Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):425-431
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900007
PURPOSE: To evaluate the prevalence of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) among women candidates to in vitro fertilization (IVF) in a reference public service in southeastern Brazil. METHODS: Women who were referred for IVF from April 1st, 2008 to December 31st, 2009 were enrolled sequentially in the study. A ginecological-obstetrical background questionnaire was applied and endocervical swab samples were obtained to search for CT and NG using hybrid capture and PCR. The variables studied were: age, color, education, duration of infertility, number of pregnancies and living children, history of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, number of sex partners, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), pelvic surgery, manipulation of the uterine cavity, smoking, and illicit drug use. The women were distributed according to the presence/absence of confirmed chlamydia infection and descriptive analysis was employed. RESULTS: Among 176 women tested the prevalence of CT infection was 1.1% and there was no NG infection. Two thirds of the women were >30 years old, with schooling >8 years and <5 years of infertility, and 56.2% had no children. The main background data were pelvic surgery (77.8%), manipulation of the uterine cavity (62.5%) and PID (27.8%). The tubal factor was the most prevalent, 73.3% of women (from 129), 37.5% had been sterilized, 35.8% had not been sterilized, and other factors had a prevalence <30%. CONCLUSIONS: CT and NG infections had a low prevalence in this sample. Studies at other centers in the country are needed to confirm the prevalence of infection in this particular group of infertile women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):432-437
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900008
PURPOSE: To verify the coverage, by Pap testing, of older women and the associated factors. METHODS: A population-based study was conducted by home interviews. The inclusion criteria were women aged 60 and over, living on the north side of the city of Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil, self-sufficient to answer the questionnaire or having someone to answer on their behalf. The interview consisted of sociodemographic questions, regarding the general health of the older women, and preventive practices in women's health. The selection was made by random sampling, stratified and clustered in multiple stages. To analyze associated factors, a theoretical model was formulated with three hierarchical blocks of variables, adjusted to each other in each block. The variables that had a level of significance of 0.2 or less were included in the Poisson regression model and adjusted to their next highest level (p<0.1). RESULTS: Pap testing occurred in 84.1% of cases (95%CI 79.0-88.4). Based on multivariate regression analysis, three variables remained significantly associated with access to Pap testing: the marital status "without partner" (older women who were single, widowed, separated or divorced), self-sufficiency to perform Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs) and adherence to mammography. In the interblock analysis these variables remained significantly associated with the outcome variable, and self-sufficiency for IADLs had the highest association. CONCLUSIONS: Among the older women comprising the study sample, was observed variation in the use of Pap testing. An adjustment of public health policies towards the formulation of policies giving priority to universal preventive care may be an alternative to solve the disparities observed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):362-368
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800004
PURPOSE: To determine the nutritional status of vitamin E in breastfeeding women through the analysis of alpha-tocopherol concentration in serum and colostrum, to analyze its relation with maternal variables and to determine the prevalence of vitamin E deficiency in these women. METHODS: The study included 103 mothers who were classified according to maternal variables: age, nutritional status before pregnancy, gestational weight gain, parity and mode of delivery. Colostrum and serum samples were collected under fasting conditions in the immediate postpartum period. Alpha-tocopherol was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). A serum cutoff of 697.7 μg/dL was adopted to define the nutritional status of vitamin E. Statistical analysis was performed with the Student's t test for independent samples and Pearson's correlation. Differences were significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: The average concentration of alpha-tocopherol was 1.125±551.0 μg/dL in colostrum and 1,138.6±346.0 μg/dL in serum, indicating adequate biochemical nutritional status. However, when analyzing the mothers individually, a 16% rate of subclinical vitamin E deficiency was detected. Women undergoing cesarean delivery had significantly higher alpha-tocopherol levels in colostrum (1.280±591 μg/dL) compared with those undergoing normal delivery (961.7±370 μg/dL) (p<0.05). It was found that mothers who were overweight before pregnancy had higher vitamin concentration in colostrum (1,331.5±548 μg/dL) when compared to underweight women (982.1±374 μg/dL) or women of normal weight (992.3±346 μg/dL) (p<0.05). However, the other variables were not associated with alpha-tocopherol in colostrum. Moreover, no variable showed association with vitamin E levels in maternal serum and no correlation was demonstrated between the alpha-tocopherol levels in serum and in milk. CONCLUSIONS: Despite the diagnosis of satisfactory nutritional status, breastfeeding women showed significant risk of subclinical vitamin E deficiency. We suggest that the concentration of alpha-tocopherol in colostrum be associated with type of delivery and pre-gestational nutritional status of women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):351-356
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800002
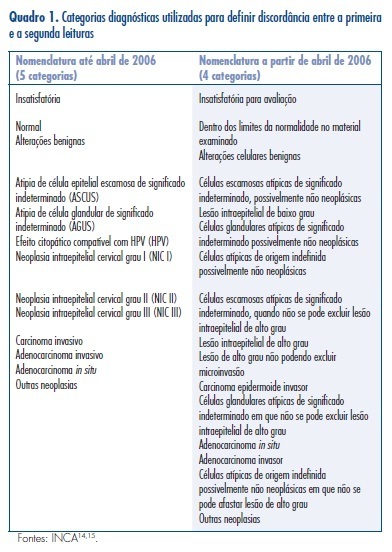
PURPOSE: To evaluate the diagnostic agreement between the cytopathology reports issued by accredited laboratories and those obtained by quality control. METHODS: We calculated the overall agreement and Cohen's kappa coefficients of a convenience sample of smears selected monthly by the Information System of Cervical Cancer (SISCOLO) for External Quality Control of the 15 laboratories that performed cytopathological PAP tests for the Brazilian Public Health System (SUS) between 2002 and 2011 in Mato Grosso do Sul, a State of the Midwest Region of the country. A comparison of the reliability values (coefficient of concordance and Kappa coefficient) between the initial and final years was computed by the absolute change (delta) and relative percent difference (RPD). RESULTS: There were 15.989 smears sent for rereading, 48.1% of which had a report of normal/benign changes, followed by atypical/low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (36.3%), high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion/carcinoma/adenocarcinoma (4.2%), and unsatisfactory (11.4%). The overall correlation coefficient ranged between 0.2 and 1.0, and the median value increased from 0.7 in 2002 to 1 in 2011 (RPD=+36.6%). During the same period, the median values of the Kappa coefficient increased from 0.5 to 0.9 (RPD=+80.8%). CONCLUSIONS: These results emphasize the feasibility of the External Quality Control of cytopathology at the state level and its implementation results in improvement in the diagnoses performed in the SUS network.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):369-375
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800005
PURPOSE: To determine the epidemiological profile of women admitted for urinary tract infection as well as to verify the most prevalent agents and response to antibiotic therapy. METHODS: A retrospective study of 106 pregnant women admitted to a university hospital for urinary tract infection treatment during the period between January 2007 to December 2010. The evaluation was based on analysis of the medical records of these pregnant women, with the observation of hospitalization and pregnancy data, as well as its outcome. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Science, version 15.0. The bilateral Fisher exact test and Student's t test were used for data analysis, as well as descriptive statistical methods. RESULTS: Positive urine cultures were observed in 60.5% of pregnant women admitted due to urinary tract infection. The most frequent infectious agent was Escherichia coli and no difference in resistance, recurrence or complications was observed between the most frequent etiologic agents. Pregnant women with previous UTI had a higher recurrence risk (OR=10.8; p<0.05). The antibiotics most commonly used during hospitalization were ampicillin and cefazolin. Change of therapeutic agent due to bacterial resistance occurred in 11.9% of patients who took cefazolin and in 20% of patients who took ampicillin (OR=5.5; p<0.05). The rate of gestational complications was the same for both treatments. There was no difference in mean number of days of hospitalization between the treatments. CONCLUSION: In the studied population ampicillin showed a higher rate of bacterial resistance than cefazolin, requiring a larger number of treatment regimen exchanges, without resulting in differences in clinical outcome or time of hospitalization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):376-380
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800006
PURPOSES: To describe the process of gait initiation of pregnant women and to compare the behavior of the pressure center in the three trimesters of pregnancy. METHODS: Fifty-seven low-risk pregnant women were evaluated, aged 18 to 35 years, selected for convenience location during the three trimesters of pregnancy. The women were divided into three groups of 19 subjects each, according to gestational age - 1st quarter (4-12 weeks), 2nd quarter (13-28 weeks), and 3rd quarter (29-42 weeks,). Each patient was positioned standing up with one foot on each AMTI force platform until she heard a beep indicating that she should start walking a distance of four meter. Data were analyzed using the SPSS software. The Kolmogorov Smirnov test, Tukey's test and Spearman correlation coefficient were used for group comparisons, with 5% significance level in all tests. RESULTS: Significant differences were found between the 1st quarter (GFT) and 3rd quarter (GTT) groups regarding mediolateral oscillation amplitude (GFT: 0.4 cm and GTT: 0.2 cm) and mediolateral displacement rate (GFT: 0.9 cm/s and GTT: 0.4 cm/s). There was a gradual decrease in anteroposterior and mediolateral oscillation rate, and in the speed of displacement from platform 1 to platform 2 in GFT. There was a significant difference in oscillation amplitude and mediolateral displacement speed between GFT and GTT. CONCLUSION: The variables analyzed showed minor differences and do not constitute an imminent risk for the stability dynamics of pregnant woman.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):381-385
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800007
PURPOSE: To assess perinatal factors associated with term newborns with pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery and 5th min Apgar score<7,0. METHODS: Retrospective case-control study carried out after reviewing the medical records of all births from September/1998 to March/2008, that occurred at the General Hospital of Caxias do Sul. The inclusion criterion was term newborns who presented a 5th min Apgar score <7.0 and umbilical artery pH<7.10. In the univariate analysis, we used the Student's t-test and the Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables, the c² test for dichotomous variables and risk estimation by the odds ratio (OR). The level of significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: Of a total of 15,495 consecutive births, 25 term neonates (0.16%) had pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery and a 5th min Apgar score <7.0. Breech presentation (OR=12.9, p<0.005), cesarean section (OR=3.5, p<0.01) and modified intrapartum cardiotocography (OR=7.8, p<0.02) presented a significant association with the acidosis event. Among the fetal characteristics, need for hospitalization in the neonatal intensive care unit (OR=79.7, p <0.0001), need for resuscitation (OR=12.2, p <0.0001) and base deficit were associated with the event (15.0 versus -4.5, p<0.0001). CONCLUSION: Low Apgar score at the 5th min of life associated with pH<7.1 in the umbilical artery can predict adverse neonatal outcomes.