Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):455-459
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005271
To analyze the obstetrical and neonatal outcomes of pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses after 35 weeks based on umbilical cord nucleated red blood cells count (NRBC).
NRBC per 100 white blood cells were analyzed in 61 pregnancies with small for gestation age fetuses and normal Doppler findings for the umbilical artery. The pregnancies were assigned to 2 groups: NRBC≥10 (study group, n=18) and NRBC<10 (control group, n=43). Obstetrical and neonatal outcomes were compared between these groups. The χ2 test or Student's t-test was applied for statistical analysis. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The mean±standard deviation for NRBC per 100 white blood cells was 25.0±13.5 for the study group and 3.9±2.2 for the control group. The NRBC≥10 group and NRBC<10 group were not significantly different in relation to maternal age (24.0 versus 26.0), primiparity (55.8 versus 50%), comorbidities (39.5 versus55.6%) and gestational age at birth (37.4 versus 37.0 weeks). The NRBC≥10 group showed higher rate of caesarean delivery (83.3 versus 48.8%, p=0.02), fetal distress (60 versus 0%, p<0.001) and pH<7.20 (42.9 versus 11.8%, p<0.001). The birth weight and percentile of birth weight for gestational age were significantly lower on NRBC≥10 group (2,013 versus 2,309 g; p<0.001 and 3.8 versus 5.1; p=0.004; respectively). There was no case described of 5th minute Apgar score below 7.
An NRBC higher than 10 per 100 white blood cells in umbilical cord was able to identify higher risk for caesarean delivery, fetal distress and acidosis on birth in small for gestational age fetuses with normal Doppler findings.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):417-420
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005217
To investigate the influence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in the expression of virulence factors of Candida albicans in vitro.
A suspension of L. rhamnosus was initially grown in MRS agar. The other day, Sabouraud dextrose agar was added on the growth of lactobacilli and C. albicans was seeded for 24, 48 and 72 hours. Candida strains were then isolated for investigation of the ability of biofilm formation, by means of cultivation into 96 wells plaque, and reading the optical densities and counting colony forming units per mL. Also the ability of germ tube formation was investigated, after incubation in horse serum and counting of 200 cells. The results were compared to Candida strains grown in the absence of L. rhamnosus, using Student's t test for statistical analysis.
there was a significant reduction in the growth of C. albicans in the presence of lactobacilli after 24, 48 or 72 hours. Significant reduction was also observed in germ tube formation after interaction for 48 or 72 hours. For biofilm formation, no statistically significant difference was observed between the Candida strains grown in the presence or absence of lactobacilli.
The results suggest that L. rhamnosus is able to influence significantly the growth and expression of virulence factors of C. albicans in vitro, and may interfere with pathogenicity of these micro-organisms.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):434-439
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005368
To evaluate breast ultrasonographic features and hemodynamic indexes of the internal mammary arteries in normal pregnant women, and their correlation with the gestational periods.
Observational and cross-sectional, epidemiological, study, conducted between August 2013 and February 2015, with 93 women divided into three groups: first trimester, second trimester and third trimester. The dependent variables were thickness of the skin, of subcutaneous tissue, fibroglandular tissue, and retrommamary adipose tissue, the diameter of the ducts, as well as the pulsatility and resistance indexes of the internal mammary arteries. Independent variables were the three periods of gestation. Repeated measures ANOVA with the multiple comparison Tukey test and a test of contrasts were used for statistical analysis. The Levene test was used to test the homogeneity of variances between periods of gestation. Student's t-test was used to evaluate the difference between nulliparous and non -nulliparous women, and Pearson's correlation coefficient was used for correlation analysis between the two breasts. The level of significance was set at 5%.
Mean age was 26.6±4.6 years, with no significant difference among groups. Breast location (right/left) and gestational period had no significant effect on the thickness of the skin, of subcutaneous tissue and adipose retromammary tissue. However, the thickness of fibroglandular tissue and the diameter of the ducts showed a significant difference according to gestational period (p<0.001), i.e., from the first to the second and to the third trimesters. Doppler flowmetry of the internal mammary arteries showed a difference between breasts and between gestational periods, i.e., the measurements of the right breast were greater than those of the left, and these values decreased throughout pregnancy (p<0.001).
The average thickness of fibroglandular tissue and the diameter of the ducts showed significant differences from the first to the second and to the third trimesters, with no differences being observed between the two breasts. The pulsatility and resistance indexes of the internal mammary arteries decreased progressively throughout pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(8):347-352
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005209
To investigate the association of the HLA-A, -B and -DRB1 alleles with the occurrence of Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion.
A case-control study of 200 women aged 18 to 35 years, consisting of a convenience sample of 100 women who had idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion and 100 women without abortion and with two or more children. Peripheral blood genomic DNA was extracted from 500l of Buffy Coat stored at -20°C. HLA typing was performed by the PCR-SSOP method (Polymerase Chain Reaction - Specific Sequence of Oligonucleotides Probes, One Lambda(r), CA, USA). The regions of the amplified DNA were exon 2 and 3 for the A and B loci and only exon 3 for the DRB1 locus. The HLA FUSIONTM program (One Lambda, Canoga Park, CA, USA, version 3.0) was used for HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-DRB1 genotyping. Absolute frequencies and percentages and calculation of mean and standard deviation were used for standard statistical analysis. The qualitative variables were compared by the χ2 test with Yates correction or by Fisher's exact test. The odds ratio with the 95%CI was used for the comparisons, with the level of significance set at p<0.05.
The frequency of the A*34 allele was significantly higher in the case group compared to control (4.0 versus 0.5%; p<0.05). Alleles A*24 (6.0 versus 12.5%; p<0.05) and B*35 (8.0 versus 20.5%; p<0.05) were significantly less frequent in the case group. Among the class II alleles, DRB1*03 showed a slightly higher frequency in the case group (11.0 versus 5.5%, p = 0.056).
It was shown that the HLA-A*34 allele is a risk factor for recurrent spontaneous abortion, while the HLA-A*24 and HLA-B*35 alleles are associated with protection, and no allele of the DRB1 locus was associated with RSA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(8):353-358
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005338
To investigate the association between genetic, behavioral, biological and medical risk factors and the occurrence of preterm birth.
A retrospective case-control study was conducted. The real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze the influence of the rs12473815 polymorphism of the follicle stimulating hormone receptor gene (FSHR) and the rs1942836 polymorphism of the progesterone receptor gene (PGR). Other proposed risk factors were assessed using validated or specifically developed questionnaires and analysis of electronically recorded medical data. A total of 157 patients were included (45 cases who went into labor before 37 weeks of pregnancy and 112 controls who went into labor after 37 and before 42 weeks of pregnancy).
The genotypes CT of rs12473815 and CT and CC of rs1942836 were associated with a higher chance of premature delivery. There was an association between preterm birth and alcohol intake when consumption occurred 2 or more times per month. Low pre-pregnancy body mass index was a predictor of spontaneous preterm birth, while high body mass index reduced this likelihood.
The results suggest that excessive alcohol intake, a low level of pre-pregnancy body mass and the risk alleles of rs12473815 and rs1942836 polymorphisms of the FSHR and PGR genes, respectively, influence the occurrence of preterm birth.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(8):359-365
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005415
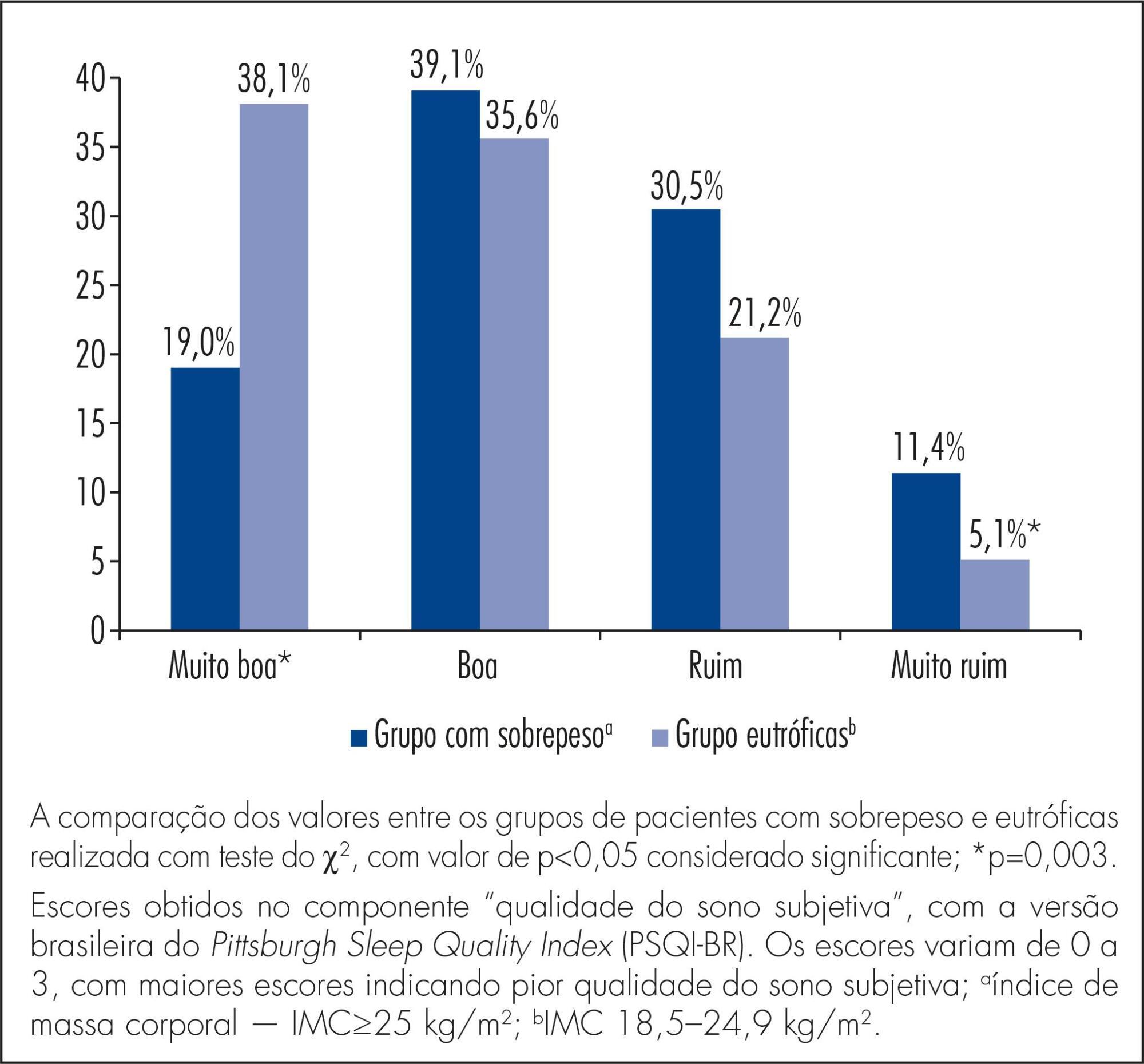
To compare sleep quality of overweight versus normal weight women in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
A cross-sectional study involving 223 women with 14 or more weeks of pregnancy, 105 of them overweight (pre-pregnancy body mass index - BMI - ≥25.0 kg/m2) and 118 of normal weight (BMI 18.5-24.9 kg/m2), attending the prenatal care clinic. The Brazilian version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI-BR) questionnaire was used to evaluate sleep quality. The Student t-test and the chi-square test were used to compare differences between groups and a p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Most of the participants (67.7%) were poor sleepers (total score >5); this proportion was significantly higher among overweight (80/105) versus normal weight (67/118) women (76.2 versus 56.8%, p=0,004). During the second trimester, this difference did not reach statistical significance (72.5 versus 53.7%, respectively, p=0.06) but mean total PSQI-BR scores were significantly higher among overweight participants (7.0±3.8 versus 5.5±3.2, p=0.02). In the 2nd trimester, overweight women also had higher scores for sleep latency (1.4±1.0 versus 1.0±0.9, p=0.02) and subjective sleep quality (1.3±0.8 versus 0.8±0.8, p=0.02). In the third trimester, the proportion of women with poor sleep quality was significantly higher in the overweight group, but did not reach statistical significance (79.6 versus 60.8%, p=0.06). During this period, total mean scores were similar for women with and without excess weight (9.4±4.2 versus 8.3±4.6, p=0.2). However, overweight women had higher mean scores for sleep disturbance (2.3±0.7 versus 2.0±0.8, p=0.04).
Overweight women had a poorer sleep quality than normal weight women in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(8):366-373
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005420
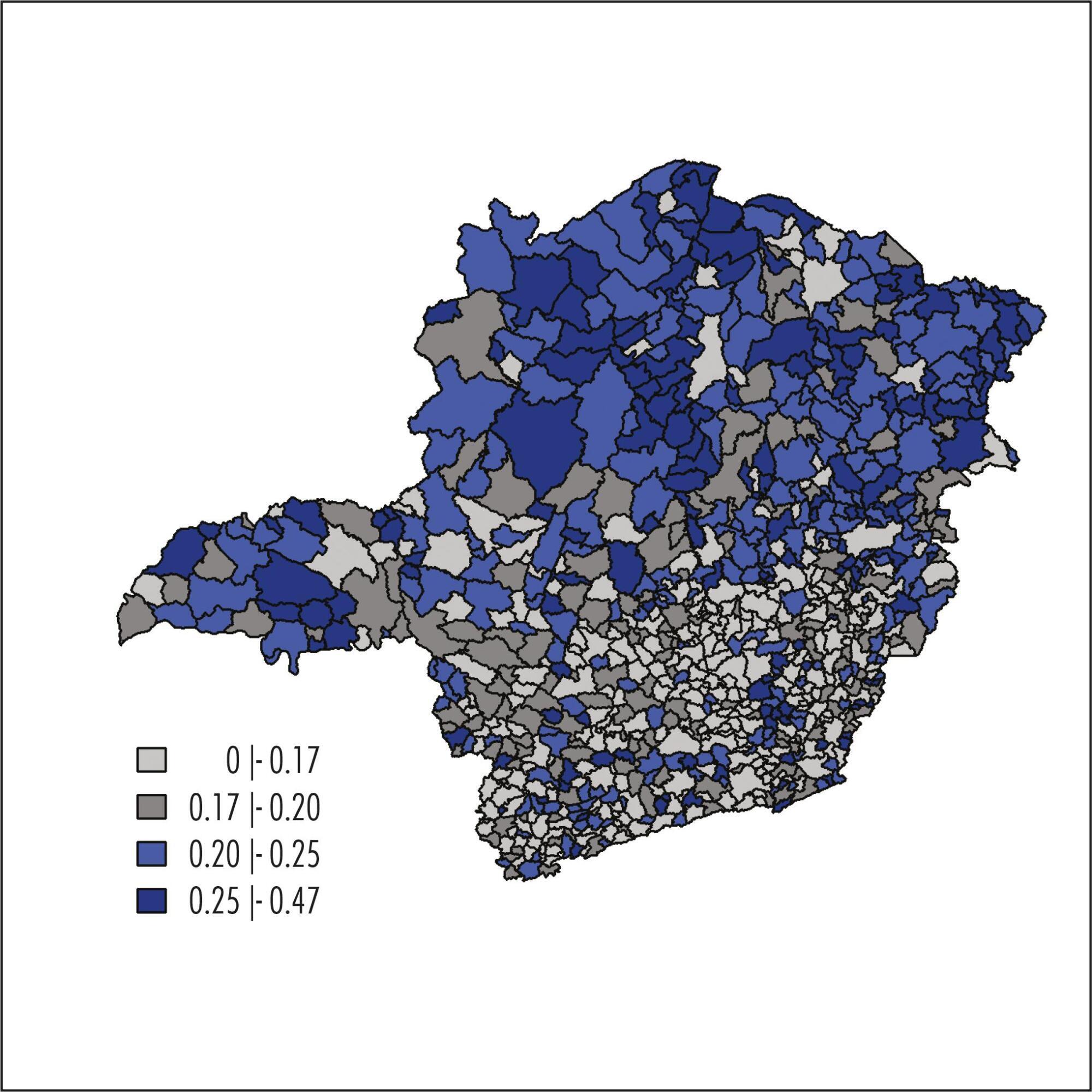
To describe associations between pregnancy rates in adolescence and socioeconomic and social responsibility indicators in the municipalities of the State of Minas Gerais, Southeast of Brazil, in the year of 2010.
Ecological study using data from the Brazilian Live Birth Information System (SINASC). The percentage of live births to adolescent mothers (LBAM) for each municipality was calculated based on the quotient between number of born alive infants of mothers aged 10-19 years old and total number of live births in the year of 2010. Fully Bayesian models were used to obtain the percentages of LBAM adjusted for spatial effects and to assess possible associations with socioeconomic and social responsibility indicators.
The crude percentage of LBAM for the total number of live births in the municipalities of Minas Gerais in 2010 ranged from 0 to 46.4%, with median percentage being 19.6% and the first and third quartiles being 15.6 and 23.1%, respectively. This study has demonstrated a close relationship between adolescent pregnancy and socioeconomic indicators. LBAM percentages were found to be higher in municipalities with low population density, low human development index and other low development indicators.
The strong relationship between LBAM percentages and socioeconomic indicators suggests that adolescent pregnancy is more a social than a biological problem. Therefore, programs and actions should go beyond sexual education and information on preventive health methods.