Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(12):395-400
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001200004
PURPOSE: To assess the prevalence of Streptococcus agalactiae, a Group B streptococcus, in pregnant women, and their possible risk factors, as well as the impact of perinatal colonization and antimicrobial susceptibility. METHODS: We evaluated 213 pregnant women from 20 weeks of gestation, regardless of risk factors, attending a tertiary teaching hospital. The technique used was a single sterile swab to collect secretions from the vaginal and perianal regions. The newly obtained samples were stored in Stuart transport medium and taken to the laboratory, where they were inoculated in Todd-Hewitt selective medium supplemented with Gentamicin (8 ug/mL) and nalidixic acid (15 ug/mL), with subsequent cultivation on blood agar plates. The materials were tested with Gram, catalase with hydrogen peroxide and CAMP (Christie, Atkins, Munch-Petersen), and results were serologically confirmed with the Streptococcal Grouping Kit, Oxoid®. The positive samples were tested for antimicrobial susceptibility. We also assessed socioeconomic, reproductive, clinical, and obstetric variables, and newborn care. Statistical analysis was performed with Epi-Info 6.04. RESULTS: The prevalence of colonization obtained by field tests was 9.8% by CAMP test, but only 4.2% by serology. The only protective factor was white skin color (p=0.01, 0.45>OR>0.94, 95%CI). There was no difference in prevalence of Group B streptococcus regarding other reproductive and obstetric variables. Infection occurred in only one of the newborns from colonized mothers; although it was revealed infection with Pseudomonas spp. High resistance to ampicillin (4/9), cephalothin (4/9), penicillin (4/9), erythromycin (3/9), clindamycin (7/9), and cloramphenicol (1/9) was detected. CONCLUSIONS: The infection rate was lower than that found in other studies, although a high rate of resistance to antibiotics commonly used for treatment was detected. Since there are no studies on the prevalence of Group B streptococcus in Ceará, we cannot perform a comparative analysis of the population, and further studies are needed with geographically similar groups to validate these results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(12):381-387
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001200002
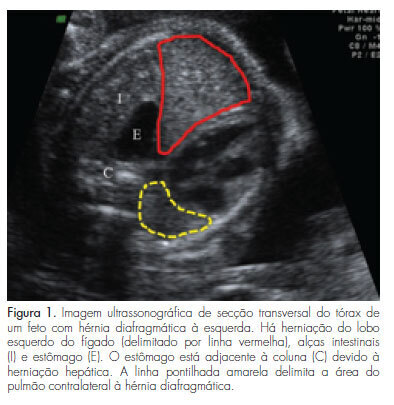
PURPOSE: To compare postnatal survival to hospital discharge of fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia, who underwent tracheal occlusion, with that of nonrandomized contemporaneous controls. METHODS: Experimental nonrandomized controlled study, performed from April 2007 to September 2011. Fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia with liver herniation into the chest and lung area-to-head circumference ratio <1.0, who underwent tracheal occlusion (study group) or expectant management (non-randomized contemporaneous controls), were compared in terms of lung area-to-head circumference ratio and observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio) at the time of diagnosis, gestational age at birth, and survival to hospital discharge. Modifications in lung area-to-head circumference ratio and o/e lung area-to-head circumference ratio after tracheal occlusion were also analyzed. Fisher's exact test, Mann-Whitney's or Wilcoxon's tests were used for the comparisons. RESULTS: There were no significant differences between the Study Group (TO=28) and Controls (n=13) in terms of the lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p=0.709) and the observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p=0.5) at the time of diagnosis and gestational age at birth (p=0.146). The survival to hospital discharge was higher (p=0.012) in the tracheal occlusion group (10/28=35.7%) than in controls (0/13=0.0%). There was a significant increase in lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p<0.001) and observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio (p<0.001) between the diagnosis of the congenital diaphragmatic hernia [lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 0.80 (0.40-0.94); observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 27.0 (15.3-45.0)], and the day before retrieval of the balloon [lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 1.2 (0.50-1.80); observed/expected lung area-to-head circumference ratio: 40.0 (17.5-60.0)]. CONCLUSIONS: There was a significant improvement in the survival rate to hospital discharge of fetuses with severe isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia, who underwent tracheal occlusion in comparison to nonrandomized contemporaneous controls.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):361-366
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100007
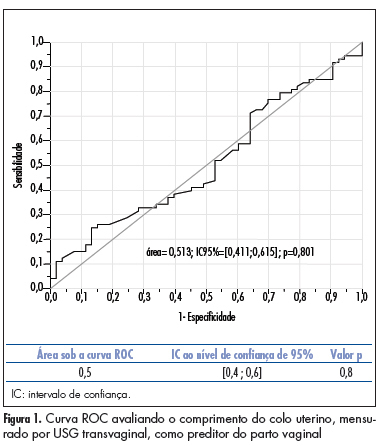
PURPOSE: to compare the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasonographic measurement of the uterine cervix with Bishop’s score for the prediction of vaginal delivery after labor induction, with 25 mcg of misoprostol. METHODS: a prospective study for the validation of a diagnostic test was conducted on 126 pregnant women with indication for labor induction. The patients were evaluated by Bishop’s score and transvaginal ultrasonography for cervical measurement. They also undergone obstetric transabdominal ultrasound to evaluate static and fetal weight, as well as the amniotic fluid index, and basal cardiotocography for the evaluation of fetal vitality. Labor was induced with vaginal and sublingual misoprostol, one of the tablets containing 25 mcg of the drug and the other only placebo. The tablets were administered every six hours, with a maximum number of eight. Frequency tables were obtained, and measures of central tendency and dispersion were calculated. ROC curves were constructed for the evaluation of Bishop’s score and ultrasonographic measurement of the uterine cervix for the prediction of vaginal delivery. RESULTS: the area under the ROC curve was 0.5 (p=0.8) for the ultrasonographic measurement of the uterine cervix, and 0.6 (p=0.02) for Bishop’s score (cut point ³4). Bishop’s score had a sensitivity of 56.2% and specificity of 67.9% for prediction of vaginal delivery, with a positive likelihood ratio of 1.75 and a negative one of 0.65. CONCLUSIONS: ultrasonographic measurement of the uterine cervix was not a good predictor of evolution to vaginal delivery among patients with misoprostol-induced labor. Bishop’s score was a better predictor of vaginal delivery under these circumstances.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):354-360
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100006
PURPOSE: To analyze the association of pregnancy in adolescence and prematurity. METHODS: The study included all the patients who delivered at a teaching hospital in Maranhão State, from July to December 2006. The patients were divided into two groups: adolescents (10 to 19 years old) and adults (20 to 34 years old). The variables studied were: educational level, marital status, number of prenatal visits, gestational age at the onset of prenatal care, duration of gestation, delivery route and birth weight. Statistical analysis was performed using the Epi-Info software, version 3.4.1, and the associations between variables were analyzed by the odds ratio (OR), with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Models of logistic regression were also used. The level of significance adopted was 0.05. RESULTS: The study evaluated 1,978 patients. The frequency of deliveries in adolescents was 25.4%. This group presented low educational level, no mates, low number of prenatal visits, late onset of prenatal care, low birth weight and prematurity. In the analysis of prematurity as the outcome variable, there was a clear association with low number of prenatal visits (OR 3.0; 95%CI 2.2-4.0) and late onset of prenatal care (OR 1.9; 95%CI 1.3-2.6) and low educational level (OR 1.9; 95%CI 1.4-2.5) related to adolescence (OR 1.5; 95%CI 1.1-1.9). The incidence of caesarean delivery was significantly lower among adolescents (33.3%) than among adults (49.4%), with a lower association with pre-eclampsia and cephalo-pelvic disproportion. CONCLUSIONS: Pregnancy in adolescence was associated with late onset of prenatal care and low number of visits, as well as low educational level, low birth weight, prematurity and a lower incidence of cephalo-pelvic disproportion and pre-eclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):348-353
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100005
PURPOSE: To describe the obstetric outcome of women with overweight/obesity treated at the prenatal care clinic of a public maternity hospital in Rio de Janeiro. METHODS: A descriptive cross-sectional study which investigated 433 women (³20 years-old, without any chronic diseases) and their newborns treated at public hospitals in Rio de Janeiro. Information was collected from medical records and through interviews. The characteristics of mothers and newborns evaluated were divided into maternal (social habits, anthropometric measurements and clinical, obstetric, and prenatal care) and newborn groups (birth conditions). Data regarding the categories of nutritional status were analyzed using the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). RESULTS: The prevalence of overweight/obesity in this sample was 24.5% (n=106). There was an association between inadequate weight gain and the prevalence of overweight/obesity (OR 2.7, 95%CI 1.5-4.9, p<0.05). Overweight/obese women had an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR 3.3, 95%CI 1.1--9.9, p=0.03). Regarding birth conditions, mean birth weight was 3291.3 g (±455.2), with rates of low birth weight of 4.7% (n=5) and rates of macrosomia of 2.8% (n=3). CONCLUSIONS: There was an alarming prevalence of inadequate nutritional status before and during pregnancy, which may be associated with increased risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality. This suggests the need for nutritional monitoring of these pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):341-347
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100004
PURPOSE: To evaluate the pregnancy rate in intrauterine insemination (IUI), and to determine possible prognostic factors of successful pregnancy. METHODS: A retrospective study of IUI cycles performed in the Reproductive Medicine Unit of Vila Nova de Gaia Hospital, between January 2007 and July 2010. The IUI cycles were preceded by ovarian stimulation and monitored by vaginal ultrasound. Clinical pregnancy rates were analyzed according to the woman’s age, type and duration of infertility, spermatozoa parameters assessed in the spermogram, number of mature follicles and the drug used for ovarian stimulation. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS17), with the level of significance set at p<0.05. RESULTS: The study comprised 139 couples who underwent 220 IUI cycles. The absolute pregnancy rate per cycle was 18.6%. Of the 41 clinical pregnancies, 5 were twin pregnancies (12.1%). The pregnancy rate was higher at ages <30 years (28.5 vs 15.7%; p=0.024), duration of infertility <3 years (23.8 vs 13.9%; p=0.05), normal sperm motility (23.2 vs 10.3%; p=0.01) and with two follicles at the time of insemination (27.7 vs 14.2% for monofollicular growth; p=0.030). The pregnancy rates obtained with clomiphene citrate, gonadotropins and combined clomiphene citrate/gonadotropin were 13.0, 26.1 and 28.6%, respectively, with a statistically significant difference in clinical pregnancy rate between clomiphene citrate and gonadotropin. CONCLUSIONS: IUI remains a natural starting point for conveniently selected couples with infertility. Younger age and normal sperm motility are good prognostic factors. Gonadotrophin stimulation seems to be an important tool for improving the pregnancy rate of IUI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):334-340
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100003
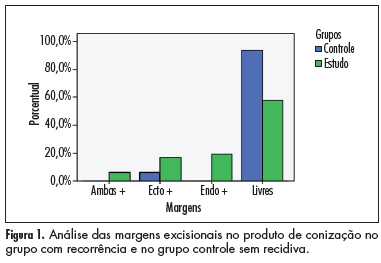
PURPOSE: To evaluate the ability of various factors related to the conization process in cytological/histological cervical intraepithelial neoplasias (CIN), after therapeutic conization. METHODS: A retrospective review was conducted of patients who had undergone conization due to CIN 2 and 3, from January 1999 to January 2006. They were divided into two groups: case group (residual disease or recurrence) and control group (without residual disease or recurrence), during 18 months of follow up. Univariate and multivariate analysis were used to define the predictive factors of disease recurrence. The c2 test or Fisher exact test was used for statistical analysis, with the level of significance set at p£0.05. RESULTS: Forty-eight patients showed recurrence/progression of CIN (case group) and 65 showed no recurrence/progression of disease (control group). Age and parity were similar in the two groups, as determined by calculation of the mean and standard deviation. There was no difference in smoking habits or in the use of contraceptive methods. The recurrence rate was 14.6%. Only conization positive margins were predictors of recurrence/progression (p<0.001). The conization techinique, the surgeon, CIN grade, gland involvement, and size of the uterine volume removed were not related to the evolution of disease after surgery. CONCLUSION: The recurrence of CIN 2 and 3 was related to positive margins in the product of conization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):328-333
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100002
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of Chlamydia and gonorrhea in a sample of women from Curitiba. METHODS: this was a cross-sectional study with a sample of sexually active non-pregnant women aged between 16 and 23 years-old, with an intact uterus, with up to four sexual partners, without evidence of fever or purulent cervicitis, submitted to pelvic examination and PCR-based urine- testing for Chlamydia and gonorrhea. Exclusion criteria included: vaccination for HPV, vaccination history for the past 21 days, previous abnormal cytology, history of genital warts, splenectomy, immune disorders, and use of immunosuppressive drugs. An interview regarding sociodemographic and obstetric data and gynecological risk behavior for sexual transmitted diseases was applied. For statistical analysis, we used the c2 or Fisher’s exact test to assess the association between variables. RESULTS: the prevalence of Chlamydia and gonorrhea infection in the study group was 10.7 and 1.5%, respectively, and the rate of coinfection was 0.9%. No correlation was found between the age range of the volunteers, the onset of sexual activity, the number of sexual partners and of new sexual partners in the last six months, and the presence of Chlamydia or gonorrhea. In women who had vaginal discharge or ectropion, the prevalence of Chlamydia infection was two times higher than in those without such signs. CONCLUSIONS: the results of this study were similar to national studies using PCR in urine samples for the detection of Chlamydia and gonorrhea in samples of non-pregnant women of the same age groups and with the same background. Since the volunteers with more than four sexual partners and those who had purulent endocervicitis were excluded, it is believed that the prevalence of Chlamydia and gonorrhea infection could have been greater in this population.