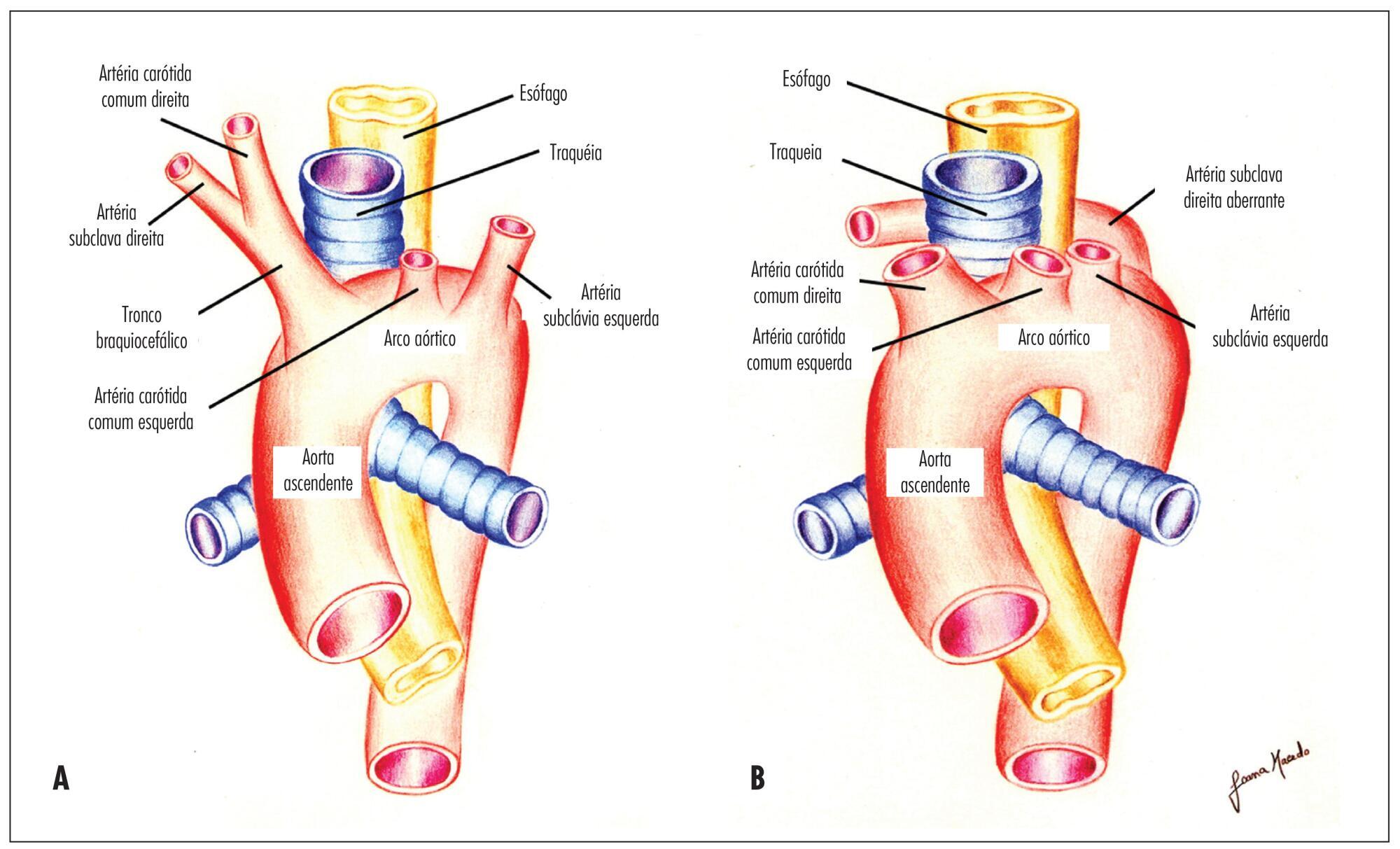
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):252-257
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005278
To determine the feasibility of evaluation of the right subclavian artery during
the first trimester ultrasound scan, as well as to describe the technique for its
evaluation and, in case of aberrant right subclavian artery (ARSA) identification,
to determine its association with chromosomal abnormalities and/or cardiac
malformations and its management.
A prospective study for evaluation of the right subclavian artery during the
first trimester ultrasound scan (crown-to-rump length between 45 and 84 mm), in
all consecutive single pregnancies, by a single examiner, using a Voluson E8
system (GE Healthcare, Zipf, Austria) with a 2 to 8 MHz RAB 4-8-D transabdominal
probe, within a short period of time (less than 2 minutes), in a general low risk
population. Color and/or power Doppler flow mapping was used to classify the right
subclavian artery as normal or aberrant. Regression analysis with the IBM SPSS
Statistics software for Windows, version 20.0 was used to determine the
significance of the association between failure to examine/classify the right
subclavian artery and both fetal crown-rump length and maternal body mass index.
Median maternal age was 30 years (range: 17-43 years) and median gestational age
at the time of evaluation of the right subclavian artery was 12 weeks (range:
11-13 weeks). The evaluation of the right subclavian artery was successful in
138/176 (78.4%) of the cases. ARSA was diagnosed in a single case (0.7%). This
fetus with ARSA also presented a hyperechogenic focus on the left cardiac
ventricle. Fetal echocardiography at 16 weeks of gestation was performed and
confirmed ARSA and the hyperechogenic focus. Amniocentesis revealed a normal 46,
XX karyotype.
ARSA can be identified during a routine first trimester ultrasound scan. Our
single ARSA case had a normal karyotype and no associated cardiac
malformations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):208-215
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005321
To describe the evolution of the prevalence of anemia in pregnant adolescents
attended at a public maternity in the city of Rio de Janeiro from 2004 to 2013.
A retrospective cross-sectional study with 628 pregnant/postpartum women divided
into 3 groups: Group A (2004-2006), Group B (2007-2010) and Group C (2013).
Information about anthropometric, clinical, sociodemographic data and obstetric
and prenatal care of adolescents was obtained from medical records of the pregnant
women. A hemoglobin concentration n<11 g/dL was considered to be anemia. Data
were analyzed statistically by the chi-square test, Student's t-test and ANOVA,
and the post hoc Tukey test.
The prevalence of gestational anemia over the years was 43% (GA=138), 36% (GB=80)
and 47.1% (GC=40) and the overall prevalence for the 2004-2013 period was 41.1%
(n=258). The occurrence of anemic pregnant women increased with the progression of
pregnancy; however, in the 3rd quarter there was a decrease in the prevalence of
anemia in GB (29.3%) compared to GA (38.7%; p=0.04). Factors associated with
anemia were number of prenatal visits and prenatal nutritional assistance, place
of residence, pre-pregnancy BMI, and gestational weight gain.
The results showed that the prevalence of anemia among pregnant adolescents seen
at a public maternity is high. There was no reduction of anemia during the study
period and other factors in addition to iron deficiency were involved in the
genesis of anemia in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):203-207
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005293
To determine the frequency of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in the placenta, in the
colostrum and in the umbilical cord blood of parturient women and their newborns
assisted at the Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the University Hospital of
Rio Grande (RS), Brazil.
Biopsies were collected from 150 placentas on the maternal side, 150 on the fetal
side, 138 samples of umbilical cord blood and 118 of the colostrum. The placenta
biopsies were collected from the central and peripheral portions. DNA was
extracted according to the manufacturer's protocol and to a reference found in the
literature. HPV was detected by the nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR-Nested)
using primers MY09/11 and GP5/GP6. Genotyping was performed by direct sequencing.
The participants responded to a self-applied questionnaire with demographic and
clinical data, in order to characterize the sample.
HPV was detected in 4% (6/150) of cases on the mother's side of the placentas, in
3.3% (5/150) on the fetal side, in 2.2% (3/138) in umbilical cord blood and in
0.84% (1/118) in colostrum samples. The vertical transmission rate was 50%. HPV-6
was the low-risk genotype found (60%) and the high-risk genotypes were HPV-16 and
HPV-18 (20% each).
These results suggest that HPV can infect the placenta, the colostrum and the
umbilical cord blood.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):233-240
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005333
To assess the effect of tibolone on mammary tissue of castrated rats over 3
different periods of time.
Sixty virgin female Wistar rats were submitted to oophorectomy. Twenty-one days
after surgery, with hypoestrogenism confirmed, the experimental rats were randomly
assigned to six groups: Tibolone 1 (n=10) received tibolone 1 mg/day for 23 days,
tibolone 2 (n=10) for 59 days and tibolone 3 (n=10) for 118 days. The groups
control 1 (n=8), control 2 (n=7) and control 2 (n=10) received distilled water for
23, 59 and 118 days, respectively. After treatment, all six pairs of mammary
glands were removed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) for histological
analysis after euthanasia. The histological parameters evaluated were: epithelial
cell proliferation and secretory activity. The variables were analyzed
statistically, with the level of significance set at 0.05.
Histological changes were observed in 20/55 rats, mild epithelial hyperplasia in
7/55, moderate epithelial hyperplasia in 5/55, alveolar-nodular hyperplasia in
7/55, atypia without epithelial proliferation in 1/55, and no cases of severe
epithelial hyperplasia were found. Secretory activity was observed in 31/55 rats.
The secretory activity was significantly higher in the tibolone groups compared to
control at all the time points assessed (p=0,001). The histological changes were
did not show significance when the control and tibolone groups were compared. The
time of exposure to tibolone did not show significance when the three different
periods of evaluation were compared.
No relation between histological modification and tibolone treatment was verified
after short-, medium- and long-term treatment.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):229-232
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005295
To compare the frequency of an ASCUS Pap Smear result in pregnant and
non-pregnant women, stratified by age group.
We analyzed the results of 1,336,180 cytopathologyc exams of Pap smears performed
between 2000 and 2009 (ten years) with the purpose of screening for cervical
carcinoma. Comparisons were made between pregnant and non-pregnant women, and the
sample was stratified into three age groups (20-24, 25-29 and 30-34 years). The
χ2 test was used and the magnitude of association was determined by
the by Odds Ratio (OR) with the 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
A Total of 447,489 samples were excluded on the basis of the criteria adopted,
for a total final sample of 37,137 pregnant women and 851,554 non-pregnant women.
An ASCUS result was detected in 1.2% of cases, with a significant difference
between pregnant and non-pregnant women in the age groups of 20-24 years (OR=0.85;
95%CI 0.75-0.97) and 25-29 years (OR=0.78; 95%CI 0.63-0.96). There was no
difference in the group between 30-34 years (OR=0.76; 95%CI 0.57-1.03).
This study suggested that non-pregnant women have a higher frequency of ASCUS,
most evident in the age group of 20 to 29 years. The collection of cervical cancer
screening should not be a compulsory part of the prenatal routine.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):222-228
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005183
To estimate the prevalence of bacterial vaginosis (BV), candidiasis and
trichomoniasis and compare the findings of physical examination of the vaginal
secretion with the microbiological diagnosis obtained by cytology study of a
vaginal smear using the Papanicolaou method.
A cross-sectional study of 302 women aged 20 to 87 years, interviewed and
submitted to a gynecology test for the evaluation of vaginal secretion and
collection of a cytology smear, from June 2012 to May 2013. Sensitivity analyses
were carried out and specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative
predictive value (NPV) with their respective 95%CI were determined to assess the
accuracy of the characteristics of vaginal secretion in relation to the
microbiological diagnosis of the cytology smear . The kappa index (k) was used to
assess the degree of agreement between the clinical features of vaginal secretion
and the microbiological findings obtained by cytology.
The prevalence of BV, candidiasis and trichomoniasis was 25.5, 9.3 and 2.0%,
respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of the clinical
characteristics of vaginal secretion for the cytological diagnosis of BV were 74,
78.6, 54.3 and 89.9%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and the NPV
of the clinical characteristics of vaginal secretion for the cytological diagnosis
of candidiasis were 46.4, 86.2, 25.5 and 94%, respectively. The correlation
between the clinical evaluation of vaginal secretion and the microbiological
diagnosis of BV, candidiasis and trichomoniasis, assessed by the kappa index, was
0.47, 0.23 and 0.28, respectively.
The most common cause of abnormal vaginal secretion was BV. The clinical
evaluation of vaginal secretion presented amoderate to weak agreement with the
microbiological diagnosis, indicating the need for complementary investigation of
the clinical findings of abnormal vaginal secretion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):178-185
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005184
To conduct a comparative study between two groups of women (HIV positive and negative) analyzing: the prevalence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical HPV infection; viral risk and relationship with development of CIN; and sociodemographic and behavioral parameters that influence cervical HPV infection and the development of CIN.
A cross-sectional study in which 202 HIV-positive women and 164 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of CIN and 171 HIV-positive women and 160 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of cervical HPV infection. The following procedures were performed on the occasion of each medical visit: collection of cervical samples for cytology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect HPV DNA; colposcopy; standardized questionnaire to collect demographic and behavioral data; and biopsy of all colposcopic changes. Histopathology was the gold standard for the diagnosis of CIN.
The prevalence of CIN was 2.4 and 15.3% (p<0.001) and the prevalence of cervical HPV infection was 37.1 and 55.5% (p=0.002), respectively, among HIV-negative and -positive women. HIV-positive women had a higher risk of HPV infection (35.7 and 23.6%) (p=0.02). HPV 16 was the most prevalent virus type, occurring in 11.3 and 10.2% of HIV-positive and negative women and was also more prevalent among women presenting CIN in both groups. Factors associated fwith the development of CIN were: HIV infection (HT=4.64; 95%CI 2.23-9.65), age (HT=0.95; 95%CI 0.93-0.98 for each year of life) and marital status(HT=0.49; 95%CI 0.30-0.80). Associated factors for HPV infection were: HIV presence (HT=2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.17), greater number of sexual partners (HT=1.87; 95%CI 1.23-2.84), age (HT=0.97; 95%CI 0.95-0.99 for each year of life) and marital status (HT=0.65; 95%CI 0.42-1.0 for stable union/widows).
The prevalence of CIN and cervical HPV infection was higher in HIV-positive women, who also presented a higher risk of HPV infections and multiple viral types. Type 16 was predominant in both groups and in women with CIN. Older women and women with stable union/widows were less likely to acquire cervical HPV infection and CIN.
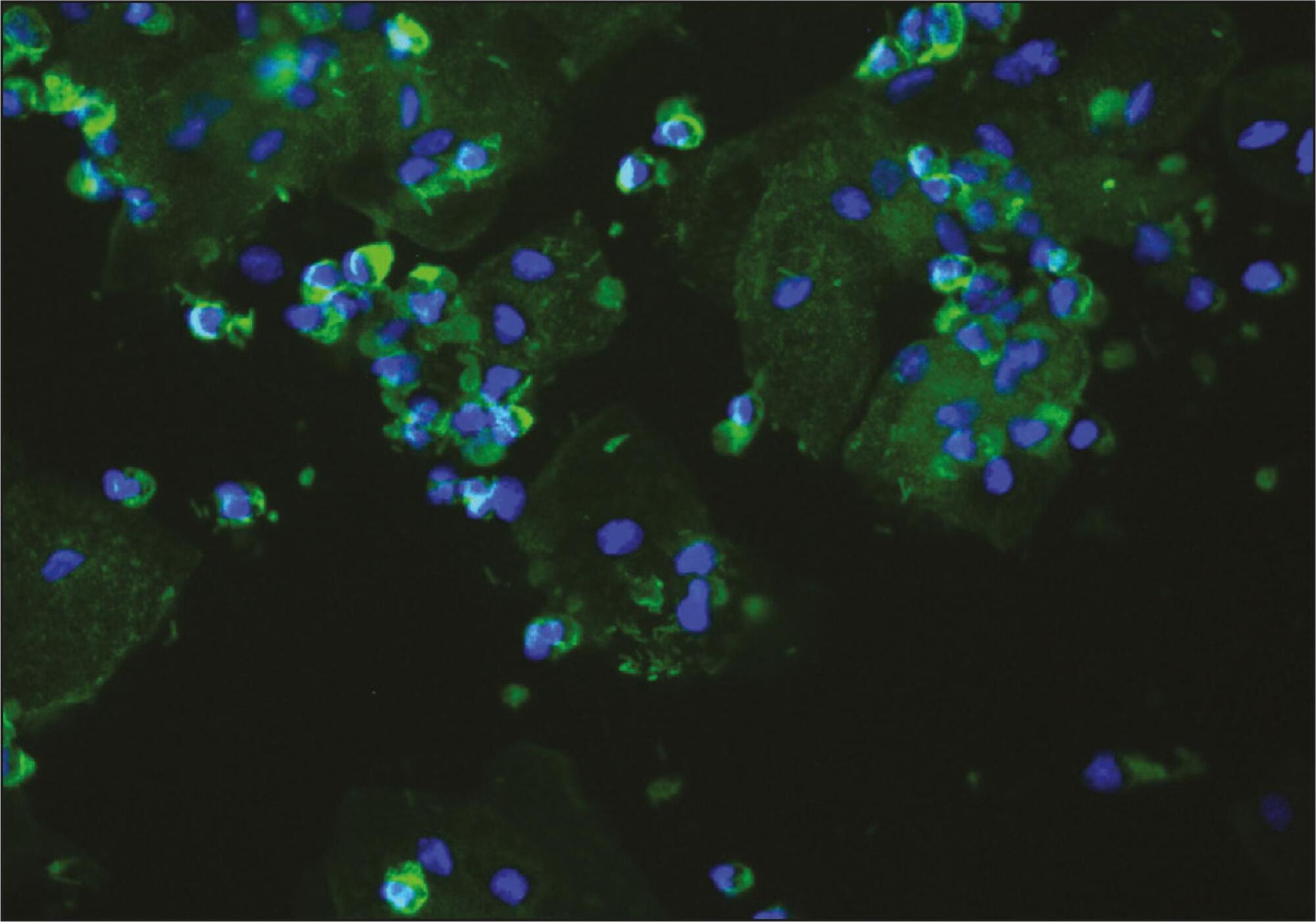
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):172-177
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005238
To evaluate the presence of podocyturia in chronic hypertensive pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy and its possible association with renal disease.
This was an observational study of a convenience sample of 38 chronic hypertensive pregnant women. The podocytes were labeled by the indirect immunofluorescence technique with anti-podocin and diamidino-phenylindole (DAPI). The count was made on 30 random fields analyzed and corrected according to urinary creatinine (podocytes/mg creatinine). The patients were assigned to two groups: NG (normal glomerular function), up to 100 podocytes, and GP (probable glomerulopathy), more than 100 podocytes. Urinary creatinine was measured by the alkaline picrate method. The variables analyzed were body mass index, gestational age, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure at the time of sample collection. Data were analyzed using the SPSS - version 16.0 (IBM - USA). Statistical analysis was performed by the χ2 test, and significant differences were considered when p<0.05.
The median podocyte count was 20.3 (0.0-98.1) for group GN, and 176.9 (109.1-490.6) for GP. The mean body mass index was 30.2 kg/m2 (SD=5.6), mean gestational age was 35.1 weeks (SD=2.5), median systolic blood pressure was 130.0 mmHg (100.0-160.0) and median diastolic blood pressure was 80.0 mmHg (60.0-110.0). There was no significant correlation between podocyturia and body mass index (p=0.305), gestational age (p=0.392), systolic blood pressure (p=0.540) or diastolic blood pressure (p=0.540).
In this study, there was no podocyturia pattern consistent with the presence of active renal disease, although some of the women studied (15.8%) exhibited a significant loss. We believe that it is premature to recommend the inclusion of the determination of podocyturia in routine prenatal clinical practice in chronically hypertensive pregnant women.