Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(7):401-406
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000700006
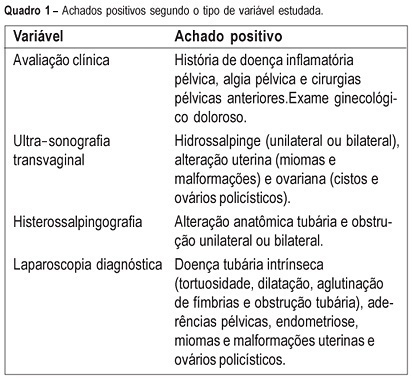
PURPOSE: to evaluate the agreement between noninvasive methods - pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound and hysterosalpingography - and the gynecologic endoscopy approach for the diagnosis of tuboperitoneal factors responsible for conjugal infertility. METHODS: this is a cross-sectional study including 149 infertile patients who were submitted to clinical evaluation, transvaginal ultrasound, hysterosalpingography, hysteroscopy, and laparoscopy. In the evaluation of pelvic pain, the following complaints were considered to be abnormal: pelvic pain of the dyspareunia type, dysmenorrhea or acyclic pain, and pain upon mobilization of the cervix and palpation of the adnexa. Ultrasonographic examination was considered to be altered when adnexal or uterine morphological changes (hydrosalpinx, myomas or uterine malformations) were detected. Hysterosalpingography was considered to be abnormal in the presence of anatomical tubal changes and unilateral or bilateral obstruction. The agreement between noninvasive methods and endoscopy was evaluated by kappa statistics. RESULTS: the agreements between pelvic pain, transvaginal ultrasound, and hysterosalpingography and the endoscopic approach were 46.3% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), 24% (kappa=-0.052; CI 95%: -0.148 to 0.043), and 46% (kappa=0.092; CI 95%: -0.043 to 0.228), respectively. When at least one alteration detected by noninvasive methods was considered, the agreement with endoscopic approach was 63% (kappa=-0.014; CI 95%: -0.227 to 0.199). Sensitivity and specificity in predicting alterations on endoscopic approach were 39.5 and 80% in the presence of pelvic pain, 14.5 and 72% in the presence of alteration on transvaginal ultrasound, 39.5 and 80% in the presence of alteration on hysterosalpingography, and 70.2 and 28% in the presence of at least one alteration by noninvasive methods. CONCLUSION: there is a poor diagnostic agreement between the several noninvasive methods and endoscopy in the investigation of conjugal infertility secondary to tuboperitoneal factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):303-309
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600003
PURPOSE: to diagnose intrauterine growth restriction (IGR) and its connection with early neonatal morbidity and mortality, through Roher's ponderal index (PI). METHODS: this was a retrospective, descriptive study of transversal cohort, in which 2741 newborns (NB) were included, 2053 of them from healthy pregnant women, 228 from women with mild pregnancy-related hypertension, 52 from those with severe pregnancy-related hypertension, 25 from those with mild pregnancy-related hypertension that evolved to eclampsia, 136 from those with premature membrane rupture, and 247 from women who smoked along gestation. Roher's PI was calculated by the equation: PI = weight/height ³ x 100 and the values 2.25 and 3.10 of Lubchenco's 10 and 90 percentiles were used to classify the types of IGR. IGR was classified as asymmetric for NB with PI < 2.25 and weight lower than percentile 10, as symmetric, with PI from 2.25 to 3.10 and weight lower than percentile 10, and adequate for gestational age with PI from 2.25 to 3.10, and weight from 10 to 90 percentiles. Statistical analysis was performed using the non-paired t test, the non-parametric chi2 test and Fisher's exact test, with significance set at a value of p<0.05. RESULTS: low birth weight (< 2,500 g) was present in 3.6% (100/2741) of the cases, while the rate of IGR diagnosed through PI was 15.7% (430/2741), 14.0% being asymmetric and 1.7% symmetric. The most frequent complication among the asymmetric IGRNB was transient tachypnea (8.3%), followed by asphyxia (5.7%) and infection (2.6%). Transient tachypnea was present in 6.5% of symmetric IGRNB, followed by asphyxia (4.3%), meconium aspiration syndrome (2.2%), hypoglycemia (2.2%) and infection (2.2%). Early neonatal death was similar for NB with restricted IGR and adequate IGR for gestational age, both groups reaching a rate of 0.3%. CONCLUSIONS: Rohrer's PI was able to diagnose the different IGR patterns, which would not be known if the birth weight had been calculated in terms of gestational age. The asymmetric NB presented a higher incidence of transient tachypnea and asphyxia, without statistical significance in relation the other IGR patterns. The frequency of early neonatal death was similar for the asymmetric and adequate for gestational age NB groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600004
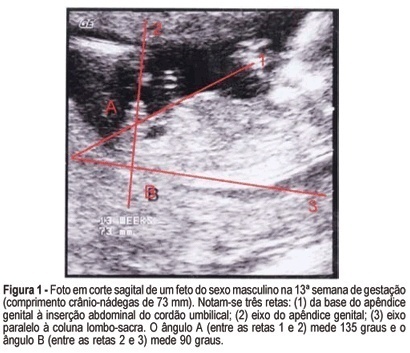
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of fetal gender prediction at 11 to 13 weeks and 6 days by measuring the anterior and posterior genital tubercle angles. MESTHODS: the anterior and posterior genital tubercle angles were measured in a midsagittal plane in 455 fetuses from 11 to 13 weeks and 6 days. The probability of a correct fetal sex prediction (confirmed after birth) was categorized in accordance with the angle measurements, gestational age and crump-rump length. The optimal accuracy cutoffs were derived from a ROC-plot. The interobserver variability was evaluated by a Bland-Altman plot. RESULTS: the correct fetal sex prediction rate increased with gestational age and crump-rump length. Using a 42-degree anterior angle as a cutoff, a correct fetal sex prediction occurred in 72% of the fetuses from 11 to 11 weeks and 6 days, 86% from 12 to 12 weeks and 6 days and 88% from 13 to 13 weeks and 6 days. Using a 24-degree posterior angle as a cutoff, a correct fetal gender prediction occurred in 70, 87 and 87%, respectively. The interobserver variability evaluation revealed a mean difference between paired measurements of 15.7 and 9 degrees for the posterior and anterior angles, respectively. CONCLUSION: the measurement of the genital tubercle angles showed a high accuracy in correctly predicting the fetal sex from the 12th week of gestation on. However, accuracy was still not high enough for clinical use in pregnancies at risk of serious X-linked diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):316-322
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the relationship between renal transplantation and pregnancy through the analysis of clinical and obstetric intercurrent events and perinatal outcomes. METHODS: a retrospective series of 39 cases of pregnancy in 37 women with renal transplantation from January 1997 to December 2003 was evaluated. A control group consisted of 66 pregnant women with no previous clinical pathologies. This group received prenatal care and these patients delivered during 2002 and 2003. Preeclampsia, premature rupture of membranes, premature delivery, and intrauterine growth restriction were used to compare these variables. Demographic characteristics of these groups were related to the mean age at conception, ethnic characteristics and obstetric past. Regarding renal transplantation the type of donator and used immunosuppressive drugs were evaluated. The studied clinical variables were chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection. The interval between the surgery and conception, occurrence of dysfunction, rejection and loss of the allograft were characteristcs related to the allograft. Obstetric variables were related to the type of delivery, incidence of preeclampsia and premature rupture of membranes. Perinatal outcomes were premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction and these results were compared with renal function. The used statistical methods were the chi2 and Fisher's exact tests. The significance level was fixed always as less than or equal to 0.05 (5%). RESULTS: the mean age at conception was 27 years. The live donator was the most frequent among the patients. Among the immunosuppressive drugs, cyclosporine was the most used. Chronic hypertension occurred in 82% of the cases, anemia in 77% and urinary tract infection in 38.5%. The incidence of renal dysfunction was 47.4% and preeclampsia was the main cause. The loss of the renal transplantation occurred in 10.2%. Delivery by cesarean section was performed in 53.8% of the patients, and the main causes were hypertensive syndromes. Preeclampsia occurred in 28.2%. Among the perinatal outcomes, premature delivery occurred in 46.1% of the cases, with a significant relation to creatinine level greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL at the start of prenatal care. Another observed intercurrent event was intrauterine growth restriction, which occurred in 41.0%, and here we found no relation between this event and creatinine levels. CONCLUSIONS: young patients constituted the study group. Chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection were very common. Renal dysfunction was frequent and must be investigated during prenatal care. There were four cases of loss of the transplant due to clinical or obstetric causes. Cesarean delivery had the highest incidence, but vaginal delivery should be the first choice in these cases. Preeclampsia occurred very frequently and this complication should be considered as a high risk. Preterm delivery and intrauterine growth restriction were the main perinatal complications. Premature deliveries before 37 weeks of gestation were related to allograft function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):323-330
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600006
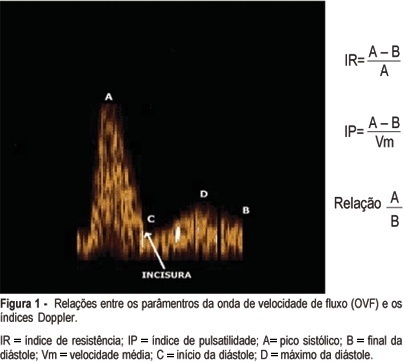
PURPOSE: to determine the validity of uterine artery Doppler velocimetry for the prediction of pregnancy complications in a population of low-risk nulliparae. SUBJECTS: a prospective study was conducted on 45 patients in their first pregnancy with no history of chronic diseases. Uterine artery Doppler velocimetry was performed between 24 and 26 weeks, with the determination of resistance index (RI), pulsatility index (PI), S/D ratio, and the presence or absence of incisure in the flow velocity wave. Data were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney test for non-parametric samples, and the Fisher exact test was used in the evaluation of the qualitative parameters. RESULTS: pregnancy complications were observed in twelve patients, with four cases of preeclampsia, one case of small for gestational age newborn (SGA NB), one case of SGA NB + preterm delivery (PTD), three cases of PTD, one case of fetal centralization, and two cases of presence of thick meconium in the amniotic fluid at the time of pregnancy resolution. We noted that RI (median 0.56 x 0.68), PI (median 0.98 x 1.29) and S/D ratio (median 2.2 x 2.9) were higher at the examination performed between 24 and 26 weeks in patients with complications and did not differ in preeclampsia and SGA cases. The presence of bilateral incisure showed 100 and 90% sensitivity, 60.2 and 62.5% specificity, 29.4 and 42,9% positive predictive value (PPV), and 100 and 95.2% negative predictive value (NPV) for the detection of preeclampsia or SGA and of any complication of pregnancy, respectively. An altered Doppler showed 83.3 and 83.3% sensitivity, 69.7 and 69.7% specificity, 33.3 and 50.0% PPV, and 95.8 and 92.0% NPV for the detection of preeclampsia or SGA and of any complication of pregnancy, respectively. CONCLUSION: high impedance indices and the presence of a bilateral incisure in the uterine arteries between 24 and 26 weeks of pregnancy seem to be good predictors of pregnancy and perinatal complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):331-339
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the epidemiologic data and signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia in patients with complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) and to estimate the risk associated with the persistence of the disease. METHODS:: we evaluated 214 patients with CHM submitted to uterine evacuation between 1980 and 2001. The patients were included prospectively. All patients were followed until negative bHCG with weekly clinical evaluation and bHCG quantification. We considered persistence when the patient needed another treatment after uterine evacuation. The risk factors for persistence were evaluated through univariate and multivariate analysis, and the odds ratio (OR) was calculated for each one. RESULTS: among the epidemiologic factors, only negative Rh was significant (OR=2.28). All signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia, represented by uterine size larger than expected, sonographic uterine volume, tecaluteinic cysts, and betaHCG higher than 10(5) were associated with risk for the presistence of the disease. The presence of at least one sign of trophoblastic hyperplasia showed sensitivity of 82% and predictive positive value of 35.1% (OR=4.8). The logistic regression identified larger uterine size than expected and bHCG higher than 10(5) as risk factors for persistence of the gestational trophoblastic disease (OR=4.1 and 5.5, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: the signs of trophoblastic hyperplasia showed good sensitivity to predict persistence of the disease; however, the low predictive positive value does not allow using these criteria to change treatment. It is very important to reinforce the importance of serial betaHCG quantification in these high-risk patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):340-346
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600008
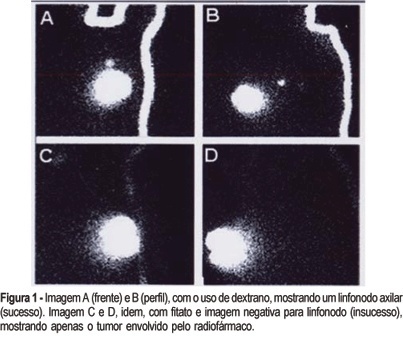
PURPOSE: a case-control study comparing two radiocolloids used in scintigraphy to map the sentinel lymph nodes (SLN) in breast cancer patients. METHODS: forty patients were prospectively enrolled between May 2002 and April 2004, after signing an informed consent form. In the present double-blind study, each patient was submitted twice to the same examination, a mammary scintigraphy, one with 99mTc-dextran 500 (dextran) and the other with 99mTc-phytate (phytate), on different days. A volume of 2 ml with 1-1.5 mCi of each radiopharmaceutical, in divided aliquots, was injected in the breast parenchyma in four points around in the tumor and the subcutaneous area superficial to the tumor. The image was obtained 2 h after the injection, using a gamma camera with high-resolution collimator. The lymph nodes were identified by anterior and lateral static scintigraphic images. Statistical analysis was done with the use of McNemar and Z tests. RESULTS: in the analysis of the 40 patients, we had 15 pairs with positive identical images, 4 pairs with negative images and 21 pairs with inconsistent images, either because one of them was negative, or because the SLN numbers were different. When the protocol was opened, we found 35 and 27 positive images and 5 and 13 negative images for dextran and phytate treatment groups, respectively. Among the negative images, 4 were shared by both groups. The McNemar test, used for the statistical analysis, showed p=0.026, odds ratio (OR) = 0.11 with 95% CI 0.01 < OR < 0.85. The accuracy, evaluated by the success ratio of the SLN mapping, was 67.5% for phytate and 87.5% for dextran, with p=0.032. Analysis of variance of the SLN number in lymphoscintigraphy images showed p=0.008. CONCLUSION: these results recommend the use of dextran instead of phytate for the SLN study of breast carcinoma by scintigraphy, when the same methodology is being used.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):347-352
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600009
PURPOSE: to assess the interference of two vaginal lubricants (vaseline and silicone) in the interpretation of cervical oncotic cytology. METHODS: a prospective research on one hundred women from August to October 2003. The women were divided into two groups of 50 patients each, according to the type of lubricant used. Two smears were obtained from every patient: the first specimen soon after the introduction of non-lubricated speculum and the second after the use of lubricated speculum with vaseline (Group V) or silicone (Group S). The samples were analyzed by two cytotechnicians, who were unaware of the origin of the smears. RESULTS: among the 100 pairs of slides, 8 results were partially different. The reasons for the differences were not directly related to the use of lubricant and did not interfere with the cytologic findings. The number of discordant results was 6 in Group S and 2 in Group V, without a statistically significant difference (p=0.269). The number of satisfactory and satisfactory but limited results was statistically similar regarding the use or not of lubricant: Group S: 46 satisfactory slides and 4 satisfactory but limited slides (p=0.001 and kappa=0.802) and Group V: 48 satisfactory and 2 satisfactory but limited slides (p=0.001 and kappa=0.953). There were no unsatisfactory results. No artefacts were found in slides obtained with lubricated speculum. CONCLUSION: the use of lubricated speculum with vaseline or silicone does not affect cervical oncotic cytology outcome.