Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):186-191
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005252
To evaluate genes differentially expressed in ovaries from lean (wild type) and obese (ob/ob) female mice and cyclic AMP production in both groups.
The expression on messenger RNA levels of 84 genes concerning obesity was analyzed through the PCR array, and cyclic AMP was quantified by the enzyme immunoassay method.
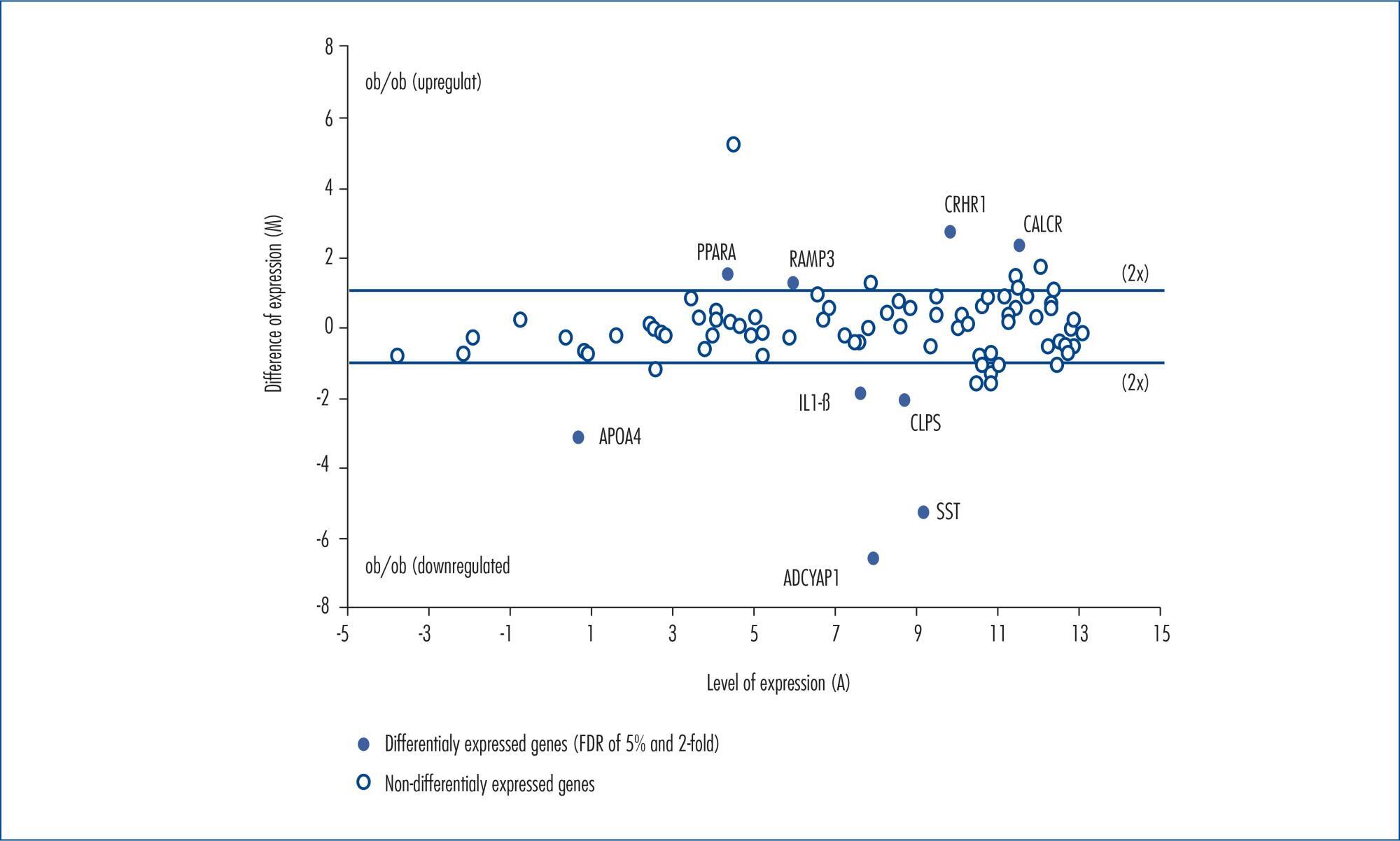
The most downregulated genes in the Obesity Group included adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type 1, somatostatin, apolipoprotein A4, pancreatic colipase, and interleukin-1 beta. The mean decrease in expression levels of these genes was around 96, 40, 9, 4.2 and 3.6-fold, respectively. On the other hand, the most upregulated genes in the Obesity Group were receptor (calcitonin) activity-modifying protein 3, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha, calcitonin receptor, and corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1. The increase means in the expression levels of such genes were 2.3, 2.7, 4.8 and 6.3-fold, respectively. The ovarian cyclic AMP production was significantly higher in ob/ob female mice (2,229±52 fMol) compared to the Control Group (1,814±45 fMol).
Obese and anovulatory female mice have reduced reproductive hormone levels and altered ovogenesis. Several genes have their expression levels altered when leptin is absent, especially adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide type 1.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):105-109
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005201
To determine whether paraspinal block reduces pain scores compared to placebo in women with chronic pelvic pain refractory to drug therapy.
Subjects with chronic pelvic pain due to benign conditions and refractory to drug therapy were invited to participate in a randomized, double blind, superiority trial at a tertiary reference center. Subjects were randomly allocated to receive paraspinal anesthetic block with 1% lidocaine without epinephrine or placebo (control). Lidocaine was injected along the spinal process of the painful segment in the supra- and interspinal ligaments using a 25G X 2" needle. Placebo consisted of introduction of the needle in the same segment without injecting any substance. The main outcome measured was the pain score based on a visual analog scale at T0 (baseline), T1 (within 15 min after the procedure) and T2 (one week after the procedure). Data were statistically analyzed by ANOVA and the 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
Mean age was similar for both groups, i.e., 51.2 (paraspinal anesthetic block) and 51.8 years (control). A blind examiner measured the degree of pain according to the visual analog scale from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain imaginable). Based on the visual analog scale, the mean pain scores of the paraspinal anesthetic block group at T0, T1 and T2 were 5.50 (SD=2.92; 95%CI 3.84-7.15), 2.72 (SD=2.10; 95%CI 1.53-3.90), and 4.36 (SD=2.37; 95%CI 1.89-6.82), respectively. The difference between T0 and T1 was statistically significant, with p=0.03.
Paraspinal anesthetic block had a small effect on visual analog scale pain score immediately after the injections, but no sustained benefit after one week. Further studies are needed to determine the efficacy of paraspinal anesthetic block with different lidocaine doses for the treatment of visceral pain of other causes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):110-114
DOI 10.1590/SO-720320150005258
To assess the reproductive outcomes after hysteroscopic septoplasty.
A retrospective observational study was performed with analysis of the medical records of 28 women with infertility or recurrent abortions undergoing hysteroscopic septoplasty. To evaluate reproductive outcomes we consulted the medical records of our hospital and of primary health care units between septoplasty and the present or first pregnancy. Primary outcomes were pregnancy rate, newborns, and abortions after septoplasty. Uterine septum was diagnosed by 2D or 3D ultrasound and classified according to the American Fertility Society. All procedures were performed in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle using monopolar or bipolar energy and/or microscissors. To compare the reproductive outcomes before and after septoplasty we used Microsoft Excel and SPSS version 17. Fisher's exact test was considered statistically significant if p<0.05.
Hysteroscopic septoplasty was performed in 20 patients (72%) with secondary infertility and in 8 patients (28%) with primary infertility. The septum was incompletely removed during the first hysteroscopy in 5 cases (18%), which required a second surgery. One case was complicated with minor uterine perforation. After hysteroscopic septoplasty, 64% of women became pregnant and 48% live neonates were delivered; 4% of the patients had a tubal pregnancy; and 19% had miscarriages.
The results of this study are consistent with those described in the literature. Patients obtained a significant improvement of reproductive outcomes with a fivefold reduction in miscarriage rate after hysteroscopic septoplasty.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):115-118
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005257
To evaluate the treatment outcome of tubo-ovarian abscesses managed by transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration.
Descriptive analysis of all patients with tubo-ovarian abscesses treated with a minimally invasive procedure, ultrasound-guided drainage, at the Department of Gynecology, Centro Hospitalar Vila Nova de Gaia/Espinho, during a period of 5 years (from June 2009 to June 2014).
Twenty-six cases were included in the study. The mean age of the study group was 42.8 years. All patients were submitted to transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration and sclerosis with iodated solution, as well as received broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics. The mean time from admission to drainage was 2.5 days. Cultures for aerobic and anaerobic pathogens were positive in 14 of the 26 cases. A complete response was noted in 23 of the 26 cases. No complications or morbidity were noted as a consequence of the drainage procedures.
Minimally invasive treatment of tubo-ovarian abscesses by transvaginal ultrasound-guided drainage is an effective and safe approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):119-126
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005247
To assess fatigue and quality of life in disease-free breast cancer survivors in relation to a sample of age-matched women with no cancer history and to explore the relationship between fatigue and quality of life.
A cross-sectional study was conducted in a sample of 202 consecutive disease-free Brazilian breast cancer survivors, all of whom had completed treatment, treated at 2 large hospitals. The patients were compared to age-matched women with no cancer history attending a primary health care center. The Piper Fatigue Scale-Revised and the World Health Organization Quality of Life Instrument (WHOQOL-BREF) were used to measure the fatigue and quality of life, respectively. Socio-demographic and clinical variables were also obtained. The χ2 test, generalized linear model, and Spearman correlation coefficient were used for statistical purposes. The adopted level of significance was 5%.
Breast cancer survivors experienced significantly greater total and subscale fatigue scores than comparison group (all p-values<0.05). In addition, survivors reported a poorer quality of life in physical (p=0.002), psychological (p=0.03), and social relationships (p=0.03) domains than comparison group. No difference was found for the environmental domain (p=0.08) for both groups. For survivors of breast cancer and for comparison group, the total and subscale fatigue scores were related to lower quality of life (all p-values<0.01).
The findings of this study highlight the importance of assessing fatigue and quality of life in breast cancer survivors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):127-132
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005120
To describe the maternal and fetal outcomes with the use of the Foley catheter for induction of labor in high-risk pregnant women with previous caesarean section.
An interventive and descriptive study was conducted from November 2013 to June 2014. A total of 39 pregnant women at term, with a live fetus, cephalic presentation, estimated fetal weight <4,000 g, with previous cesarean section, medical indications for induction of labor, Bishop score ≤6 and amniotic fluid index >5 cm were included. A number 16F Foley catheter was introduced for a maximum of 24 hours, and was considered to be satisfactory when the patient began labor within 24 hours.
Labor was successfully induced in 79.5% of pregnant women. Nine women achieved vaginal delivery (23.1%), with a frequency of 18% of vaginal births occurring within 24 hours. The main indications for the induction of labor were hypertensive disorders (75%). The mean interval between the placement of the Foley catheter and the beginning of labor and delivery were 8.7±7.1 and 14.7±9.8 hours, respectively. Meconium-stained amniotic fluid was observed in two patients; and an Apgar score <7 in the first minute was detected in 5 newborns (12.8%).
The Foley catheter is an alternative for the induction of labor in women with previous caesarean section, despite the low vaginal delivery rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(3):133-139
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005132
To determine fetal heart rate (FHR) responses to maternal resistance exercise for the upper and lower body at two different volumes, and after 25 minutes post-exercise.
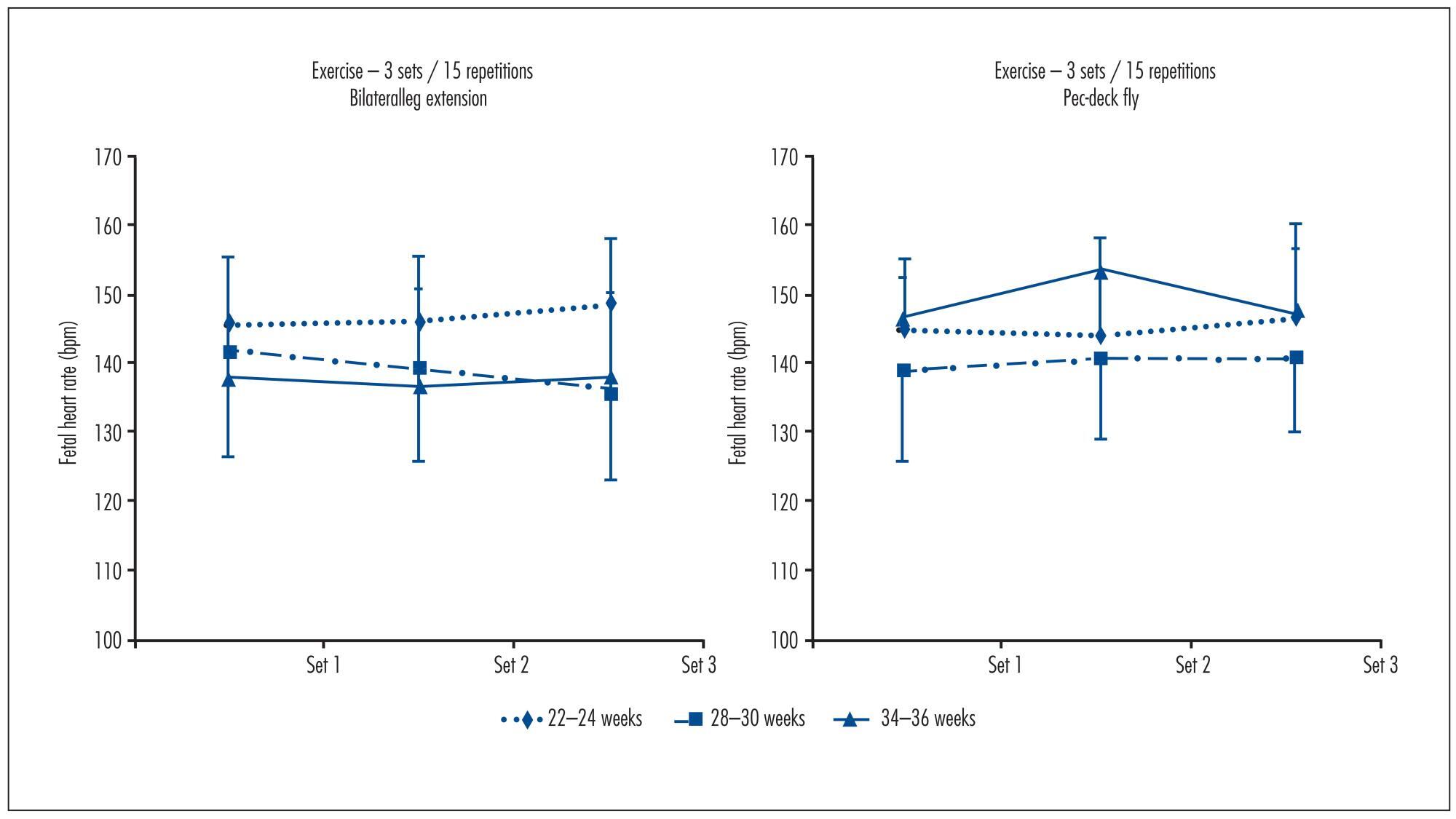
Ten pregnant women (22-24 weeks gestation, 25.2±4.4 years of age, 69.8±9.5 kg, 161.6±5.2 cm tall) performed, at 22-24, 28-32 and 34-36 weeks, the following experimental sessions: Session 1 was a familiarization with the equipment and the determination of one estimated maximum repetition. For sessions 2, 3, 4 and 5,FHR was determined during the execution of resistance exercise on bilateral leg extension and pec-deck fly machines, with 1 and 3 sets of 15 repetitions; 50% of the weight load and an estimated repetition maximum. FHR was assessed with a portable digital cardiotocograph. Results were analyzed using Student's t test, ANOVA with repeated measures and Bonferroni (α=0.05; SPSS 17.0).
FHR showed no significant differences between the exercises at 22-24 weeks (bilateral leg extension=143.8±9.4 bpm, pec-deck fly=140.2±10.2 bpm, p=0.34), 28-30 weeks (bilateral leg extension=138.4±12.2 bpm, pec-deck fly=137.6±14.0 bpm, p=0.75) and 34-36 weeks (bilateral leg extension=135.7±5.8 bpm, pec-deck fly=139.7±13.3 bpm, p=0.38), between the volumes(bilateral leg extension at 22-24 weeks: p=0.36, at 28-30 weeks: p=0.19 and at 34-36 weeks: p=0.87; pec-deck fly at 22-24 weeks: p=0.43, at 28-30 weeks: p=0.61 and at 34-36 weeks: p=0.49) and after 25 minutes post-exercise.
Results of this pilot study would suggest that maternal resistance exercise is safe for the fetus.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(2):59-63
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005180
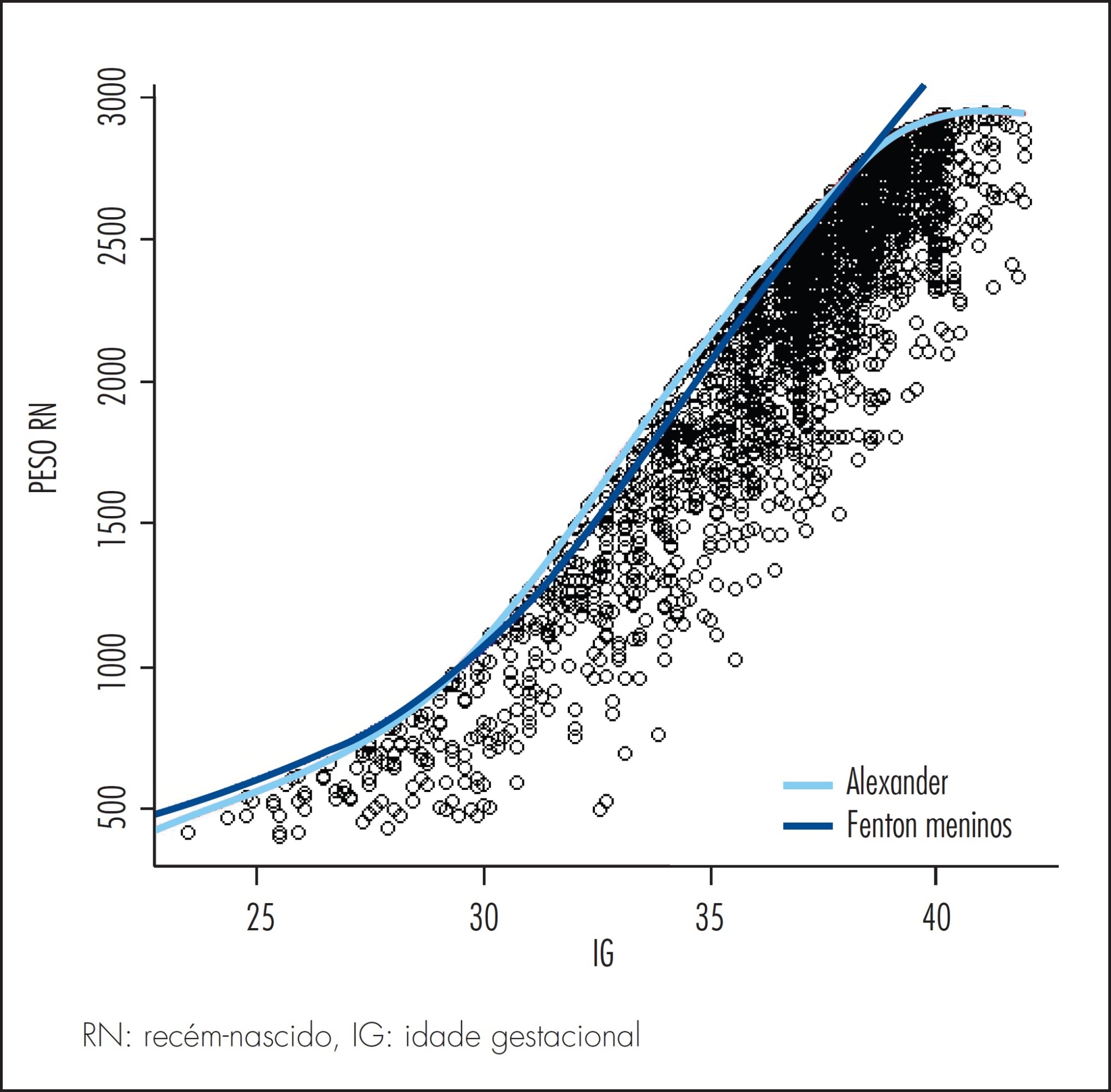
It was to compare the use of two growth curves for the diagnosis of small-for-gestational-age (SGA) infants, having the 10thpercentile as reference.
In a retrospective study, data of 20,567 singleton live births from January 2003 to June 2014 were analyzed, and divided according to gestational age: (a) 23 to 26, (b) 26 to 29, (c) 29 to 32, (d) 32 to 35, (e) 35 to 38, (f) 38 to 41 and (g) >41 weeks. Data were paired and analyzed using the McNemar test, with the level of significance set at 0.05.
The curve designed by Alexander indicated a higher percentage of diagnosis of SGA than the curve constructed by Fenton for every category of gestational age up to 41 weeks, more markedly in the 32-35 week group (18.5%). Between 37 and 40 weeks of gestational age, Alexander's curve exceeded Fenton's curve in 9.1% of the cases in the diagnosis of SGA.
The Fenton curve provides a more accurate evaluation of an infant's growth since it is gender-specific and allows measurement of three parameters. It has also been constructed with newer data and more sophisticated statistical tools.