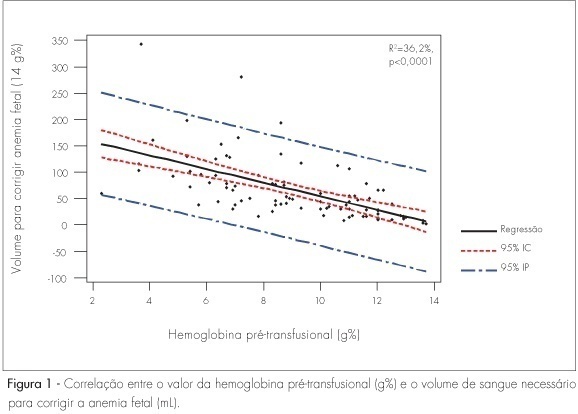
PURPOSE: to obtain an equation to estimate the volume of red blood cells concentrate to be infused to correct anemia in fetuses of pregnant women with Rh factor isoimmunization, based in parameters obtained along the cordocentesis previous to intrauterine transfusion. METHODS: a transversal study analyzing 89 intrauterine transfusions to correct anemia in 48 fetuses followed-up in the Centro de Medicina Fetal do Hospital das Clínicas da Universidade de Minas Gerais. The median gestational age at the cordocentesis was 29 weeks and the average number of procedures was 2.1. Fetal hemoglobin was assayed before and after cordocentesis, leading to the volume of transfused red blood cells concentrate. The determination of an equation to estimate the blood volume necessary to correct the fetal anemia was based in the blood volume necessary to raise the fetal hemoglobin in 1 g% (the difference between the final and the initial hemoglobin concentration divided by the transfused volume) and in the volume of the amount necessary to reach 14 g%, in the multiple regression analysis. RESULTS: the concentration of pre-transfusion hemoglobin varied between 2.3 and 15.7 g%. The prevalence of fetal anemia (Hb<10 g%) was 52%. The regression equation obtained in the determination of blood volume necessary to reach the concentration of 14 g% of Hb was: transfusion volume (mL)=18.2 - 13.4 x pre- intrauterine transfusion hemoglobin + 6.0 x gestational age in weeks. This equation was statistically significant (p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: the study has shown that it is possible to estimate the transfusion volume necessary to correct fetal anemia, based on easily obtainable parameters: gestational age and level of pre-transfusion hemoglobin.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(3):127-134
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000300005
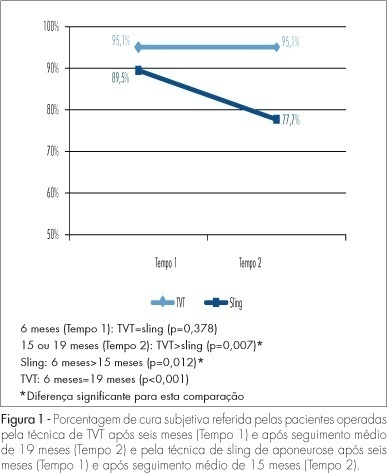
PURPOSE: to compare sling operations of aponeurosis and tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) for the correction of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) regarding: the rates of subjective and objective healing, the mobility of the bladder neck with ultrasonography, the variation of the absorbent test, the urodynamic alterations and the incidence of complications. METHODS: eighty patients with SUI were selected. Among them, 61 underwent a TVT surgery and 19, an abdominal rectum sling operation of aponeurosis. Average age, index of body mass and parity were 50.1 years old, 29.7 kg/m² and 4.1 deliveries (median=3) for the patients with aponeurosis sling, and 51.7 years old, 28.1 kg/m² and 4.1 deliveries (median=3) for the ones with TVT. All of them have undergone anamnesis, physical examination, bladder neck ultrasonography, absorbent test and urodynamic evaluation before and at least six months after the surgery. After 15 or 19 months and after about four or five years, they were again interviewed concerning the surgery results. RESULTS: after six months, 96.7% of the women with TVT and 89.5% of the ones with sling thought they were healed in the subjective evaluation. Nevertheless, after 15 to 19 months, the TVT Group kept the same subjective healing rate, while among the Sling Group the rate decreased to 77.8%. There was a significant decrease in the mobility of the neck bladder that was similar in both groups and an improvement in the absorbent test. At the end of the urodynamic study, 93.4% of the women from the TVT Group and 78.9% of the ones from the Sling Group were classified as having an objective healing. The average time of bladder probing was higher in the Sling Group. Urinary retention was observed in 42.1% of the sling cases and in 9.8% of the TVT's. The rates of late healing were 90% for TVT and 55.6% for sling. CONCLUSIONS: TVT surgery provided better subjective healing after 15 or 19 months, but the rate of objective healing was the same in both techniques at that time. Among the complications detected, the urinary retention was higher in the Sling Group, in the post-surgery period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):55-60
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200002
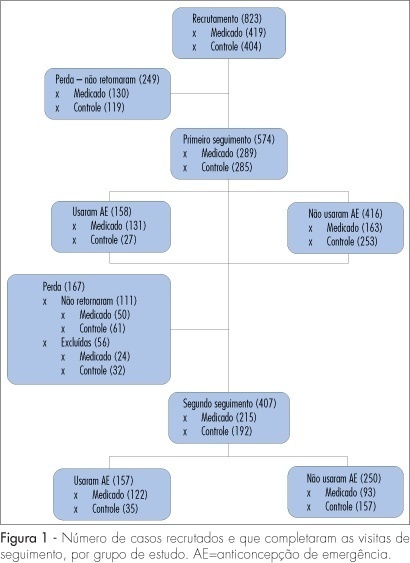
PURPOSE: to compare two strategies of access to emergency contraception: only information and information with previous delivery of this contraceptive method, and its relationship with the use of this method and the regular use of contraceptives. METHODS: from August 2004 to January 2005, 18 to 49-year-old volunteers, attended at reproductive health clinics from six Brazilian towns were recruited. The subjects were randomly distributed in a group getting information about emergency contraception (Control Group), or in a group getting information about this method and previous delivery of the contraceptive (Medicated Group). Follow-up visits occurred into four and eight months. Person and McNemar's tests were used for the statistical analysis. RESULTS: from the 823 recruited subjects, 407 completed the 8-month-observation period and were the sample analyzed. Most of the subjects (61%) did not use the emergency contraceptive. The subjects from the Medicated Group used more emergency contraceptives (57%) than the ones from the Control Group (18%), and they did it more precociously, concerning the time since the unprotected sexual intercourse. There was a significant increase of regular use of contraceptives among the subjects who used emergency contraceptives in the Medicated Group (88% versus 97%) and a statistically nonsignificant decrease in the Control Group. CONCLUSIONS: information and previous delivery intensified the access and use of emergency contraceptives, and did not reduce the regular use of contraceptives, including condoms.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):61-66
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200003
PURPOSE: to demonstrate the expression of biomarkers, detected by immunohistochemical techniques in healthy tissues, as well as in preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions of the uterine cervix. METHODS: in order to evaluate the immunohistochemical reactivity of tissues from the uterine cervix to p16 and to type 2 herpes simplex virus (HSV-2), 187 samples of low-grade intraepithelial lesions (LG-IEL) and high-grade intraepithelial lesions (HG-IEL), and of uterine cervix carcinoma were compared with a group of patients without uterine cervix lesions. Statistical analysis was done by the chi2 test for trends. The significance level was alpha=0.05. RESULTS: the reactivity to p16 was assessed showing the following distribution: group without uterine cervix lesions: 56% (24/43), LG-IEL: 92% (43/47), HG-IEL: 94% (43/46), and cancer: 98% (46/47) (p<0.001, linear trend). Concerning the HSV-2: group without uterine cervix lesions: 27% (12/45), LG-IEL: 58% (22/38), HG-IEL: 78% (35/45), and cancer: 59 % (29/49) (p<0.001, linear trend). There was an increase in the reactivity ratio for the two markers in the pathological groups (LG-IEL, HG-IEL and uterine cervix cancer, at p<0.001) compared to controls. There was no significant difference between the LG-IEL and the HG-IEL groups. CONCLUSIONS: a progressive increase of reactivity ratios of the studied immunohistochemical markers as a function of lesion severity was observed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):67-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200004
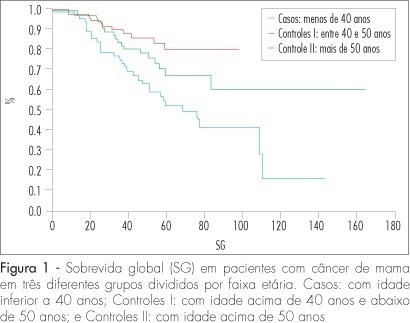
PURPOSE: to compare the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics, and the follow-up of breast cancer in women diagnosed under and over 40 years of age. METHODS: a retrospective study, case-control type, with analysis of information obtained from medical records of patients attended from January 1994 to June 2004. Cases of intraductal carcinoma and at stage IV were excluded. Three groups were formed: patients under 40 years old at the diagnosis (n=72); patients between 40 and 50 (n=68) and patients over 50 (n=75). Data about age at the moment of diagnosis, lesion largest diameter, clinical stage, type, histological grade, presence of hormonal receptors and state of the lymph nodes were collected and analyzed. The chi2 test was used for qualitative variables. For quantitative variables without normal distribution (such as number of axillary nodes with metastasis and follow-up duration), the Kruskal-Wallis' test was used. For delineating the curves of free-of-disease and global survival, the log-rank test was used. RESULTS: there was no difference among the groups in the stage distribution, concerning the tumoral differentiation grade or in the distribution of histological types, and in the estrogen receptor and c-erb-B2 expression. Difference was found in the RP expression, which was less frequent in the group of patients under 40, than in the group of patients over 50 (36.2% versus 58.4%) respectively. There was no difference among the groups in the mean tumoral diameter (5.1, 4.7 and 5 cm, respectively). There was also no difference among the groups, concerning the rate of axillary lymph node metastasis (63.9, 46.9 and 50%, respectively). The average follow-up was 54 months for all the groups. Disease recurrence occurred in 22.6% of patients under 40 years old, in 60% of patients between 40 and 50, and in 22.6% of patients over 50, with a significant difference among groups (p<0.0001). Death caused by the disease was higher among patients under 40 (46.9%) than among patients between 40 and 50 (26.9%) and over 50 (22.6%), p=0.0019. The logistic analysis showed that "age under 40" and the "presence of more than one metastatic axillary node" were independent death risk factors. CONCLUSIONS: age under 40 is an independent risk factor for breast cancer. The traditional prognostic indicators, such as stage, tumoral diameter, axillary involvement and presence of hormonal receptors are not associated with the disease evolution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):75-79
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200005
PURPOSE: the aim of this study is to evaluate the accuracy of mammography in the diagnosis of suspicious breast microcalcifications, using BI-RADS TM and Le Gal's classifications. METHODS: one hundred and thirty cases were selected with mammograms contain only microcalcifications of file and initially classified as suspicious (categories 4 and 5) without lesions clinical detectable and reclassified by two examiners, getting a consensus diagnosis. The biopsies were reviewed by two pathologists getting also a consensus diagnosis. Both, mammogram and histopathologic analysis were double blinded reviewed. Qui-square test, Fleiss-square statistic and EPI-INFO 6.0 were used in this study. RESULTS: the correlation between histopathological and mammographic analysis using BI-RADS TM and Le Gal classification showed the same sensitivity of 96.4%, specificity of 55.9 and 30.3%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 37.5 and 27.5%, and accuracy of 64.6 and 44.6% respectively. The PPV by BI-RADS TM categories was: category 2, 0%; category 3, 1.8%; category 4, 30.8%; and category 5, 60%. The PPV by Le Gal classification was: category 2, 3.1%; category 3, 18.1%; category 4, 26.4%;category 5, 66.7%, and non classified 5.2%. CONCLUSIONS: the results were better for the classification of BI-RADS™, but it did not get to reduce the ambiguity in assessment of breast microcalcifications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):80-86
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200006
PURPOSE: to describe the clinical and laboratorial profile of HELLP syndrome patients admitted at an Obstetric Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and included in a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in this clinical setting. METHODS: the present study is a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial design to evaluate the efficacy of dexamethasone in patients with HELLP syndrome. This sample of patients was composed of patients in the puerperium, with the diagnosis of HELLP syndrome (diagnosis made before or after delivery) who were not chronic corticosteroid users and not carriers of any chronic disease which could modify HELLP syndrome's laboratorial parameters. Patients who were too critical or whose condition did not allow them to consent to participate were not included. Data were extracted from the records used in the randomized clinical trial. Age, parity, gestational age at admission and delivery, time of diagnosis (before or after delivery), HELLP syndrome classification (partial or complete), arterial blood pressure, and diuresis at admission were considered for analysis. Among laboratorial findings, hemoglobin, platelet count, liver enzymes, LDH, and serum bilirubin were analyzed. Complications presented by the patients were also analyzed as well as need of blood transfusions and duration of hospitalization. Analysis was made by the Epi-Info 3.3.2 program. RESULTS: one hundred and five patients were analyzed. Age varied from 14 to 49 years (means of 26.7). Regarding parity, 56 patients (53.8%) were primiparas. Analyzing the timing of the diagnosis, 47 patients (45.2%) had the diagnosis before delivery. The mean gestational age in these patients was 32.4 weeks. Hemorrhagic manifestations were observed in 36 patients (34.3%), oliguria was present in 49 patients (46.7%) and criteria for acute renal failure were seen in 21 (20%) of the cases. Hemotransfusions were necessary in 35 (33.3%) patients. Seven patients (6.7%) had pulmonary edema and four patients died, corresponding to 3.8% of the cases. The mean time from diagnosis of HELLP syndrome to discharge or death was 10.3 days, varying from 1 to 33 days. CONCLUSIONS: HELLP syndrome is an ominous diagnosis, which implicates in elevated maternal morbimortality. Among complications, oliguria and hemorrhagic manifestations were the most common findings and hemotransfusions were frequently required. Lethality reached 3.8%.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(2):87-92
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000200007
PURPOSE: to test a therapeutic approach using atosiban for tocolysis, evaluating its safety and maternal and fetal side effects. METHODS: prospective study with 80 pregnant women with preterm labor admitted for tocolysis. Inclusion criteria: singleton pregnancy, regular uterine activity, cervical dilatation between 1 to 3 cm, cervical enfacement greater than 50%, 23 to 33 weeks and six days of gestational age, intact membranes, amniotic fluid index between 5 and 25, no maternal, fetal or placental diseases, no fetal growth restriction, no cervical incompetence, no fever. Exclusion criteria: chorioamnionitis or fever during tocolysis. Atosiban group: women received 6.75 mg atosiban iv in bolus, 300 mcg/min for three hours, then 100 mcg/min for three hours and thirty minutes. If uterine activity persisted, it was maintained iv infusion of 100 mcg/min for 12.5 hand that so for as long as 45 hours. Control group: women received terbutaline (five ampoules, 500 mL crystalloid solution) iv infusion, 20 mL/h. If uterine activity persisted, infusion velocity was raised (20 mL/h) until uterine contractions were absent. The dose was maintained for 24 hours. RESULTS: gestational age at birth was 29 weeks and five days to 40 weeks and six days. In atosiban group, the proportion of women who had not delivered at 48 hours was 97.5%, mean interval between tocolysis and birth of 28.2 days. In control group, birth occurred before 48 hours in 22.5% of the cases; mean interval between tocolysis and birth of 5.3 days. Maternal side effects were observed in 27.5% of cases of the atosiban group, none with tachycardia, dyspnea or tachypnea. In the control group, 75% of the cases referred palpitations, tachycardia, tachypnea or headache (drug infusion was interrupted in four cases). Fetal tachycardia was observed in 22.5% of the cases (n=9). No early neonatal death was observed. CONCLUSIONS: the therapeutic approach used showed to be effective for tocolysis, with low incidence of maternal, fetal and neonatal side effects.