Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):102-106
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300002
: Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common conditions during pregnancy. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of germs and the antimicrobial susceptibility profile in urine culture isolates from pregnant patients treated at a tertiary maternity hospital in Porto Alegre, Brazil.
: A cross-sectional, retrospective and descriptive study was carried out at Hospital Fêmina, a leading institution in prenatal, birth and postnatal healthcare in the city of Porto Alegre, Brazil. A total of 482 microbial community results were analyzed out of 1,558 positive urine cultures of pregnant women in all gestational ages treated at Fêmina Hospital between January 2007 and July 2013.
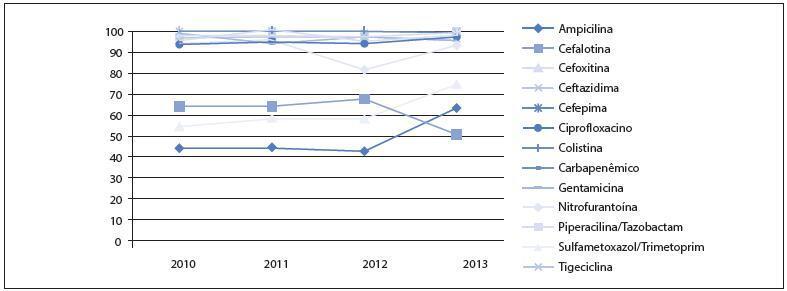
The susceptibility pattern presented in this research shows that the choice for UTI treatment during pregnancy should be nitrofurantoin (for uncomplicated infections) or second-generation cephalosporins such as cefuroxime (for uncomplicated and complicated infections), over ampicillin, first-generation cephalosporins and sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
: Empirical treatment for UTI in pregnancy should be started according to the susceptibility patterns described in the literature and re-analyzed after the results of the urine culture.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300003
To evaluate the impact of sexual and reproductive health theme insertion in the undergraduate medical curriculum at a Brazilian public university.
We developed an instrument for cognitive assessment in sexual and reproductive health based on the subjects addressed in the optional curriculum component Reproductive Health, resulting in an objective multiple choice test containing 27 items. The selected topics were: human, sexual and reproductive rights (HSRR), sexuality, institutional violence, gender, sexual violence, conception, contraception, abortion/legal interruption of pregnancy, maternal mortality and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - HIV/AIDS. The subjects were grouped into three dimensions of knowledge: HSRR, legal/institutional and biomedical. Two multivariate models were adjusted in the analysis of covariance.
The study included 183 students, 127 of the group who took the elective curriculum course reproductive health (RH Group) and 56 who did not (Non-RH Group). Ninety-six students (52.5%) were males and 87 (47.5%) were females. Mean age was 24.7±1.9 years for the RH Group and 24.4±2.6 for the Non-RH Group. The average performance of the SR Group was higher than that of Non-RH subjects regarding the following subjects: HSRR, sexuality, institutional violence, sexual violence, abortion/legal interruption, and STDs - HIV/AIDS. There was no gender difference in performance, except for the theme maternal mortality, in which males scored worse than females (6.9±0.2 and 7.8±0.2, respectively; p<0.05).
The participation of students in the elective curriculum component Reproductive Health was associated with better performance in some dimensions of cognitive assessment, suggesting a positive impact of this initiative on general medical education.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):118-123
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300005
To assess the feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasound combined with ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (US-FNA) cytology and clinical examination of axillary lymph node in patients with breast cancer.
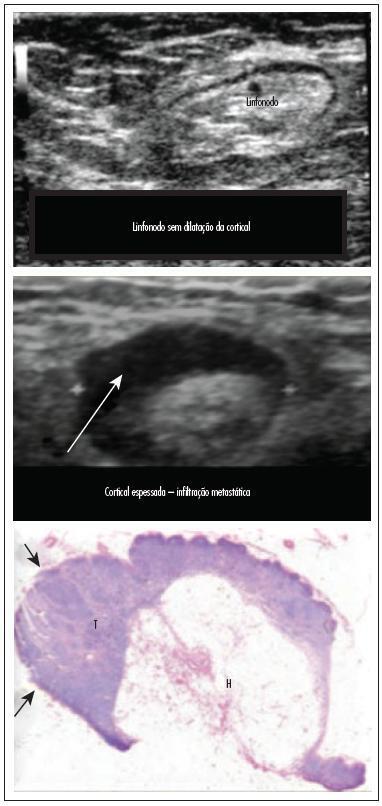
In this prospective study, 171 axillae of patients with breast cancer were evaluated by clinical examination and ultrasonography (US) with and without fine needle aspiration (FNA). Lymph nodes with maximum ultrasonographic cortical thickness > 2.3 mm were considered suspicious and submitted to US-FNA.
Logistic regression analysis showed no statistically significant correlation between clinical examination and pathologically positive axillae. However, in axillae considered suspicious by ultrasonography, the risk of positive anatomopathological findings increased 12.6-fold. Cohen's Kappa value was 0.12 for clinical examination, 0.48 for US, and 0.80 for US-FNA. Accuracy was 61.4% for clinical examination, 73.1% for US and 90.1% for US-FA. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis demonstrated that a cortical thickness of 2.75 mm corresponded to the highest sensitivity and specificity in predicting axillary metastasis (82.7 and 82.2%, respectively).
Ultrasonography combined with fine-needle aspiration is more accurate than clinical examination in assessing preoperative axillary status in women with breast cancer. Those who are US-FNA positive can be directed towards axillary lymph node dissection straight away, and only those who are US-FNA negative should be considered for sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):124-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300006
To assess clinical factors, histopathologic diagnoses, operative time and differences in complication rates between women undergoing laparoscopy or laparotomy to diagnose and treat an adnexal mass and their association with laparoscopy failure.
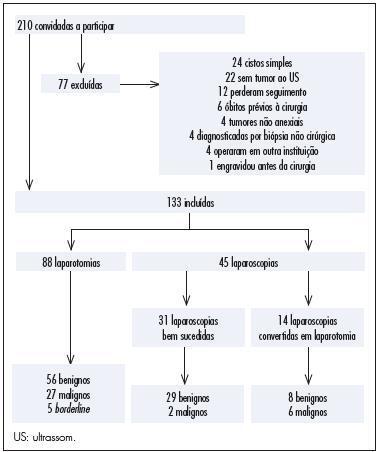
In this prospective study, 210 women were invited to participate and 133 of them were included. Eighty-eight women underwent laparotomy and 45 underwent laparoscopy. Fourteen of the 45 laparoscopies were converted to laparotomy intraoperatively. We assessed whether age, body mass index (BMI), previous abdominal surgeries, CA-125, Index of Risk of Malignancy (IRM), tumor diameter, histological diagnosis, operative time and surgical complication rates differed between the laparoscopy group and the group converted to laparotomy and whether those factors were associated with conversion of laparoscopy to laparotomy. We also assessed surgical logs to evaluate the reasons, as stated by the surgeons, to convert a laparoscopy to laparotomy.
In this research, 30% of the women had malignant tumors. CA-125, IRM, tumor diameter and operative times were higher for the laparotomy group than the laparoscopy group. Complication rates were similar for both groups and also for the successful laparoscopy and unsuccessful laparoscopy groups. The surgical complication rate in women with benign tumors was lower for the laparoscopy group than for the laparotomy group. The factors associated with conversion to laparotomy were tumor diameter and malignancy. During laparoscopy, adhesions a large tumor diameter were the principal causes of conversion.
This study suggests that laparoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of adnexal masses is safe and does not increase complication rates even in patients who need conversion to laparotomy. However, when doubt about the safety of the procedure and about the presence of malignancy persists, consultation with an expert gynecology-oncologist with experience in advanced laparoscopy is recommended. A large tumor diameter was associated with the necessity of conversion to laparotomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300007
To adapt the Pregnancy and Sexual Function Questionnaire (PSFQ) for use in Brazil and to evaluate its psychometric properties.
An adaptation and validation study was performed with women in the last trimester of pregnancy living in Rio Branco, Acre. The questionnaire was translated into Portuguese, reviewed and evaluated by specialists, and a pretest was carried out. Construct validity was evaluated by factor analysis; internal consistency was estimated by Cronbach's alpha coefficient and MacDonald's omega, and reproducibility was evaluated by the kappa statistics and test-retest in a sample of pregnant women.
Factor analysis identified the following six domains: subjectivity, pain and discomfort; frequency and receptivity; desirability; satisfaction; orgasm; and stimulus. The internal consistency by Cronbach's alpha was 0.6, while MacDonald's omega was 0.7. The kappa value was higher than 0.7 in all questions.
The Portuguese version of the PSFQ was considered to be adequate for evaluating sexual function during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(12):536-540
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001200002
PURPOSE: To evaluate weight retention 12 months postpartum and factors associated among women who had received prenatal care at Health Care Centers in Porto Alegre, southern Brazil. METHODS: Pregnant women in the last trimester were identified at 20 Health Care Centers. Socioeconomic, demographic and anthropometrics data were obtained. Six and 12 months after delivery, the women received home visits for anthropometric measures. The gestational weight gain was defined by pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI). Weight retention was defined as the difference between pre-gestational weight and weight at postpartum. Data were analyzed using McNemar's Test, ANOVA with Bonferroni correction and multiple linear regression. RESULTS: Of the 715 pregnant women recruited, 545 were assessed 12 months after delivery. Women were more likely to be overweight 12 months postpartum compared to the pre-pregnancy period (52.9 versus 36.7%) and weight retention during the 12 months postpartum was more than 10 kg in 30.7% of the women. Weight retention in the postpartum period was higher among women who were overweight (9.9±7.7 kg) compared to those who were of normal weight during the pre-pregnancy period (7.6±6.2 kg). Pre-pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, and maternal age were associated with gestational weight retention 12 months postpartum (p<0.001). CONCLUSION: Adequate prenatal care is necessary to minimize the adverse effects of excessive weight gain during pregnancy on women's health.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(12):541-548
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001200003
PURPOSE: To determine the prevalence of low back pain in pregnant women and to describe its characteristics and associated factors. METHODS: The participants were 269 pregnant women in the first to the third trimester of pregnancy, seen at the obstetrics outpatient clinic of a University Hospital in the Brazilian Northeast. We applied a questionnaire in order to obtain data regarding socio-demographic variables, obstetric history and characteristics of low back pain, as well as the Oswestry and Rolland Morris questionnaires to assess disability and a visual analog pain scale to measure pain intensity. RESULTS: The prevalence of low back pain was 73%, with the following characteristics: stabbing (62/31.6%), irradiation (162/82.6%), of daily frequency (105/53.5%), usually starting at night (83/42.3%) when it was also more intense (122/62.2%), and lasting about 1 hour in 118 women (60.2%). Pain improved with rest (100/51%), worsened when the women stood or sat for a long time (86/43.9%) and when they did housework (85/43.4%). The level of disability ranged from "mild" to "moderate" in most cases. Urinary tract infection (p=0.02) and the scores of the Oswestry and Rolland Morris questionnaires showed significant association with the visual analogue pain scale. CONCLUSION: The prevalence of back pain among pregnant women is high, with varying characteristics. The degree of disability is usually moderate and the presence of urinary infection and higher disability scores were associated with greater intensity of low back pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(12):549-553
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001200004
PURPOSE: To analyze the perinatal mortality rate in cases of gastroschisis and possible associated factors. METHODS: A retrospective cohort study was conducted between 1992 and 2012. All cases of gastroschisis born in Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA) during that period were included. The diagnosis of gastroschisis was obtained by morphological ultrasound examination or clinical examination at birth in prenatally unknown cases. The variables of birth (birthweight, gestational age and Apgar score, mode of delivery, type of gastroschisis and associated anomalies) and the surgical ones (type of surgical closure, reintervention and sepsis) were compared between surviving cases and deaths. The results of this comparison were analyzed according to the type of variable using parametric and non-parametric tests (Mann-Whitney or Student's t-test, χ² or Fisher's exact test), with the level of significance set at 5% (p=0.05). RESULTS: Sixty-four newborns with gastroschisis were included, 59 of them (92.2%) diagnosed during the prenatal period. Twenty-six patients (40.6%) had only exposed intestines, classified as simple gastroschisis, 22 had exposure of the intestines and stomach (34.4%) and 16 had exposure of the intestine and other organs (25%), for a total of 38 cases of complex gastroschisis. Primary surgical repair was performed in 44 cases (68.8%). The mortality rate was 23.4% (15 deaths). Babies who died had significantly lower birth weight (p=0.001), gestational age (p=0.03) and Apgar score (p=0.03) than survivors. There was no difference in mode of delivery (p=0.8) and, with respect to gut contents, there was no difference between the cases of simple and complex gastroschisis (p=0.06). Mortality was significantly higher in patients with sepsis (p=0.008) and reintervention (p=0.001). CONCLUSION: in the present study, perinatal mortality due to gastroschisis seemed to depend mainly on prematurity, low birth weight, and surgical complications.