Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(3):158-164
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300004
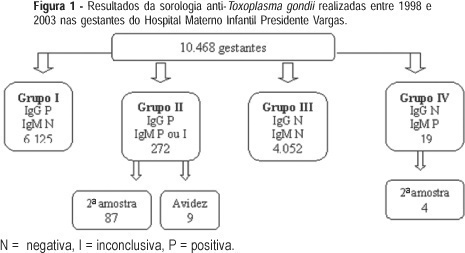
PURPOSE: to describe and analyze the results of conventional serology for toxoplasmosis in pregnant women during prenatal care at the Hospital Materno-Infantil Presidente Vargas in Porto Alegre. METHODS: specific IgG and IgM determinations were performed using fluorometric tests, with IgM capture. A second sample within two to three weeks was requested from all IgM-positive pregnant women and IgG avidity was performed in IgM-positive pregnant women at the beginning of pregnancy. Neonatal IgM was obtained when the delivery occurred at the institution. The analysis was based on the binomial distribution, through simple ratio estimate, to assess soropositivity prevalence and susceptibility to T. gondi infection. RESULTS: the prevalence of infection in 10,468 pregnant women was 61.1% and 38.7% pregnant women were susceptible. Among the 272 IgG and IgM-positive pregnant women, 87 returned for a second test and in 84 of them the antibody levels remained unchanged. Of nine pregnant women with avidity, there was only one low avidity and her newborn was IgM positive. In 44 newborns delivered at the institution, the neonatal IgM was positive in four. CONCLUSIONS: a high prevalence of infection and congenital toxoplasmosis was found in pregnant women, even without data on seroconversion. Most of the IgM-positive serologies were related to past infection. The cost-benefit ratio of prenatal care in isolated samples may be optimized analyzing the risk of mother-to-child transmission in IgM-positive pregnant women. When there is a risk, a neonatal IgM test must be requested and the newborn should be followed during the first year of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):227-231
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400004
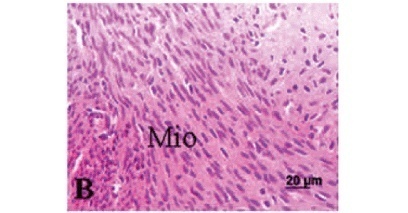
PURPOSE: to evaluate histomorphometric changes in the rat myometrium upon treatment with isoflavones, as compared with estrogens, using histological and morphometric techniques. METHODS: twenty-eight oophorectomized adult rats were randomly divided into four treatment groups: GPropi = propylene glycol (control); GExtr10 - 10 mg/kg soybean extract; GExtr300 - 300 mg/kg soy bean extract; GCee - 200 µg/kg conjugated equine estrogens (Cee). Drugs or drug vehicle were administered by gavage once a day for 21 days. Upon sacrifice, the uteri were removed and weighed. Fragments of uterine horns were collected and fixed in 10% formaldehyde and processed for paraffin inclusion. The histological sections were stained by hematoxylin and eosin and evaluated microscopically by means of an image analyzer to quantify the myometrial thickness and the number of blood vessels and eosinophils. The data were studied by analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test. RESULTS: isoflavones in the concentration of 300 mg/kg induced a significant increase in the myometrium thickness (GExtr300=25.6±5.0 mm) compared to control (GPropi=5.5±0.5 mm). The effect of this high dose is similar to the estrogen effect (GCee=27.5±7.9 mm). In low doses (10 mg/kg), the effect was similar to control. Isoflavones (GExtr300) induced also an increase in the number of blood vessels (GPropi=3.5±1.6; GExtr300=10.2±3.6 vessels/mm²) and of eosinophils (CPropi=0.15±0.01; GExtr300=4.3±0.9 eosinophils/mm²). These effects were comparable to those produced by Cee treatment in GCee (9.2±1.1 eosinophils/mm²). CONCLUSION: a high-dose treatment with isoflavones (300 mg/kg per day, 21 days) elicited an estrogen-like, highly significant proliferative action on the rat myometrium.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):220-226
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400003
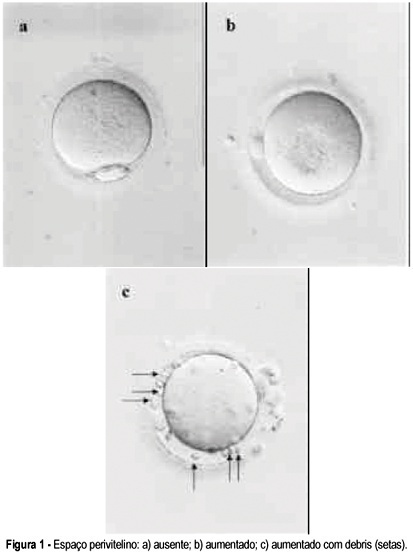
PURPOSE: to verify the possibility of identifying oocytes that would result in a higher fertilization rate. METHODS: retrospective analysis of the fertilization rate after ICSI of 957 oocytes in metaphase II according to three morphology parameters: cytoplasm inclusions, thickness of the perivitelline space, and fragmentation of the first polar body. Oocytes were obtained from 115 cycles performed among 107 women attended at the "Centro de Reprodução Humana de Campinas", from April to December of 2004. For the statistical analysis of differences in the fertilization rate between 'normal' oocytes and those presenting each alteration, the chi2 test was used with confidence levels of 5 and 10%. RESULTS: no significant difference in fertilization rate was observed regarding characteristics of the polar body or thickness of the perivitelline space. Fertilization rate among oocytes with perivitelline space with debris was 14 percentage points lower than among oocytes with absent space (p=0.055) and the rate among oocytes with granular cytoplasm was seven percentage points lower than among oocytes with normal cytoplasm (p<0.10>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the morphological parameters of oocytes currently being evaluated do not allow us to clearly distinguish those that would lead to a higher fertilization rate and could be used in clinical practice.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(3):151-157
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300003
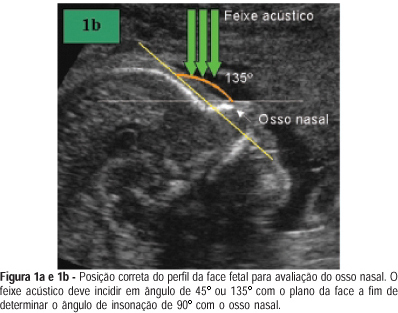
PURPOSE: the absence of fetal nasal bone is correlated with trisomy 21. Although a hypoplastic nasal bone is also correlated with trisomy 21, there is no clear definition of this term in the literature. Our objective was to establish the reference values for fetal nasal bone size throughout gestation in a local population in Brazil. METHODS: it is a cross-sectional study on 902 fetuses at 10 to 39 weeks of gestation. After having excluded fetal malformations and maternal diseases which are known to interfere with fetal growth, 625 fetuses were selected. We obtained a mid-sagittal view of the fetal profile by holding the ultrasound bean at an angle of 45º or 135º. The nasal bone size mean was calculated by using polynomial regression. The Anderson-Darling test proved the normal distribution of the measurements (p>0.05). RESULTS: of the 625 fetuses, 88.3% were from single gestations and 11.7% from multiple ones. There was a direct correlation between fetal nasal bone size and gestational age. The variability of nasal bone size became larger as gestational age increased. Minimal length of 1.0 and 4.7 mm in the first and second trimesters, respectively, were found. CONCLUSIONS: there is a direct correlation between fetal nasal bone size and gestational age. This correlation is valid either for a single gestation or a multiple one. These measurements of the fetal nasal bone will allow us to use them as a screening test for cromosomal abnormalities. This is a useful study if we consider the large miscegenation of the Brazilian population. However, further systematic and standardized approach to study the fetal nasal bone is needed to establish its real value in fetuses once classified as at high or low risk for aneuploidies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):214-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the characteristics of mammography use and the social demographic profile of women accessing public and private health care services. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was carried out in the city of Taubaté, southeast Brazil. Six hundred and forty-three women who underwent mammographic examinations in the available health care services were interviewed, 472 of them in public and 171 in private health services. The social demographic and reproductive profiles of the women interviewed and the characteristics of the mammography use, such as the proportion of the women interviewed who had been previously screened, the age when the screening began, the interval between the screenings and their frequency, were evaluated by means of the Fisher exact, Wilcoxon and chi2 tests. RESULTS: the mean age of the interviewed women was similar in both studied groups. The proportion of women previously screened 54.2 and 79.5% in public and private services, respectively as well as the age when the screening began 46.8 years (SD 10.2%) in public services and 40.2 years (SD 7.7) in private services differed significantly (p<0.01). Twenty-five percent of women older than 50 years did not follow the adequate standards of periodic screening. CONCLUSIONS: the way of accessing health services has influenced the proportion of women previously screened and the age at which this screening began, being more adequate in the private health system. Although there was a later start in the public health services, the age when the mammographic screening began was earlier than the current official recommendations. There has been a failure of compliance with mammographic screening in women older than 50 years, in both researched groups.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(3):143-150
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300002
PURPOSE: to analyze the effect of cigarette smoke on weight gain and food consumption of female pregnant rats, as well as of their offspring's weight and length at birth METHODS: Wistar rats were studied from the second day until the end of pregnancy. Fifty-one female rats were divided into three groups: Group F: 15 rats exposed to tobacco smoke (2 cigarettes/animal/day) plus air flush (10 L/min); Group Air: 18 rats exposed to air flush only (10 L/min); Group C: 18 non-exposed, non-manipulated controls. Body weight was measured every 5 days and food consumption every seven days (expressed as medium consumption per day). Offspring weight and length were measured on the first day of life. The Lavene test was used to verify the behavior of numeric variable distribution and for parametric one-way ANOVA analysis and Student's t test were used, according to the case. Results with p<0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS: the rats of Group F consumed less food per day [Group F=18.9 g (±1.2) vs Group Air=21.7 g (±1,6) vs Group C=24.2g (±1,7); (p<0,05)], gained less weight during pregnancy than the animals of the air flush group and the control group: Group F=338.9 g (±13.7) vs Group Air=352.3g (±15,9) vs Group C=366.3 g (±13.1) (p<0.05). Pups birth weight and length were significantly smaller in the smoking group when compared to controls and to the air flush group, while these last two groups did not differ: Group F=5.5 g (±0.3) vs Group Air=5.9 g (±0,5) vs Group C=5.9 g (±0.4) - (p<0,01); Group F=6.8 cm (±0.2) vs Group Air=6.9 cm (±0,2) vs Group C=6.9 cm (±0.1) - (p<0.05), respectively. CONCLUSIONS: tobacco smoke exposure reduced the weight gain and food consumption during pregnancy and reduced the offspring weight and length evaluated at birth.
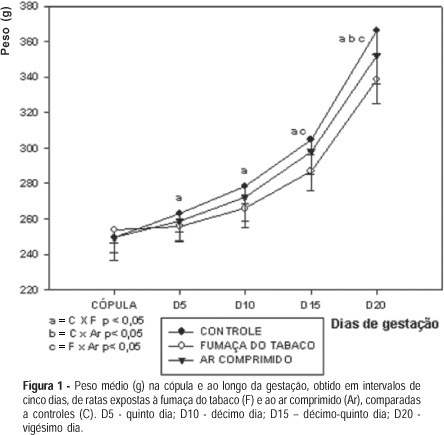
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):91-100
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficacy of the use of isoflavones in the treatment of depressive symptoms in climacteric women. METHODS: placebo-controlled, randomized double-blind experimental study with 84 climacteric women who were assisted at the Lauro Wanderley University Hospital Ambulatory, in João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. In the evaluation of the depressive symptoms the Self-evaluation questionnare of Hamilton's rating scale for depresion (QAEH-D) was used in the pretreatment visit (VT1), and in the 8th (VT2) and 16th (VT3) week after treatment. The experimental group (GExp) received soy extract with isoflavones, 120 mg per day, and the control group (GCont), placebo. The comparison of the scores of the QAEH-D between the VT1, VT2 and VT3 groups constituted the primary measure of efficacy (t test, p<0.05). Secondary analysis included the estimate of the "domino hypothesis" and the clinical and laboratory evaluation of side effects. RESULTS: there was a significant reduction of the QAEH-D scores in the GExp (VT2
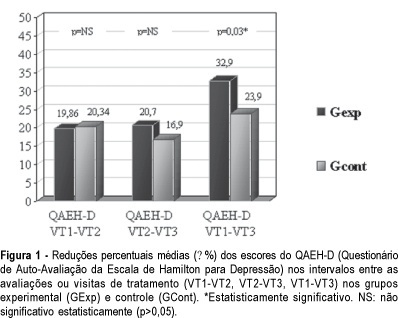
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(2):81-90
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the incidence and types of major congenital malformations (MCM) in liveborn children conceived by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). METHODS: a total of 680 liveborn children resulted from 511 couples submitted to ICSI from January, 1999 to December, 2002. Data collection of the children was performed through standardized questionnaire and clinical examination. Of the 511 couples, 366 had been contacted for a sampling of 371 gestations. Of the 680 liveborn, 520 had been evaluated, 250 of them (48.1%) through questionnaire and 270 (51.9%) through questionnaire and physical examination. Two hundred and fifty children were from singleton pregnancies and 270 from multiple pregnancies. Malformations were classified according to the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health. Only MCM were analyzed in this study. The incidence of MCM was compared with that of the general population obtained by the Latin American Collaborative Study of Congenital Malformations. The statistical analysis was performed by the c² test (level of significance p<0.05). RESULTS: of the 520 children, 15 presented MCM, resulting in an incidence of 2.9%. There was no difference in relation to the control group (p>0.05), which showed 2.6% incidence of MCM. The most frequent malformations were of cardiac origin (four isolated and two associated), corresponding to 40% of the total. The other types of MCM were: renal (three), neural tube (two), skull (one), cleft lip (one), genital (one), Down syndrome (associated with cardiac malformations) (two), and musculoskeletal (one). Six MCM occurred in children from singleton pregnancies and nine in children from multiple pregnancies. CONCLUSION: the liveborn children conceived by ICSI presented incidence of major congenital malformations (2.9%) near to the expected for the general population (2.6%). However, to establish the risks of MCM with precision it is necessary to continue the evaluation of the children conceived by ICSI.