Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):549-555
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100006
PURPOSE: the purpose of this research was to evaluate the morphological aspects and vasculature of the corpus luteum (CL) based on ultrasound parameters during early pregnancy and to assess their relationship with early pregnancy loss. METHODS: this was a prospective cohort study of 90 pregnant patients between 6 and 8 weeks plus 6 days weeks of gestation. We included women at low risk, without acute or chronic systemic disease and with spontaneous conception. Exclusion criteria: use of drugs or smoking, drugs inducing ovulation, history of more than one abortion, no heartbeat visible in the embryo and impossibility of visualization of the corpus luteum. The size, volume, morphological aspects, resistive index, and peak systolic velocity of the corpus luteum were measured by transvaginal sonography. RESULTS: ninety patients were included in the study. Maternal age ranged from 15 to 41 years (mean 28.6±5.8 years). The corpus luteum could be visualized in 87 patients (96.7%), 79 patients had normal pregnancies (90.1%), whereas spontaneous losses occurred in 8 cases (9.9%). In a comparison of the survivors and losses, there was no difference in mean CL diameter (21.8 versus 20.0 mm; p=0.108, Mann-Whitney test), mean CL volume (4.2 versus 3.0 cm³; p=0.076, Mann-Whitney test), mean resistive index (0.55 versus 0,58; p=0.220, Mann-Whitney test), peak systolic velocity (15 versus 15 cm/s; p=0.757, Mann-Whitney test). There was a positive relation between maternal age and resistive index. CONCLUSIONS: no apparent correlation was found between the morphological and vascular aspects of the corpus luteum in early normal pregnancies and first-trimester pregnancy losses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):541-548
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100005
PURPOSE: to reassess the adrenal function of patients with PCOS after the introduction of the Rotterdam's criteria. METHODS: descriptive and cross-sectional study including 53 patients 26±5.1 years old. Glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, lipids, estradiol, progesterone, 17-OHP4, DHEAS, FSH, LH, TSH, PRL, androstenedione, free thyroxine, insulin, total testosterone, SHBG, and free androgen index were measured. Insulin resistance was considered to be present with a homeostatic model assessment index >2.8. The adrenal response to cortrosyn was assessed by the hormonal rise observed at 60 minutes, and by the area under the response curve. RESULTS: biochemical hyperandrogenism was found in 43 of 53 eligible patients (81.1%). Thirty-three women had adrenal hyperandrogenism (62.2%). The weight of these 33 women, aging 25.1±5.0 years, was 74.9±14.9 kg, BMI was 28.8±6.0 and the waist/hip ratio was 0.8±0.1. DHEAS was >6.7 nmol/L in 13 (39.4%) and androstenendione was >8.7 nmol/L in 31 (93.9%). The increments in 17-OHP4, cortisol, A, and progesterone were 163%, 153%, 32%, and 79%, respectively. The homeostatic insulin resistance model was >2.8 in 14 (42.4%). Insulin and estradiol were not correlated with cortisol or androgens. CONCLUSIONS: the use of multiple endocrine parameters showed a high prevalence of biochemical hyperandrogenism in patients with PCOS. Two thirds of the patients had adrenal hyperandrogenism, and estradiol and insulin did not influence adrenal secretion.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):530-535
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100003
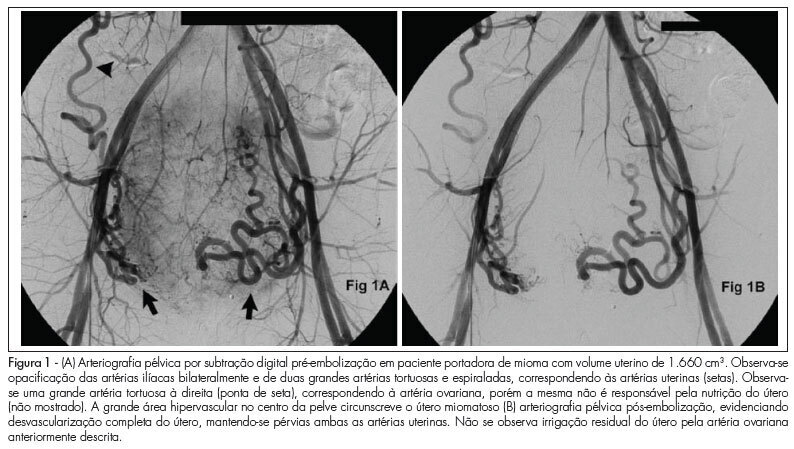
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effectiveness of uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) in patients with giant fibroids, with regard to both clinical outcomes and size reduction. METHODS: twenty-six patients with a mean age of 36.5 years, carrying symptomatic fibroids with a volume over 1,000 cm³, were referred for UFE. All patients had indication for percutaneous treatment. The procedures were performed under epidural anesthesia and sedation, using an institutional protocol. By unilateral femoral access, selective catheterization of uterine arteries and infusion of calibrated microspheres through microcatheter were carried out. Clinical evaluation was performed by means of regular outpatient gynecology consultation. All patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before the procedure and 15 patients underwent control MRI after 6 months. RESULTS: technical success was 100%. There was no complication related to the procedures. Mean uterine volume of the 15 patients studied was 1,401 cm³ before embolization (min 1,045 cm³, max 2,137 cm³) and 799 cm³ after 6 months (525 cm³ min, max. 1,604 cm³), resulting in a total reduction of 42.9%. Clinical improvement was observed in 25 of 26 patients. One woman with uterine volume of 1,098 cm³ who developed necrosis and partial fibroid expulsion underwent myomectomy. Another patient was submitted to myomectomy six months after the procedure because she wanted to become pregnant, despite partial fibroid size reduction. One patient with a uterine volume of 2,201 cm³ required a second intervention to achieve an adequate angiographic result. No patient underwent hysterectomy. On average, 9.2 microsphere syringes were used per patient. CONCLUSION: embolization of giant uterine fibroids is a feasible procedure with acceptable clinical and radiological outcomes. It can be considered an option for patients who desire to preserve the uterus, and it may serve as adjuvant therapy for high-risk myomectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):525-529
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the characteristics of the menstrual cycle and to identify the occurrence of ovulation in nulliparous young women with sickle cell anemia (SCA). METHODS: we conducted a case-control study including 26 nulliparous women of reproductive age, divided into two groups: "cases", consisting of 13 women with SCA, and "Control" Group, consisting of 13 healthy women with the same interval since menarche. The characteristics of the menstrual cycle were reported by the participants, who were also submitted to measurements of serum progesterone, basal body temperature curves and transabdominal ultrasound in three consecutive cycles (total: 78 cycles) in order to identify the occurrence of ovulation. The results were compared between groups using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney or Kruskal Wallis tests, and the differences were considered significant when p-value < 0.05. RESULTS: no significant difference was found in mean chronological age between the two groups (p = 0.2) in the pattern of the menstrual cycle when duration of flow (p = 0.4) and interval between cycles (p = 0.3) were compared. There was no difference between groups in age at menarche (p = 0.05). Mean hemoglobin value was 8.4 g/dL (± 0.9) in the group of women with SCA and 12.6 g/dL (± 0.8) in the control group (p < 0.01). The frequency of ovulatory cycles was similar for cases (76.9%) and controls (92.3%) (p = 0.5), with a predominance of individuals with three ovulatory cycles in the control group (84.6%) compared to 23.1% in the case group (p = 0.04). CONCLUSION: the findings justify the need for effective guidance for patients with SCA regarding sexual activity, the possibility of pregnancy and the alternatives for contraception.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(11):563-569
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001100008
PURPOSE: to evaluate the evolution of adequacy of the care process among pregnant users of the Brazilian Single Health System (SUS, acronym in Portuguese) and to consolidate a methodology for monitoring the prenatal care. METHODS: this is a multiple time series study with auditing of prenatal cards of pregnant women who were attended for prenatal care in a city of the Brazilian Southeast (Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais) in the initial semesters of 2002 and 2004 (370 and 1,200 cards, respectively) and gave birth using SUS services in term pregnancies (p < 0.05). A three complementary level sequence was respected: utilization of prenatal care (beginning and number of visits) at level 1; utilization of prenatal care and obligatory clinical-obstetric procedures during prenatal visits (assessment of blood pressure (BP), weight, uterine fundal height (FH), gestational age (GA), fetal heart rate (FHR) and fetal presentation) at level 2; and utilization of prenatal care, obligatory clinical-obstetric procedures and basic laboratory tests, according to the Humanization Program of Prenatal Care and Birth (PHPN, acronym in Portuguese) (ABO/Rh, hemoglobin/hematocrit (Hb/Htc), VDRL, glycemia and urinalisys) at level 3. RESULTS: it was confirmed the high prenatal care coverage (99%), the increased mean number of visits per pregnant woman (6.4 versus 7.2%) and the decreased gestational age at the time of the first visit (17.4 versus 15.7 weeks). The proper registration of procedures and exams (exceptions: fetal presentation and blood typing) has significantly increased: BP (77.8 versus 83.9%); weight (75.4 versus 83.5%); FH (72.7 versus 81.3%); GA (58.1 versus 71.5%); FHR (79.5 versus 86.7%); Hb/Htc (14.9 versus 29%), VDRL (11.1 versus 20.7%), glycemia (16.5 versus 29%) and urinalisys (13.8 versus 29.8%). As a result, there was significant (p < 0.001) improvement of the adequacy between 2002 and 2004: 27.6 versus 44.8% (level 1); 7.8 versus 15.4% (level 2); 1.1 versus 4.5% (level 3). This trend was also noted in care provided by the majority of the municipal services/teams. CONCLUSIONS: the persistence of low adequacy, despite good coverage and PHPN implementation, confirmed the need to increase health managers, professionals and users' compliance with the rules and routines of care, including the institutionalization of a monitoring program of prenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(9):454-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900007
PURPOSE: to evaluate and compare the effects of body mass index (BMI) on the severity of female urinary incontinence (UI) using the quality of life questionnaire King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ), variables of urodynamic studies and the medical history taken. METHODS: cross-sectional clinical study. We selected 65 patients with stress urinary incontinence (SUI) who were divided into three groups: Group I (BMI: 18-25 kg/m²), Group II (BMI: 25-30 kg/m²) and Group III (BMI>30 kg/m²). The KHQ domains were compared between these groups. In addition, some clinical history urodynamic data (presence of nocturia, enuresis, urgency and urge incontinence) were also related to BMI by calculating the Odds Ratio (OR). The BMI in the presence and absence of non-inhibited detrusor contractions and Valsalva leak point pressure (VLPP) <60 or > 60 cmH2O were evaluated. Finally, the correlation between BMI and the nine KHQ domains has been tested in order to detect some association. RESULTS: the KHQ did not record deterioration of quality of life in women with UI with increasing BMI in any of its areas. The OR for the presence of enuresis in relation to a BMI was 1.003 [CI: 0.897-1.121], p=0.962. The OR for nocturia was 1.049 [CI: 0.933-1.18], p=.425. The OR for urgency was 0.975 [CI: 0.826-1.151], p=0.762, and the OR for incontinence was 0.978 [CI: 0.85-1.126], p=0.76. We studied the BMI in patients with and without non-inhibited detrusor contractions and detected medians of 26.4±4.8 and 28.3±5.7 kg/m², respectively (p=0.6). Similarly, the median BMI values for the groups with VLPP <60 and >60 cmH2O were 29.6±4.1 and 27.7±5.7 kg/m², respectively (p=0.2). Finally, we failed to demonstrate an association between BMI and any of the nine KHQ domains by means of the Spearman correlation. CONCLUSION: there was no association of KHQ scores with BMI. There was also no correlation between the parameters of clinical history and of the urodynamic study with BMI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(9):447-453
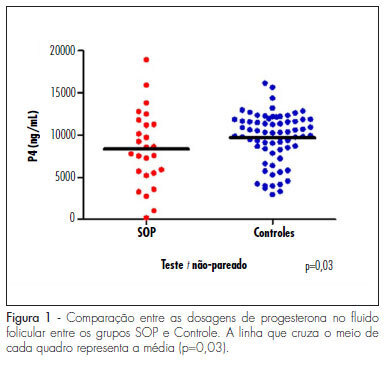
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000900006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the concentration of steroid hormones in follicular fluid (FF) of small (10-14 mm) and large (> 18 mm) follicles of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) submitted to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation (COH) and in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. METHODS: a case-control study was conducted on 13 infertile women with PCOS (17 cycles) and 31 infertile women due to male factor - Control Group (31 cycles). FF was aspirated individually and divided into four groups: G1 (FF of small follicles of the Control Group), G2 (FF of small follicles of the PCOS group), G3 (FF of large follicles of the Control Group) and G4 (FF of large follicles of the PCOS group). Estrogen, progesterone and β-hCG were determined by chemiluminescence, and testosterone and androstenedione by radioimmunoassay. The unpaired t-test was used to compare the hormone determinations in the FF of the PCOS and Control Groups, and the four groups were compared by ANOVA. Fisher's exact test was used to compare the pregnancy rates. RESULTS: the small follicles of the two groups had lower progesterone levels (8,435±3,305 ng/mL) than large follicles (10,280±3,475 ng/mL), p-value <0.01. The progesterone levels of all follicles of group PCOS (8,095±4,151 ng/mL) were lower than Control (9,824±3,128 ng/mL), p-value =0.03. Testosterone differed between G1 (326.6±124.4 ng/dL) and G3 (205.8±98.91 ng/dL), p-value <0.001, and between G3 (205.8±98.91 ng/dL) and G4 (351.10±122.1ng/dL), p-value <0.001. Small follicles had higher testosterone levels (508.9±266 ng/dL) than large follicles (245.10±123 ng/dL), p-value <0.0001. The pregnancy rates did not differ between the PCOS (5/13, 38.5%) and the Control groups (9/31, 40.9%), p-value =072. CONCLUSIONS: women with PCOS had high testosterone concentrations in the FF, regardless of the stage of follicle development, and reduced progesterone levels, suggesting that paracrine factors may inhibit the secretion of the latter by follicular cells. The pregnancy rates showed that treatment with COH and IVF is a good option for women with infertility secondary to PCOS.