Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):320-327
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004998
To present the cross-cultural adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese language of the Pregnancy and Weight Gain Attitude Scale.
This scale was developed in order to verify whether attitude toward thinness affects weight gain during pregnancy and contains statements that express different attitudes of pregnant women regarding their own weight gain. The procedures were: translation, back translation, comprehension evaluation, preparation of a final version, application of the scale to 180 pregnant women (mean age=29.6, gestational age=25.7 weeks) and psychometric analysis.
Satisfactory equivalence between the versions and satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha 0.7) were detected. The exploratory factor analysis suggested four subscales with 51.4% total variance explained.
The scale proved to be valid and can be used in studies with pregnant women in Brazil to assess attitudes toward weight gain and to detect and prevent dysfunctional behaviors during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):303-309
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005012
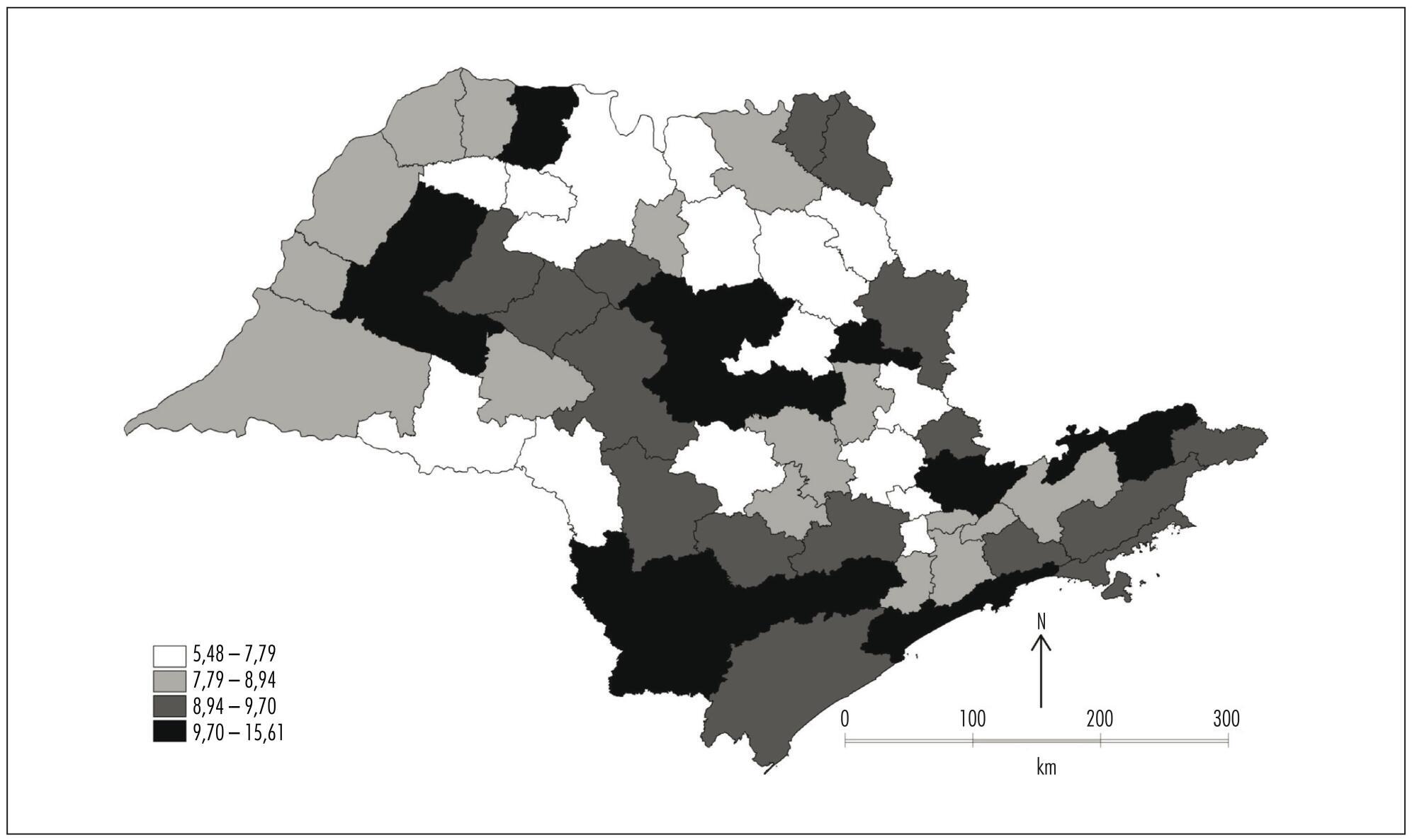
To identify spatial patterns of neonatal mortality distribution in the micro regions of São Paulo State and verify the role of avoidable causes in the composition of this health indicator.
This ecological exploratory study used neonatal mortality information obtained from Information System and Information Technology Department of the Brazilian National Healthcare System (DATASUS) in the period between the years 2007 and 2011. The digital set of micro regions of São Paulo State was obtained from Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Moran Indexes were calculated for the neonatal mortality total rate and rate from avoidable causes; thematic maps were constructed with these rates, as well as the difference between them; and the Box Map was built.
The overall neonatal mortality rate was 8.42/1,000 live births and neonatal mortality rate from avoidable causes of 6.19/1,000 live births. Moran coefficients (I) for these rates were significant (p-value<0.05) - for the total rate of neonatal mortality I=0.11 and for mortality from preventable causes I=0.19 -, and neonatal deaths were concentrated in southwest region and the Vale do Paraíba. If preventable causes were abolished, there would be a significant reduction in the average rate of overall neonatal mortality, from 8.42 to 2.23 deaths/1,000 live births, representing a decline of 73%.
This study demonstrated that neonatal mortality rate would be close to the rates of developed countries if avoidable causes were abolished.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):296-302
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004958
To describe the perinatal outcomes after preterm premature rupture of membranes.
A retrospective cohort study was carried out at Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira - IMIP from January 2008 to December 2012. A total of 124 preterm premature rupture of membranes singleton pregnancies, with gestational age <35, were included in the study. Pregnant women carrying fetuses with malformations, hypertensive syndromes, diabetes, or diagnosis of infections at admission were excluded. The pregnant women were hospitalized for conservative treatment with corticosteroids, antibiotics and tocolysis with nifedipine if necessary. The results are reported as frequency distributions and measures of central tendency and dispersion.
Seventeen patients (13.7%) had a gestational age of less than 24 weeks. Mean maternal age was 25.7 years, mean gestational age at the diagnosis of preterm premature rupture of membranes was 29 weeks, mean amniotic fluid index was 3.5 cm, and mean latency period was 10.5 days. Most patients went into spontaneous labor by the 30th week of pregnancy, and the rate of vaginal delivery was 88.2%. Chorioamnionitis was the most frequent maternal complication (34.7%). Neonatal sepsis was observed in 12% of patients, and the perinatal mortality rate was 21.5% for the group at or beyond the 24th week of gestation and 76.5% for the group with less than 24 weeks of gestational age.
A low maternal mortality rate was observed in preterm premature rupture of membranes; however, high rates of complications and perinatal death were observed, suggesting that other conduct protocols should be studied.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):259-263
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004812
To analyze the factors related to route of delivery in patients with pre-eclampsia.
A retrospective analytical study was conducted from January 2009 to January 2011, during which 250 medical records of patients diagnosed with pre-eclampsia who gave birth to live fetuses with a gestational age of 28 weeks or more were selected. The variables evaluated were: maternal age (19 years, 20−34 years and over 35 full years), gestational age at delivery (28−37 weeks and more than 37 weeks), parity (primiparous or multiparous), previous cesarean section, history of pre-eclampsia or chronic hypertension, current diagnosis of mild or severe pre-eclampsia, and birth weight of the newborn. The information was transcribed to a questionnaire based on the variables being investigated. The chi-square test was applied to identify the relationship between the variables, with the level of significance set at p<0.05, and the Odds Ratio (OR) was calculated only for the variables showing a statistically significant difference in order to determine the odds for the patient to be submitted to a cesarean section.
In this study, we observed a 78.4% rate of cesarean delivery, with 54.1% of the patients submitted to the procedure having a gestational age of 28 to 37 weeks (OR=3.1; p<0.01). Patients with a history of pre-eclampsia were 2.5 times more likely to have cesarean delivery (OR=2.5; p<0.02). All patients who had had a previous cesarean were submitted to cesarean delivery in the current pregnancy (p<0.01). Pregnant women with severe pre-eclampsia were 3.3 times more likely to progress to cesarean delivery than those with mild pre-eclampsia (OR=3.3; p<0.01).
After individual analysis, only gestational age and a diagnosis of severe pre-eclampsia showed significant differences, representing risk factors for this type of delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):237-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005010
To assess the determinants of late stage in women with cervical cancer in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of secondary basis. Women with invasive cervical cancer enrolled in the Cancer Hospital Registry between January 2000 and December 2009 were included. Late clinical stage (≥IIB) was the outcome considered. The following variables were studied: age at diagnosis, race or ethnicity, years of education, marital status, alcohol consumption, smoking status, place of residence, year of diagnosis, initial treatment received, and status after the first treatment. Odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) and a logistic regression model were used. P values<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
37,638 cases were included, with a mean age of 52.4±14.1 years. Late clinical stages were observed in 70.6% of cases and were associated with the presence of squamous cell carcinoma (OR=1.8; 95%CI 1.7-2.0), age ≥50 years (OR=1.5; 95%CI 1.4-1.6), living with a partner (OR=1.3; 95%CI 1.2-1.4), black skin color (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.4), and low educational level (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.3).
In Brazil, the diagnosis of cervical cancer is a delayed event. Although the main factor associated with late stage of cervical cancer identified in this study is a biological factors (histological type) and, consequently, not eligible for intervention, it was confirmed that socioeconomic disparities in the country are associated with late stage disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):269-275
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004907
To determine the agreement between the information on pregnant cards and on primary care medical records about prenatal assistance in the city of Vitória, Espírito Santo, Brazil.
A population study of 360 puerperal women living in this city was interviewed at three hospitals where the cards were copied. Prenatal care data were collected by reviewing the medical records at the city health unit. The information was collected, processed, and submitted to Kappa, Adjusted Kappa, and McNemar tests to check agreement and tendency to disagreement between the cards and the medical records.
The levels of agreement within prenatal care were predominantly moderate (Kappa=0.4-0.6). There was a higher tendency to keep records of appointments on the cards (McNemar=22.3; p-value<0.01). Records of supplementation with folic acid and ferrous sulphate were kept more often on the medical records (McNemar=70.8 and 69.8, respectively; p-value<0.01). The tetanus vaccination coverage was about 50%. Clinical and obstetric procedures and laboratory tests were primarily recorded on the card.
The medical records of primary care were underused as a tool for communication among health professionals, highlighting a precarious record keeping. The results suggest that thought be given to guarantee that the minimum procedures established by the Guidelines of Maternal and Infant Health are followed, and also to the importance of clinical record keeping in health services, since there is variation depending on the source of information.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):264-268
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004935
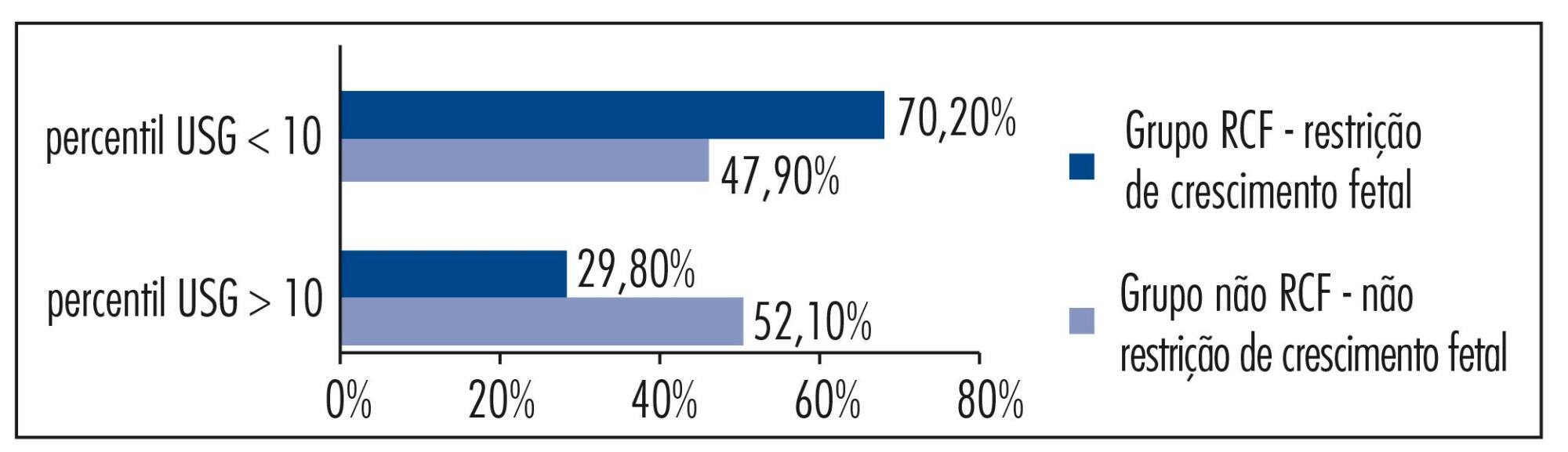
The aim of this study was to analize and describe some characteristics related to a false diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
We retrospectively included 48 pregnant women referred to our service with a suspected diagnosis of IUGR that was not confirmed after birth and we compared them to another group with confirmed IUGR. We then analyzed the characteristics of the false-positive results. The results of the study were divided into continuous and categorical variables for analysis. The χ2test or Fisher exact test was applied to compare proportions. The level of significance was set at p<0.05 for all tests.
In our sample, pregnant women with a false diagnosis of IUGR had the following characteristics: they were referred earlier (mean gestational age of 32.8 weeks); were submitted to 2 to 6 ultrasound examinations before been registered in our service; in 25% of cases ultrasound examination was performed before 12 weeks; in 66.7% of cases the symphysis-fundal height measurement was normal; in 52.1% of cases they had at least 1 sonographic exam above the 10th percentile; on average, the last ultrasound examination (performed on average at 36 weeks) was above the 18th percentile; the women were submitted to a mean number of 5 ultrasound examinations and to a mean number of 4.6 vitality exams.
The false diagnosis of IUGR involves high hospital costs and higher demand for specialists. The symphysis-fundal height measurement must be valued, and the diagnosis of IUGR must be confirmed with ultrasonography in the last weeks of pregnancy before any obstetric management is taken.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):228-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050008
It was to assess the quality of life (QOL) of HIV-infected pregnant women using the HIV/AIDS - Targeted Quality of Life (HAT-QoL) questionnaire.
A descriptive study of 60 pregnant women attended at the Multidisciplinary Nucleus of Infectious Diseases During Pregnancy (NUPAIG) - UNIFESP/EPM and in the referral network of the Municipal Office of São Paulo, conducted from February 2011 to October 2012. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were collected from 60 HIV-infected pregnant women who answered the HAT-QoL questionnaire, which included 34 questions about quality of life.
The average age was 30 years and the average period of HIV infection was 5.7 years. Only 8.3% of patients had a CD4 cell score of ≤200 cells/mm³ and 45% showed undetectable viral load. The average domain scores ranged from 47.5 to 83.7. The domains with the lowest scores were financial concerns and concerns about secrecy. The domains with the highest scores and lower impact on quality of life were concerns about medication and confidence in the professional.
In this initial study with 60 pregnant women, we concluded that the HAT-QOL can contribute to the assessment of quality of life in the population of HIV-infected pregnant women in Brazil.