Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):248-252
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500005
PURPOSE: to analyze the isoflavone and estrogen effects on the postmenopausal quality of life. METHODS: this is a randomized and double-blind study with 79 postmenopausal patients, 12 months of amenorrhea, 40 years old or more and body mass index (BMI) above 30 kg/m². The participants were randomly divided into two treatment groups: GECP received orally two capsules, every 12 hours, one contained 0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogen and another placebo (n=33); GECS received two capsules of 150 mg extract of soy, with 60 mg isoflavone (n=32). Both treatments were administered for six months. The Quality Menopause Specific Questionnaire of Life was applied before and after one, three and six months of treatment. The parameters of gynecological cancer risk were evaluated. ANOVA and the Tukey test were used for data analysis. RESULTS: there was a reduction in the values of the vasomotor parameters after six months of treatment, 1.6±0.8 and 2.4±1.6, compared to before therapy, 4.0±2.2 and 4.2±2.3 in GECP and GECS, respectively. The psychological aspects showed reduction in values after six months of therapy, 2.5±1.2 and 2.9±1.4, compared to before treatment, 3.6±1.6 and 4.1±1.9 in GECP and GECS, respectively. Similar results were obtained on the physical aspects and in the sexual symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: isoflavones may positively act on life quality of postmenopausal women. This effect was similar to conjugated equine estrogen.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):253-259
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the insulin therapy protocol and its maternal and perinatal outcome in patients with clinical or gestational diabetes in a high risk reference service. METHODS: descriptive and prospective study including 103 pregnant women with gestational or clinical diabetes treated with insulin and attended by the reference service from October 2003 to December 2005. Gemellarity, miscarriages, unfinished prenatal care and deliveries not attended by the service were excluded. The gestational age at the beginning of the treatment, dosage, doses/day, increment of insulin (UI/kg), glycemic index (GI) and perinatal outcomes were compared. ANOVA, Fisher’s exact test and Goodman’s test considering p<0.05 were used. RESULTS: multiparity (92 versus 67.9%), pre-gestational body mass index (BMI) >25 kg/m² (88 versus 58.5%), weight gain (WG) <8 kg (36 versus 17%) and a high increment of insulin characterized the gestational diabetes. For the patients with clinical diabetes, despite the highest GI (120 mg/dL (39.2 versus 24%)) at the end of the gestational period, insulin therapy started earlier (47.2 versus 4%), lasted longer (56.6 versus 6%) and higher doses of insulin (92 versus 43 UI/day) were administered up to three times a day (54.7 versus 16%). Macrosomia was higher among newborns from the cohort of patients with gestational diabetes (16 versus 3.8%), being the only significant neonatal outcome. There were no neonatal deaths, except for one fetal death in the cohort of patients with clinical diabetes. There were no differences in the other neonatal complications in both cohorts, and most of the newborns were discharged from hospital up to seven days after delivery (46% versus 55.8%). CONCLUSIONS: the analysis of these two cohorts has shown differences in the insulin therapy protocol in quantity (UI/day), dosage (UI/kg weight) and number of doses/day, higher for the clinical diabetes cohort, and in the increment of insulin, higher for the gestational diabetes cohort. Indirectly, the quality of maternal glycemic control and the satisfactory perinatal outcome have proven that the treatment protocol was adequate and did not depend on the type of diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(5):260-266
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000500007
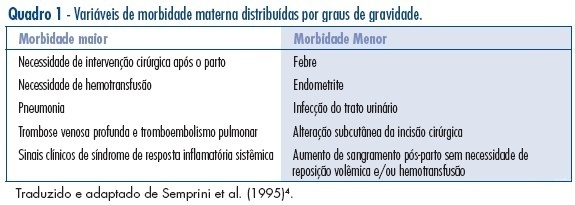
PURPOSE: to evaluate puerperal morbidity in HIV-infected and HIV non-infected puerperal women. METHODS: longitudinal and controlled study performed from July 2001 to September 2003, in 205 pregnant women admitted for birth delivery at Odete Valadares Maternity, divided in two groups: HIV-infected women (82) and HIV non-infected women (123). Postpartum morbidity evaluation was performed from birth delivery up to 15 days postpartum. Morbidity was categorized as minor (postpartum hemorrhage, fever and endometritis) or major (blood transfusion, deep alterations of the surgical wound and indication for surgical intervention), and was evaluated both according to the presence or absence of HIV infection and the mode of delivery. Continuous variables were analyzed by the Student’s t-test, and categorical variables were analyzed by chi2 and Fisher’s exact test using Epi-Info 2000 (CDC, Atlanta). RESULTS: puerperal morbidity was observed in 18 patients from the HIV group (22%) and in 17 patients from the control group (14%) with predominance of minor morbidity, without statistical significance, except for an increased risk of endometritis in the HIV group (RR=1.05; CI 95%:1.01-1.10). No significant difference was observed concerning the mode of delivery between the two groups. There were only two major morbidities: blood transfusion and necrotizing fasciitis. CONCLUSIONS: HIV-infected and non-infected puerperal women have a similar morbidity, despite the lower morbidity in the HIV non-infected group and the increased risk of endometritis in the HIV group. Clinical puerperium follow-up is a strategic control tool for an early identification of maternal morbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):175-180
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400002
PURPOSE: the premature rupture of membranes (PROM) has been a reason for many investigations, amongst which the involved immune mechanisms. Ahead of the scarcity of studies related to the subject, this work had as objective to evaluate the serum values of IgA, IgG, IgM, C3 and C4 in pregnant women with pre-term PROM. METHODS: in this transversal study, 36 pregnant women had been enclosed, with gestational age between 23 and 37 weeks. Of this total, 15 women had had laboratorial and clinical diagnosis of PROM. Patients with beginning of the childbirth work, clinical signals of infection, clinical dysfunction with systemic repercussion had been excluded. Serum concentrations of immunoglobulin (IgA), immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG), C3 and C4 had been evaluated in the patients with (study group) and without PROM (control group). Correlation among dosages; number of childbirths and time of rupture was determined by Spearman coefficient correlation (r value). RESULTS: serum levels of IgA (average±SD) had been significantly higher in the patients of the control group (271.0±107.0 versus 202.9±66.1; respectively, control and study group; p=0.024). There was no statistical difference when the levels of IgM, IgG, C3 and C4 had been compared between two groups. Significant association was not noticed between the number of childbirths and the IgA, IgM, IgG, C3 and C4 dosages (Spearman; r between -0,009 and 0,027; p>0,05). The average time of rupture of study group patients was of 19.1 hours (one - 72 hours), without association with the evaluated serum dosages. CONCLUSIONS: pregnant women with PROM show levels of IgA significantly lower than normal pregnant patients. The variable "number of childbirths" does not act as a factor of confusion in the comparative analysis of the dosages obtained in patients with or without PROM, as well as also it did not have association between the time of rupture and the immunoglobulin and complements serum dosages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):181-185
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400003
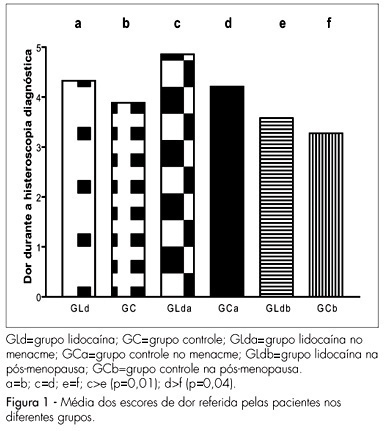
PURPOSE: to determine the efficacy of 10% lidocaine spray applied to the cervix before the procedure of diagnostic hysteroscopy, in order to reduce the painful process and the discomfort caused by the exam. METHODS: a total of 261 consecutive patients participated in the study, which was conducted from March 2004 to March 2005. The patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups: one group receiving topical lidocaine spray (lidocaine group - LdG) and the other, receiving no medication before the procedure (control group - CG). In the LdG patients, thirty milligrams of 10% lidocaine spray were applied to the surface of the cervix five minutes before hysteroscopy started. Immediately, after the end of the procedure, the patients from both groups were asked to respond to a questionnaire about pain and to quantify the pain, in centimeters, using a 10-cm non-graduated visual analog scale. The unpaired t test, the Mann-Whitney test and the chi2 test were used for statistical analyses, considering p significant if lower than 0.05. RESULTS: there was no statistically significant difference between groups regarding age, parity or percentage of patients in menacme or menopause, or regarding the indications for the procedure and the hysteroscopic findings. A biopsy was necessary in 57 of the 132 LdG patients and in 48 of the 129 CG patients (p=0.96). The mean pain score was 4.3±2.9 in LdG and 3.9±2.5 in CG (p=0.2). A difference in the mean pain score was observed only among patients in menacme and menopause receiving or not the lidocaine spray, with p=0.01 and p=0.04 respectively. CONCLUSIONS: the use of lidocaine spray during diagnostic hysteroscopy does not minimize the discomfort and pain of the patients and therefore should not be applied.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):186-191
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400004
PURPOSE: to examine the hypothesis that serum anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels reflect the ovarian follicular status. METHODS: Design: prospective study. Patients: we studied 101 IVF-ET candidates undergoing controlled ovarian hyperstimulation with GnRH agonist and FSH. After the achievement of pituitary suppression and before FSH administration (baseline), serum AMH, inhibin B, and FSH levels were measured. The number of antral follicles was determined by ultrasound at baseline (early antral follicles; 3-10 mm). RESULTS: at baseline, median serum levels of AMH, inhibin B, E2, P4 and FSH were 3.42±0.14 ng/mL, 89±4.8 pg/mL, 34±2.7 pg/mL, 0.22±0.23 ng/mL and 6.6±0.1 mIU/mL, respectively, and the mean number of early antral follicles was 17±0.39. Serum levels of AMH were negatively correlated with age (r=-0.19, p<0.04), and positively correlated with number of antral follicles (r=0.65, p<0.0001), but this did not apply to serum levels of either inhibin B, E2 or FSH. CONCLUSION: the data demonstrate an association between AMH and antral follicular counts. Therefore, AMH is probable a biomarker of ovarian follicular status.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):192-199
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400005
PURPOSE: to evaluate and compare the knowledge and the opinion of gynecologists and obstetricians regarding termination of pregnancy, in 2003 and 2005. METHODS: a structured and pre-tested questionnaire was sent to all the members of the Brazilian Federation of Gynecologists and Obstetricians (FEBRASGO). They were asked to answer the questions, anonymously, and return the questionnaire in a stamped envelope provided. They were asked about their knowledge of and opinion on Brazilian legislation related to abortion. RESULTS: in both surveys the percentage of doctors who knew under which circumstances abortion was not penalized was over 80%. However, there was a significant reduction in the percentage of doctors who knew that abortion was legal if the woman’s life was at risk. The participants who knew that abortion because of a severe congenital malformation of the fetus was not currently permitted by law increased by a third. The percentage of doctors in favor of allowing abortion increased consistently for the various circumstances presented. The proportion of those who thought that abortion should not be permitted in any circumstances decreased. The percentage of those who judged that the legal consents should not be modified decreased. There was an increase in the proportion of those who considered that abortion should not be considered a crime under any circumstance. CONCLUSIONS: in general, it seems that people have been thinking more about induced abortion during the time elapsed between the two surveys. Nevertheless, there is the need to correctly inform Brazilian gynecologists and obstetricians on the laws and norms that regulate the practice of legal abortion in the country, so as to ensure that women who need one have, in fact, access to this right.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):200-204
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400006
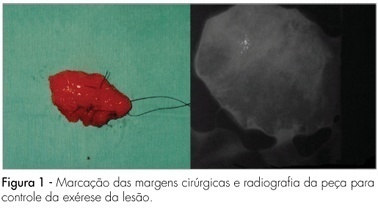
PURPOSE: the aim of this clinical study of the histological findings in nonpalpable breast lesions managed by surgical excision after wire localization. METHODS: a total of 48 women subjected to 51 preoperative localizations of nonpalpable, mammographically detected breast lesions during August 2001 to April 2005. Indications for biopsy were clustered microcalcifications, solid mass, radiologic parenchymal distortion and focal asymmetries. The lesions were localized preoperatively using hook wire methods, and all biopsies were performed under local anesthesia and venous sedation. RESULTS: histopathology revealed carcinoma in 16 biopsies (31.4%). Noninvasive carcinoma was found in 50% of malignant lesions. Successful lesion sampling was achieved at the first attempt in 100% of cases. Among all malignant lesions, positive-surgical margins were observed in 18.7%. Postoperative complications were a rare event in our series. Suture dehiscence was found in four patients (7.8%). Two of these (3.9%) had local infection. CONCLUSIONS: the hook-wire localization for nonpalpable breast lesions is a simple, accurate and safe method for detection of early breast cancers. The appropriate surgical approach in a single procedure is an excellent method for diagnosis and treatment for early stage, nonpalpable breast carcinoma.