Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):563-567
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200006
PURPOSE: To investigate the relationship between periodontitis and osteoporosis, using a case-control study about periodontal status of postmenopausal women. METHODS: A total of 99 postmenopausal women were divided into three groups: normal bone (Gn, n=45), osteopenia (Gpenia, n=31) and osteoporosis (Gporosis, n=23). The categorization of bone mass was measured by dual energy absorptiometry with X-rays in the lumbar spine (L2 - L4), by assessing bone mineral density. Clinical attachment level (CAL), gingival bleeding index (GI), plaque index (PI), and probing depth (PD) were determined in all participants by a single examiner. The data were submitted to BioEstat 2.0 software through parametric analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Bonferroni test, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Women with osteoporosis presented the highest percentage of periodontal disease, with higher average CAL (2.6±0.4 mm) and PD (2.8±0.6 mm), GI (72.8±25.9 mm) and PI (72.9±24.2 mm). Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference in periodontal situation between Gn and Gporosis (p=0,01) and between Gpenia and Gporosis (p=0,03). CONCLUSION: Osteoporosis may have an influence on periodontal condition, based on the relation between periodontitis and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):568-574
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200007
PURPOSE: To evaluate the expression of neurotrophic (NGF, NPY and VIP) and pro-inflammatory (TNF-α) mediators in the rectum and sigmoid fragments compromised by endometriosis. METHODS: Twenty-four patients were selected to undergo surgical treatment of endometriosis of the rectum and sigmoid colon with a segmental resection technique, followed by end-to-end anastomosis with a circular stapler from January 2005 to December 2007. The study included premenopausal women who underwent surgical treatment for deep endometriosis infiltrating the rectum with involvement of the rectum and sigmoid, reaching the level of the muscle layer, submucosa or mucosa. Twenty-four rectum and sigmoid fragments with histologically confirmed endometriosis, one from each of the 24 selected patients, were used for the study group. For the control group, we used a fragment of the distal resection margin called anastomosis ring from each of the 24 patients enrolled in the study. Samples were grouped into Tissue Micro Array (TMA) blocks and subjected to immunohistochemistry to evaluate the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), nerve growth factor (NGF), neuropeptide Y (NPY) and P vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), followed by semiquantitative analysis of immunostaining by reading the relative optical density (OD). RESULTS: There was higher optical density relative to TNF-α immunostaining and NGF in the study group (samples with intestinal endometriosis), DO=0.01, for the two proteins, respectively (p<0.05), compared to controls without endometriosis. There was no statistically significant difference in the optical density of immunostaining of NPY and VIP. CONCLUSION: We identified increased immunostaining of TNF-α antibodies and fragments of NGF in the rectum and sigmoid compromised by endometriosis compared to disease-free controls. We did not identify any statistical difference in immunostaining of NPY and VIP proteins.
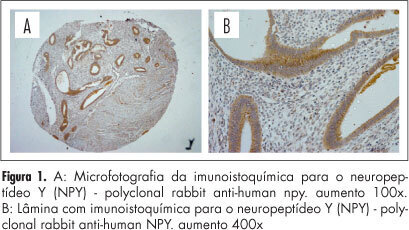
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):575-581
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200008
PURPOSE: To compare serum anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels on the seventh day of ovarian stimulation between normal and poor responders. METHODS: Nineteen women aged ≥35, presenting with regular menses, submitted to ovarian stimulation for assisted reproduction were included. Women with endometriosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome or those who were previously submitted to ovarian surgery were excluded. On the basal and seventh day of ovarian stimulation, a peripheral blood sample was drawn for the determination of AMH, FSH and estradiol levels. AMH levels were assessed by ELISA and FSH, and estradiol by immunochemiluminescence. At the end of the stimulation cycle patients were classified as normal responders (if four or more oocytes were obtained during oocyte retrieval) or poor responders (if less than four oocytes were obtained during oocyte retrieval or if the cycle was cancelled due to failure of ovulation induction) and comparatively analyzed by the t-test for hormonal levels, length of ovarian stimulation, number of follicles retrieved, and number of produced and transferred embryos. The association between AMH and these parameters was also analyzed by the Spearman correlation test. RESULTS: There was no significant difference between groups for basal or the seventh day as to AMH, FSH and estradiol levels. There was a significant correlation between seventh day AMH levels and the total amount of exogenous FSH used (p=0.02). CONCLUSIONS: AMH levels on the seventh day of the ovarian stimulation cycle do not seem to predict the pattern of ovarian response and their determination is not recommended for this purpose.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):16-20
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100004
PURPOSE: To evaluate the correlation between the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire - Urinary Incontinence/Short Form (ICIQ-UI/SF) and Urodynamic evaluation (UE) in women with urinary incontinence (UI). METHODS: Clinical data, UE and ICIQ-UI/SF scores for 358 patients from private health service were analyzed retrospectively . The correlation between ICIQ-UI/SF and urodynamic parameters was determined by Spearman's test. A ROC curve with the sensitivity and specificity of the ICIQ-UI/SF scores was utilized to establish the value of the questionnaire that would predict an altered urodynamic parameter. The c² test or Fisher's exact test was used to calculate the p-value. The level of significance was 5% and the software used was SAS 9.2. RESULTS: Sixty-seven point three percent of the patients presented Stress UI (SUI) according to the UE (urodynamic SUI); those with SUI and Detrusor overactivity (DO) at UE represented 16.2% of the women (SUI+DO), and those with only DO at UE (DO) represented 7.3% of the women. Patients with normal UE represented 9.2% of the women. There was a significant association between ICIQ-UI/SF scores ³14 and patients with urodynamic SUI, with or without DO. Patients with Valsava Leak Point Pressure (VLPP)£90 cmH2O presented ICIQ-UI/SF³15. Spearman's test showed a weak inverse correlation between ICIQ-UI/SF score and VLPP, although it did not show any correlation with maximum cystometric capacity or with bladder volume on first desire to void. CONCLUSION: There was an association between ICIQ-UI/SF score and patients with SUI, with or without DO, but no association between the score and patients with DO alone. The lower the VLPP value, the higher the ICIQ-UI/SF score. The ICIQ-UI/SF was not able to distinguish the different types of UI in the studied population
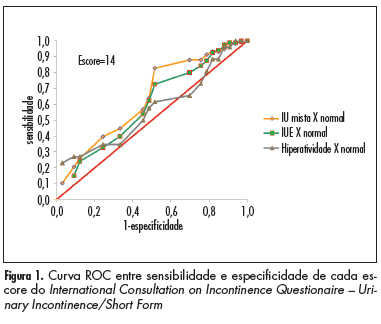
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):27-32
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100006
PURPOSE: To compare and analyze socioeconomic aspects and the emotional experience of women with spontaneous or induced abortion and in women living in the outskirts of São Paulo. METHODS: A prospective case-control study carried out from July 2008 to March 2010, involving semi-structured interviews with women who presented a previous diagnosis of abortion and who had been admitted to two public hospitals in the outskirts of São Paulo. The study included 100 women with diagnosis of abortion and were hospitalized for curettage. Eleven women who reported induced abortion (11%) represented the case group. The control group (n=22) was selected at a 2:1 ratio according to the following procedure: for every case of induced abortion, the next two cases of spontaneous abortion at the same hospital. A semistructured interview was conducted with questions regarding emotional aspects and family, social and economic context. RESULTS: The women with induced abortion compared to the group with spontaneous abortion had lower educational level, with more frequent elementary level (82 versus 36%, p=0.04), lower income (median, R$ 1,000.00 versus R$ 1,400.00, p=0.04), lower personal income (median, R$ 200.00 versus R$ 333.00, p=0.04), higher frequency of negative feelings upon suspicion (82 versus 22%, p=0.004) and confirmation (72 versus 22%, p=0.03) of pregnancy. CONCLUSION: Among women looking for health care in hospitals in the outskirts of São Paulo, induced abortion is related to unfavorable socioeconomic conditions, which affects the emotional experiences of suspicion and confirmation of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(1):33-38
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000100007
PURPOSE: To create longitudinal reference intervals for pulsatility index (PI) of the umbilical (UA), middle cerebral (MCA), uterine (UtA) arteries and ductus venosus (DV) in a Brazilian cohort. METHODS: A longitudinal observational study performed from February 2010 to May 2012. Low risk pregnancies were scanned fortnightly from 18 to 40 weeks for the measurements of PI of the UA, MCA, DV and UtA. Linear mixed models were used for the elaboration of longitudinal reference intervals (5th, 50th and 95th percentiles) of these measurements. PI obtained for the placental and abdominal portions of the umbilical artery were compared by the t-test for independent samples. Two-sided p values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS: A total of 164 patients underwent 1,242 scans. There was significant decrease in PI values of all vessels studied with gestational age (GA). From the 18th to the 40th week of pregnancy, the median PI values of UA (abdominal and placental ends of the cord), MCA, DV and the mean PI of the UtA ranged from 1.19 to 0.74, 1.33 to 0.78, 1.56 to 1.39, 0.58 to 0.41, and 0.98 to 0.66, respectively. The following equations were obtained for the prediction of the medians: PI-UA=1.5602786 - (0.020623 x GA); Logarithm of the PI-MCA=0.8149111 - (0.004168 x GA) - [0.02543 x (GA - 28.7756)²]; Logarithm of the PI-DV=-0.26691- (0.015414 x GA); PI-UtA = 1.2362403 - (0.014392 x GA). There was a significant difference between the PI-UA obtained at the abdominal and placental ends of the umbilical cord (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: Longitudinal reference intervals for the main gestational Doppler parameters were obtained in a Brazilian cohort. These intervals could be more adequate for the follow-up of maternal-fetal hemodynamic modifications in normal and abnormal pregnancies, a fact that still requires further validation.
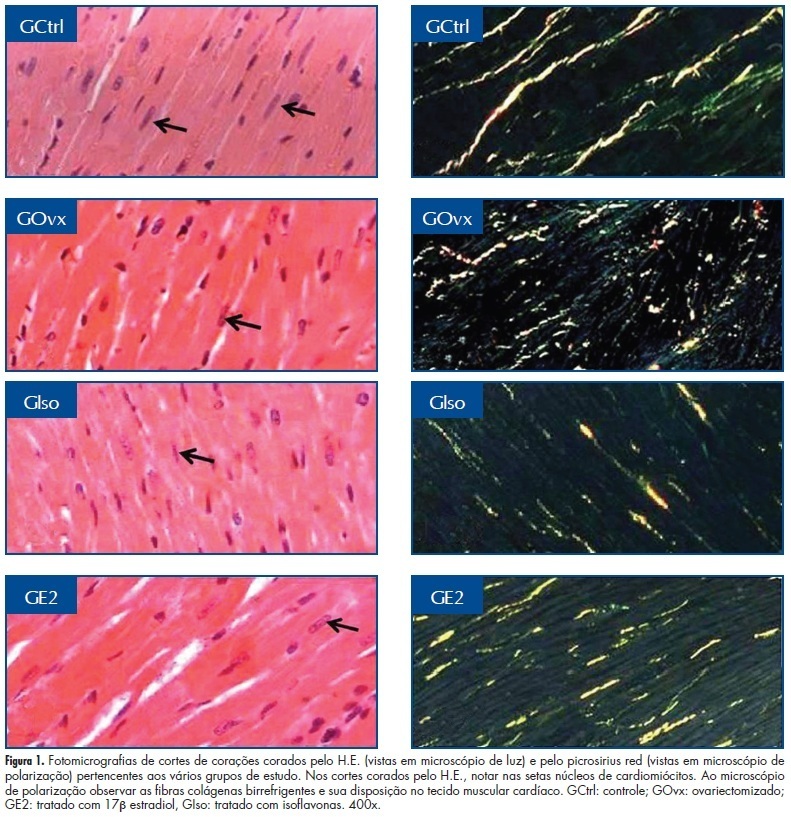
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(10):447-452
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001000003
PURPOSES: To evaluate the histomorphometry of cardiomyocytes and collagen present in the myocardium of rats treated with a concentrated extract of soy or 17β-estradiol (E2). METHODS: Twenty-eight rats were divided into four groups: GCtrl - estrus phase; GOvx - ovariectomized (Ovx) and receiving vehicle; GIso - Ovx and treated with soy extract (150 mg/kg per day); GE2 - Ovx and treated with E2 (10 µg/kg per day). The drugs and vehicle (0.2 mL propylene glycol) were administered for 30 consecutive days after ovariectomy. On the last day the animals were anesthetized, the hearts removed, submerged in 10% formaldehyde and fragments of the ventricles underwent histological procedures, and the sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin or picrosirius-red. Histomorphometric analysis (number and volume of nuclei and quantification of collagen) was performed under a light microscope with AxioVision Rel. 4.2 software, and collagen fibers were quantified using IMAGELAB-2000 software. Data were submitted to ANOVA followed by the Tukey test (p<0.05). RESULTS: We observed a higher number of cardiomyocyte nuclei in animals of the Ovx and Iso groups than in GE2 and GCtrl animals (GOvx=121.7±20.2=GIso=92.8±15.4>GE2=70.5±14,8=GCtrl=66.3±9.6; p <0.05), while the nuclear volume was greater in the Ctrl and E2 groups (GE2=35.7±4.8 GCtrl=29.9±3.6=>GIso=26.5±4.5=GOvx=22.4±2.9; p <0.05). Collagen concentration was higher in the Ovx group (GOvx=5.4±0.1>GCtrl=4.0±0.1=GIso=4.4±0.08=GE2=4.3±0.5; p <0.05). CONCLUSIONS: Estrogen may prevent the reduction of the nuclear volume of cardiomyocytes and collagen deposition between heart muscle fibers, while the administration of isoflavones only prevents the deposition of collagen, which can preserve the mechanical properties of cardiac fibers.