Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):519-524
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005100
To validate a questionnaire to be applied in order to learn and describe the perceptions of specialists in obstetrics and gynecology about their experience and self-confidence in the emergency care for vaginal delivery.
This was a prospective study for the validation of an instrument that contains statements about emergency obstetrical care: breech delivery (n=23), shoulder dystocia (n=20), postpartum haemorrhage (n=24), forceps delivery (n=32), and vacuum extractor (n=5). Participants gave their opinions on each item by applying the Likert scale (0=strongly disagree, 1=partially disagree, 2=indifferent, 3=partially agree and 4=strongly agree). The questionnaire was applied to 12 specialists in obstetrics and gynecology and it was expected to be found a level of comprehension exceeding 80%. A five-point scale was used to assess the understanding of each question (from 0=did not understand anything to 5=understood perfectly and I have no doubt). A score above 4 was considered to indicate sufficient understanding. The instrument used was specially designed to suit the specific demands. The analysis of internal reliability was done using the Cronbach alpha coefficient. For external validation, we calculated the proportion of items with full understanding for each subscale. For research purposes, the alpha should be greater than 0.7.
Participants had a mean age of 33.3 years, with 5.0 standard deviation (SD), and an average interval time since graduation from medical school of 5.8 years (SD=1.3 years). All were specialists with residency in obstetrics and gynecology. The mean proportion of participants who fully understood the items in each emergency was 97.3% for breech delivery, 96.7% for shoulder dystocia, 99.7% for postpartum hemorrhage, 97.4% for forceps delivery, and 98.3% for the use of a vacuum extractor. The results of Cronbach's alpha for the items in each emergency studied were: 0.85 for breech delivery, with 0.72 lower limit of 95% confidence interval ((%%CI), 0.74 for shoulder dystocia (lower limit of 95%CI=0.51), 0.79 for postpartum hemorrhage (lower limit of 95%CI=0.61), 0.96 for forceps delivery (lower limit of 95%CI=0.92), and 0.90 for the vacuum extractor (lower limit of 95%CI=0.79).
The validated questionnaire is useful for learning and describing the perception of physicians about their experience and self-confidence in emergency care for vaginal births.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(11):484-488
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004952
To evaluate sexual function in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques.
This is a case-control study including 278 women assisted in Human Reproduction services and at the Gynecology Clinic of the University Hospital, Federal University of Goiás, Brazil. The women were divided into a study group (168 infertile women) and a control group (110 fertile women), and they answered the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) questionnaire used the assess the sexual function. We calculated the odds ratio (OR) for the chance of sexual dysfunction in infertile women (p<0.05).
Out of the analyzed women, 33.09% reported sexual dysfunction, with no difference in the FSFI score between groups (p=0.29). The prevalence of sexual dysfunction was of 36.30% among infertile women and 28.18% among fertile women; however, there was no difference between FSFI scores (p=0.36). The desire and arousal domains were significantly different among infertile women (p=0.01). Infertile women had the same chances of having sexual dysfunction as fertile women (OR=1.4, 95%CI 0.8–2.4; p=0.2).
There were no differences between infertile and fertile women. Infertile women undergoing assisted reproduction techniques require professional approach to sexual health regarding desire and arousal.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):436-441
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005105
Pregnant women have a 2-3 fold higher probability of developing restless legs syndrome (RLS – sleep-related movement disorders) than general population. This study aims to evaluate the behavior and locomotion of rats during pregnancy in order to verify if part of these animals exhibit some RLS-like features.
We used 14 female 80-day-old Wistar rats that weighed between 200 and 250 g. The rats were distributed into control (CTRL) and pregnant (PN) groups. After a baseline evaluation of their behavior and locomotor activity in an open-field environment, the PN group was inducted into pregnancy, and their behavior and locomotor activity were evaluated on days 3, 10 and 19 of pregnancy and in the post-lactation period in parallel with the CTRL group. The serum iron and transferrin levels in the CTRL and PN groups were analyzed in blood collected after euthanasia by decapitation.
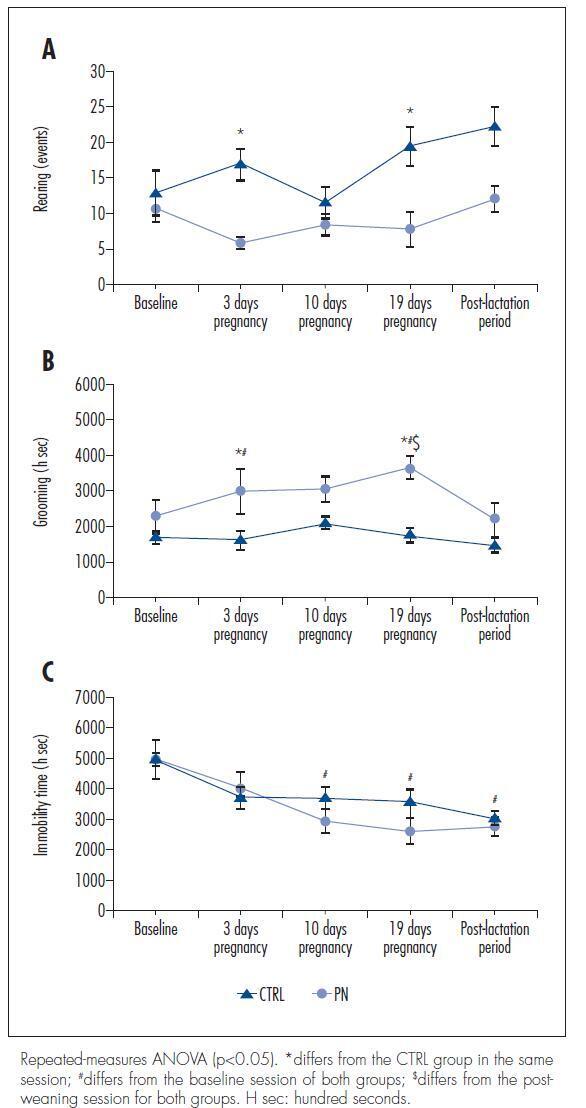
There were no significant differences in the total ambulation, grooming events, fecal boli or urine pools between the CTRL and PN groups. However, the PN group exhibited fewer rearing events, increased grooming time and reduced immobilization time than the CTRL group (ANOVA, p<0.05).
These results suggest that pregnant rats show behavioral and locomotor alterations similar to those observed in animal models of RLS, demonstrating to be a possible animal model of this sleep disorder.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):449-455
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004946
To assess cardiometabolic risk factors during normal pregnancy and the influence of maternal obesity on them.
This study included 25 healthy pregnant women with a single pregnancy and a gestational age of less than twenty weeks. Longitudinal analysis of blood pressure, body weight, body mass index (BMI), serum concentrations of leptin, adiponectin, cortisol, total cholesterol and fractions, triglycerides, uric acid, fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, HOMA-IR and insulin/glucose ratio was performed each trimester during pregnancy. In order to evaluate the impact of obesity, pregnant women were divided into two groups based on BMI for the first quarter of pregnancy: Gpn for pregnant women with BMI<25 kg/m2 and Gso for BMI≥25 kg/m2. One-Way ANOVA for repeated measurements or Friedman test and Student-t or Mann-Whitney tests for statistical comparisons and Pearson correlations test were used for statistical analysis.
The mean values for the first quarter of pregnancy for the following parameters were: age: 22 years; weight: 66.3 kg and BMI 26.4 kg/m2, with 20.2 and 30.7 kg/m2 for the Gpn and Gso groups, respectively. Mean weight gain during pregnancy was ±12.7 kg with 10.3 kg for the Gso group and 15.2 kg for the Gpn group. Regarding plasma determinations, cortisol, uric acid and lipid profile increased during all trimesters of pregnancy, except for HDL-cholesterol, which did not change. Blood pressure, insulin and HOMA-IR only increased in the third quarter of pregnancy. The Gso group tended to gain more weight and to show higher concentrations of leptin, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, VLDL-cholesterol, TG, glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, besides lower HDL-cholesterol and greater diastolic blood pressure in the 3rdquarter of pregnancy. Three pregnant women developed gestational hypertension, presented prepregnancy obesity, excessive weight gain, hyperleptinemia and an insulin/glucose ratio greater than two. Weight and BMI were positively correlated with total cholesterol and its LDL fraction, TG, uric acid, fasting blood glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR; and were negatively correlated with adiponectin and HDL-cholesterol. Leptin level was positively correlated with blood pressure.
The metabolic changes in pregnancy are more significant in obese women, suggesting, as expected, an increased risk of cardiometabolic complications. During their first visit for prenatal care, obese women should be informed about these risks, have their BMI and insulin/glucose ratio calculated along with their lipid profile to identify pregnant women at higher risk for cardiovascular diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):456-460
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005075
To identify the frequency of polymorphism in the IL-10 gene, rs1800896 (-1082 A/G), in women with preeclampsia (PE) and in women in a control group and to associate the presence of this polymorphism with protection against the development of PE.
This was a case-control study conducted on 54 women with PE, classified according to the criteria of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program, and on 172 control women with at least two healthy pregnancies. The proposed polymorphism was studied by the technique of real time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), with hydrolysis probes. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 test. Odds ratio and confidence interval of 95% were used to measure the strength of association between the studied polymorphism and the development of PE.
Statistically increased frequency of the AG genotype was observed among control women (85 versus 15% in women with PE). The G allele was significantly more frequent among control women than PE women (χ2test, p = 0.01). The odds ratio for carriers of the G allele was 2.13, indicating a lower risk of developing PE compared to non-carriers.
Thus, an association is suggested to occur between the presence of the G allele of the polymorphism in the IL-10 rs1800896 (-1082 A/G) gene and protection against the development of PE. More studies investigating the contribution of these variations and the mechanisms by which they affect the risk of developing PE still need to be undertaken.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):461-466
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005029
To compare clinical and laboratory characteristics, obstetric and perinatal outcomes of patients with pre-eclampsia versus gestational hypertension.
A retrospective study was carried out to analyze medical records of patients diagnosed with pre-eclampsia and gestational hypertension whose pregnancies were resolved within a period of 5 years, for a total of 419 cases. We collected clinical and laboratory data, obstetric and perinatal outcomes. Comparisons between groups were performed using the test suitable for the variable analyzed: unpaired t test, Mann-Whitney U test or χ2test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
Were evaluated 199 patients in the gestational hypertension group (GH) and 220 patients in the pre-eclampsia group (PE). Mean body mass index was 34.6 kg/m2 in the GH group and 32.7 kg/m2 in the PE group, with a significant difference between groups. The PE group showed higher systolic and diastolic blood pressure and higher rates of abnormal values in the laboratory tests, although the mean values were within the normal range. Cesarean section was performed in 59.1% of cases of PE and in 47.5% of the GH group; and perinatal outcomes in terms of gestational age and birth weight were significantly lower in the PE group.
Women with gestational hypertension exhibit epidemiological characteristics of patients at risk for chronic diseases. Patients with pre-eclampsia present clinical and laboratory parameters of greater severity, higher rates of cesarean delivery and worse maternal and perinatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):467-472
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005094
To evaluate factors associated with hypertension in Brazilian women of 50 years of age or more.
A cross-sectional population based study using self-reports. A total of 622 women were included. The association between sociodemographic, clinical and behavioral factors and the woman's age at the onset of hypertension was evaluated. Data were analyzed according to cumulative continuation rates without hypertension, using the life-table method and considering annual intervals. Next, a Cox multiple regression analysis model was adjusted to analyze the occurrence rates of hypertension according to various predictor variables. Significance level was pre-established at 5% (95% confidence level) and the sampling plan (primary sampling unit) was taken into consideration.
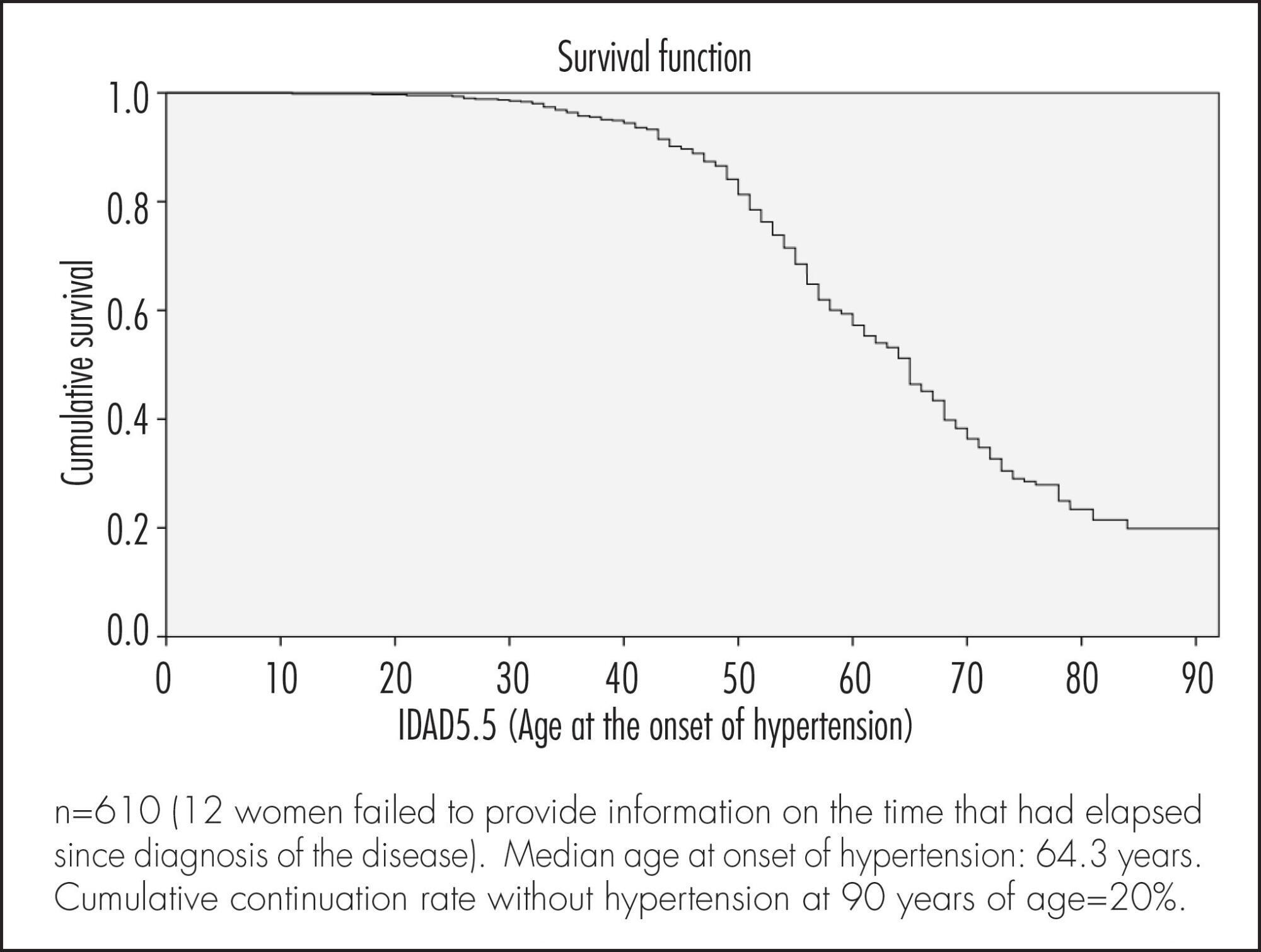
Median age at onset of hypertension was 64.3 years. Cumulative continuation rate without hypertension at 90 years was 20%. Higher body mass index (BMI) at 20–30 years of age was associated with a higher cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient=0.078; p<0.001). Being white was associated with a lower cumulative occurrence rate of hypertension over time (coefficient= -0.439; p=0.003), while smoking >15 cigarettes/day was associated with a higher rate over time (coefficient=0.485; p=0.004).
The results of the present study highlight the importance of weight control in young adulthood and of avoiding smoking in preventing hypertension in women aged ≥50 years.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):442-448
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004941
To identify obstetric and perinatal factors associated with perinatal morbidity and mortality in pregnancies that progressed with ruptured membranes.
A cross-sectional hospital-based study with secondary data from records of patients (n=87) that evolved with the premature rupture of membranes between 24 and 42 weeks of gestation, admitted from January to April 2013 to a public hospital in Acre State, North of Brazil. Data were subjected to bivariate analysis for selection of variables to be used in a multiple regression model according to Poisson logistic regression with robust error.
The prevalence of perinatal morbidity-mortality was 51.4%, including a 2.3% death rate (2 cases) and a 9.2% fetal neonatal death rate (8 cases). The variables associated with mortality in the final multiple model were: number of prenatal consultations ≥6, with a prevalence ratio (PR) of 0.5 and a 95% confidence interval (95%CI) of 0.3-0.9, gestational age ≥30 weeks (PR=0.6; 95%CI 0.4-0.8), low birth weight (PR=2.9; 95%CI 1.5-5.4), and mechanical ventilation (PR=3.8; 95%CI 2.0-7.2).
Perinatal morbidity and mortality were high among cases of ruptured membranes. Morbidity and mortality were associated with factors such as fewer prenatal visits, extreme prematurity and low birth weight in this group.