Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):163-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400040002
To assess the prevalence of Climacteric Syndrome (CS) in women from a municipality of Northeastern Brazil which is less developed socioeconomically.
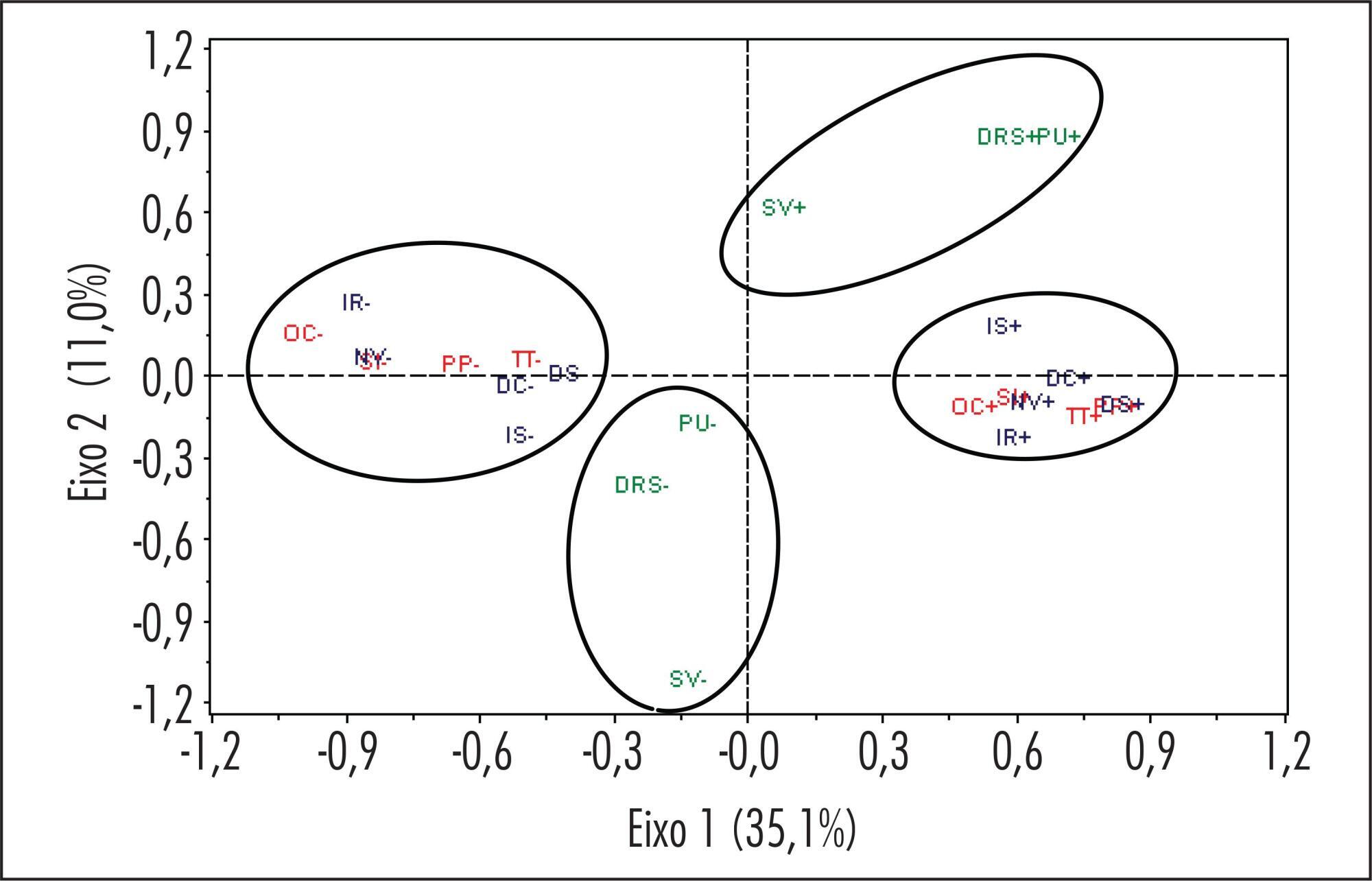
A prospective household survey was performed in São Luís, Maranhão, Brazil with 1,210 climacteric women aged 45 to 60 years. Interviews were applied using previously tested standard questionnaires from April to July 2008. The severity of climacteric symptoms was analyzed by circulatory and psychological indexes and the latter were associated with menopausal status. Multiple correspondence analysis was used to assess the relation among climacteric symptoms.
Most patients were 55 to 60 years old (35.3%), mulatto (37.9%), with 9-11 years of schooling (39.8%), with a partner (56%), Catholic (73.9%) and belonged to the socioeconomic class C (51.1%). The prevalence of CS was 85.9%, and hot flashes (56.4%) and sweating (50.4%) were the most prevalent symptoms. The most frequent psychological symptoms were nervousness (45%) and emotional liability (44.8%). The severity of vasomotor and psychological symptoms was significantly higher during the peri and postmenopausal period (p<0.05). Vaginal dryness (62.7%) was the most prevalent urogenital complaint.
The prevalence of CS was high among women from São Luís, Maranhão, Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):170-175
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0001
To examine the aspect of the uterine cavity after hysteroscopic endometrial ablation, to determine the prevalence of synechiae after the procedure, and to analyze the importance of hysteroscopy during the postoperative period.
The results of the hysteroscopic exams of 153 patients who underwent outpatient hysteroscopy after endometrial ablation due to abnormal uterine bleeding of benign etiology during the period from January 2006 to July 2011 were retrospectively reviewed. The patients were divided into two groups: HIST≤60 (n=90) consisting of patients undergoing the exam 40-60 days after the ablation procedure, and the group HIST>60 (n=63) consisting of patients undergoing the exam between 61 days and 12 months after the procedure.
In the HIST≤60 group, 30% of the patients presented some degree of synechiae: synechiae grade I in 4.4% of patients, grade II in 6.7% , grade IIa in 4.4%, grade III in 7.8%, and grade IV in 2.2%. In the HIST>60 group, 53.9% of all cases had synechiae, 3.2% were grade I, 11.1% grade II, 7.9% grade IIa, 15.9% grade III, and 4.8% grade IV. Hematometra was detected in 2.2 % of all cases in group HIST≤60 and in 6.3% of all cases in group HIST>60.
The uterine cavity of the patients submitted to diagnostic hysteroscopy up to 60 days after endometrial ablation showed significantly fewer synechiae compared to the uterine cavity of patients who underwent the exam after 60 days. Long-term follow-up is necessary to fully evaluate the importance of outpatient hysteroscopy after endometrial ablation regarding menstrual patterns, risk of cancer and prevalence of treatment failure.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(4):146-151
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140050.0003
To describe the potential influence of amniotic fluid on the maternal outcome of preterm premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
An observational, retrospective cohort study was conducted between December 2012 and January 2008 on 86 pregnant women with preterm PROM and a gestational age (GA) of 24 to 35 weeks. The amniotic fluid index (AFI) was used to measure aminiotic fluid volume. Pregnant women were compared at two cut-off points: those with AFI <5.0 and ≥5.0 cm and AFI <3.0 and ≥3.0 cm. We excluded women with hypertensive disorders, diabetesmellitus, fetal malformations and a diagnosis of infections at admission. For statistical analysis, we used the χ2test or Fisher's exact test, when appropriate, and simple linear regression analysis, with the level of significance set at 5%. We calculated the Risk Ratio (RR) and its 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
When maternal outcomes were assessed by comparing ILA ≥5.0versus <5.0 cm, no significant differences were detected. However, when considering ILA <3.0 and ≥3.0 cm, there was an increased risk of chorioamnionitis (36.7 versus10.7%, RR: 3.4, 95%CI 1.4 -8.3, p=0.004), with no significant differences for the other variables. There was also a statistically significant positive correlation between AFI and gestational age at delivery (R2=0.78, p<0.0001).
AFI <3.0 cm causes a three-fold increase in the risk for chorioamnionitis; also, the higher the ILA, the higher the gestational age at delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300007
To adapt the Pregnancy and Sexual Function Questionnaire (PSFQ) for use in Brazil and to evaluate its psychometric properties.
An adaptation and validation study was performed with women in the last trimester of pregnancy living in Rio Branco, Acre. The questionnaire was translated into Portuguese, reviewed and evaluated by specialists, and a pretest was carried out. Construct validity was evaluated by factor analysis; internal consistency was estimated by Cronbach's alpha coefficient and MacDonald's omega, and reproducibility was evaluated by the kappa statistics and test-retest in a sample of pregnant women.
Factor analysis identified the following six domains: subjectivity, pain and discomfort; frequency and receptivity; desirability; satisfaction; orgasm; and stimulus. The internal consistency by Cronbach's alpha was 0.6, while MacDonald's omega was 0.7. The kappa value was higher than 0.7 in all questions.
The Portuguese version of the PSFQ was considered to be adequate for evaluating sexual function during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):124-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300006
To assess clinical factors, histopathologic diagnoses, operative time and differences in complication rates between women undergoing laparoscopy or laparotomy to diagnose and treat an adnexal mass and their association with laparoscopy failure.
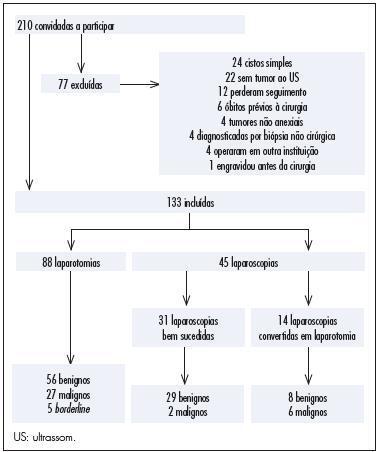
In this prospective study, 210 women were invited to participate and 133 of them were included. Eighty-eight women underwent laparotomy and 45 underwent laparoscopy. Fourteen of the 45 laparoscopies were converted to laparotomy intraoperatively. We assessed whether age, body mass index (BMI), previous abdominal surgeries, CA-125, Index of Risk of Malignancy (IRM), tumor diameter, histological diagnosis, operative time and surgical complication rates differed between the laparoscopy group and the group converted to laparotomy and whether those factors were associated with conversion of laparoscopy to laparotomy. We also assessed surgical logs to evaluate the reasons, as stated by the surgeons, to convert a laparoscopy to laparotomy.
In this research, 30% of the women had malignant tumors. CA-125, IRM, tumor diameter and operative times were higher for the laparotomy group than the laparoscopy group. Complication rates were similar for both groups and also for the successful laparoscopy and unsuccessful laparoscopy groups. The surgical complication rate in women with benign tumors was lower for the laparoscopy group than for the laparotomy group. The factors associated with conversion to laparotomy were tumor diameter and malignancy. During laparoscopy, adhesions a large tumor diameter were the principal causes of conversion.
This study suggests that laparoscopy for the diagnosis and treatment of adnexal masses is safe and does not increase complication rates even in patients who need conversion to laparotomy. However, when doubt about the safety of the procedure and about the presence of malignancy persists, consultation with an expert gynecology-oncologist with experience in advanced laparoscopy is recommended. A large tumor diameter was associated with the necessity of conversion to laparotomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):118-123
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300005
To assess the feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasound combined with ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (US-FNA) cytology and clinical examination of axillary lymph node in patients with breast cancer.
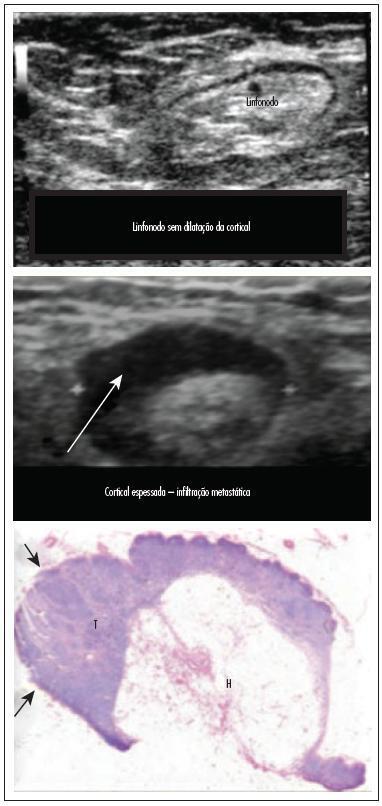
In this prospective study, 171 axillae of patients with breast cancer were evaluated by clinical examination and ultrasonography (US) with and without fine needle aspiration (FNA). Lymph nodes with maximum ultrasonographic cortical thickness > 2.3 mm were considered suspicious and submitted to US-FNA.
Logistic regression analysis showed no statistically significant correlation between clinical examination and pathologically positive axillae. However, in axillae considered suspicious by ultrasonography, the risk of positive anatomopathological findings increased 12.6-fold. Cohen's Kappa value was 0.12 for clinical examination, 0.48 for US, and 0.80 for US-FNA. Accuracy was 61.4% for clinical examination, 73.1% for US and 90.1% for US-FA. Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) analysis demonstrated that a cortical thickness of 2.75 mm corresponded to the highest sensitivity and specificity in predicting axillary metastasis (82.7 and 82.2%, respectively).
Ultrasonography combined with fine-needle aspiration is more accurate than clinical examination in assessing preoperative axillary status in women with breast cancer. Those who are US-FNA positive can be directed towards axillary lymph node dissection straight away, and only those who are US-FNA negative should be considered for sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000300003
To evaluate the impact of sexual and reproductive health theme insertion in the undergraduate medical curriculum at a Brazilian public university.
We developed an instrument for cognitive assessment in sexual and reproductive health based on the subjects addressed in the optional curriculum component Reproductive Health, resulting in an objective multiple choice test containing 27 items. The selected topics were: human, sexual and reproductive rights (HSRR), sexuality, institutional violence, gender, sexual violence, conception, contraception, abortion/legal interruption of pregnancy, maternal mortality and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) - HIV/AIDS. The subjects were grouped into three dimensions of knowledge: HSRR, legal/institutional and biomedical. Two multivariate models were adjusted in the analysis of covariance.
The study included 183 students, 127 of the group who took the elective curriculum course reproductive health (RH Group) and 56 who did not (Non-RH Group). Ninety-six students (52.5%) were males and 87 (47.5%) were females. Mean age was 24.7±1.9 years for the RH Group and 24.4±2.6 for the Non-RH Group. The average performance of the SR Group was higher than that of Non-RH subjects regarding the following subjects: HSRR, sexuality, institutional violence, sexual violence, abortion/legal interruption, and STDs - HIV/AIDS. There was no gender difference in performance, except for the theme maternal mortality, in which males scored worse than females (6.9±0.2 and 7.8±0.2, respectively; p<0.05).
The participation of students in the elective curriculum component Reproductive Health was associated with better performance in some dimensions of cognitive assessment, suggesting a positive impact of this initiative on general medical education.