Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):404-409
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005073
To evaluate the effect of 8 weeks of functional training on body composition in postmenopausal women.
The study was conducted on 38 postmenopausal women, divided into two groups: Training Group (TG) and Control Group (CG). TG women (n=21) performed a program of physical exercise for a period of 8 weeks, 3 times a week on nonconsecutive days, with 90 minutes per session. For the same period, CG women (n=17) did not perform any systematic physical activity. All participants were assessed at baseline and after 8 weeks. The evaluations were performed by the same trained raters. Analysis of body composition was performed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), which allows estimation of body composition in the whole body and by segment. TG participants performed a functional exercise program 3 days a week (non-consecutive), with 11 stations consisting of exercises developed in circuit format sessions. The objectives of the exercises were the development of strength, agility, coordination and proprioception, followed by aerobic exercise (walking). After normality of the data was determined by the Shapiro-Wilk test (p<0.05), we applied the Student t-test for independent samples to check for possible differences in anthropometric variables and body composition between groups at both times of intervention (pre and post-test). All analyses were performed using the SPSS software v. 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with the level of significance set at 5%.
At baseline, no significant difference was observed between groups regarding anthropometric body variables or age composition, indicating homogeneity of the groups. After 8 weeks of training, significant differences were observed between TG and CG regarding fat - CG=0.2±0.7 and TG=-0.4±0.5, total body fat (kg) - CG=0.2±1.3 and TG=-0.7±0.8, and total weight - CG=0.4±1.4 and TG=-0.6±1.1. Percent body fat was reduced in terms of absolute values, although without significance: CG=0.1±1.5 and TG=-0.8±1.5.
Functional training in circuit format can be used as a strategy to alter body composition in postmenopausal women, particularly in terms of reduction of adipose tissue. This is a model that promotes high adhesion on the part of the participants, suggesting that it is an attractive proposal for the investigated age group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(9):387-392
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005053
To evaluate the cases of uterine rupture and dehiscence of the uterine scar at a low-risk maternity and to point out possibilities for an improved approach to these complications.
A descriptive study was conducted at a 30-bed low-risk maternity hospital that provides care to users of the public health system. The investigation was carried out by searching for cases in the delivery room registry book and later reading the medical records in order to obtain the data. The information was inserted on a form previously elaborated for this study. Cases of uterine rupure and dehiscence of the uterine scar diagnosed from 1998 to 2012 were included, with the determination of incidence, aspects related to risk factors and diagnosis, association with the use of misoprostol and oxytocin, and the outcomes observed.
A total of 39,206 deliveries were performed in this maternity during the study period, with 12 cases of uterine rupture and 16 cases of dehiscence of uterine scar being observed. The most relevant results were a high perinatal mortality associated with uterine rupture and the unsuccessful diagnosis of this complications. It was not possible to demonstrate an association with the use of misoprostol or oxytocin.
The adverse outcomes of uterine rupture could be minimized if efforts were directed at improving the diagnostic performance of the assisting teams.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(8):372-376
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005006
To compare the concentration of serum alpha-tocopherol during the postpartum period in women admitted to public and private hospitals in Natal (RN), Brazil.
The study included 209 women in the postpartum period, 96 of them from private hospitals and 113 from public hospitals, studied between 24 and 48 hours postpartum. Inclusion criteria were: mothers aged 12 years or more, without diseases associated with pregnancy, who had given birth to a singleton with no malformations. Clinically decompensated women with multiple fetuses were excluded. A 5 mL blood sample was obtained from each participant under fasting conditions, before the first meal of the day. The concentration of alpha-tocopherol in serum (µg/dL) was determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The statistical difference between means was tested by the Student's t-test.
The mean concentration of alpha-tocopherol was 1.115.7 µg/dL in puerperae from the public network and 1.355.7±397.6 µg/dL in puerperae from the privte network , with a significant difference between groups (p=0.000687). Vitamin E concentration was determined individually and an alpha-tocopherol level <11.6 µmol/L or <499.6 µg/dL was considered to indicate deficiency. Vitamin E deficiency was detected in 5.3% of puerperae from the public network (n=6), whereas no deficiency was detected among women from the private network. However, low concentrations of alpha-tocopherol (11.6 to 16.2 µmol/L or 499.6 to 697.7 µg/dL) was detected in both groups, i.e., in 9.7% of the women from the public network (n=11) and in 4.2% for the women from the private network (n=4).
These results highlight that women assisted in the public sector were more vulnerable to developing low concentrations of alpha-tocopherol than women assisted in the private sector.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(8):367-371
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005052
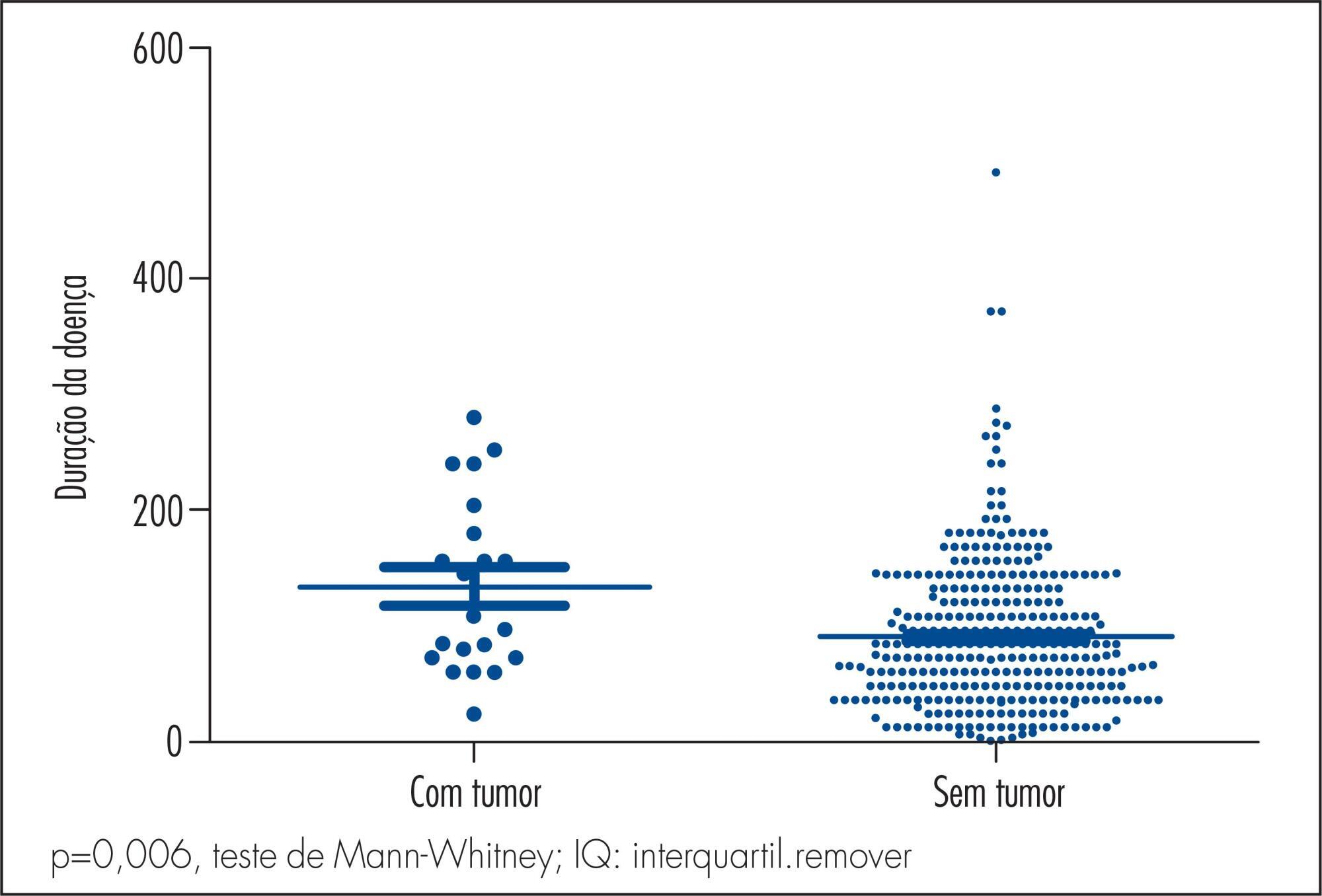
To study the incidence of tumors in a Brazilian sample of women with systemic lupus erythematosus.
This is a retrospective study of 395 medical charts from women with systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosed by the presence of at least 4 of the American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for the diagnosis of this disease and followed for the last 10 years in a rheumatology outpatient clinic. Demographic data (age and ethnicity of patients), data on disease duration, use of immunomodulators and on the presence of neoplasms were listed. Results are presented in frequency and contingency tables. The incidence rate of malignancies in women with lupus was compared with that of the general population for the same demographic region for the past ten years, using data published by the Brazilian National Cancer Institute (INCA). Association studies were carried out by the Fisher and χ tests, when the data were nominal, and by Mann-Whitney test, when numeric. The level of significance was set at 5%.
Twenty-two cases of malignant tumors were identified during these 10 years of follow-up (22 cases/395 or 5.5% of the sample), being the most common those of the uterine cervix (10 cases/395 or 2.5% of the sample) and breast cancer (9 cases/395 or 2.2% of the sample). The presence of tumors was associated with disease duration (p=0.006) and was not influenced by treatment with methotrexate (p=0.1), azathioprine (p=0.9), cyclophosphamide (p=0.6) and glucocorticoids (p=0.3). Breast and uterine cervix tumors were more common in systemic lupus erythematosus women than in the general population (p<0.0001 for both).
A high prevalence of malignant tumors was found in this sample, with tumors being more common in patients with longer disease duration. The most frequent tumors affected the breast and uterus at a higher incidence than in the general population. The presence of tumors was not influenced by the use of glucocorticoids or immunosuppressors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(8):347-352
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005061
To evaluate the validity of cervicovaginal cytology performed at LAPER, the main Laboratory of Pathology of the State of Roraima, Brazil, by interrater agreement (external monitoring) and agreement with histopathologic results.
One hundred women were included, a population-based convenience sample. Their cervical cytological exams were evaluated by the laboratory staff and reviewed by expert medical pathologists, external to the laboratory. Cohen's Kappa index, sensitivity and specificity were evaluated. The study was approved by LAPER coordination and Federal University of Roraima Research Ethics Commitee.
Regarding the prevalence of human papillomavirus-related atypical, there was no concordance between the results issued by LAPER and by the external pathologists (k=0.21). A low sensitivity (28.5%) and specificity (89,2%) was detected for the diagnostic performance of LAPER, with a high proportion of false positive and false negative results. The cytological reports of the external pathologists showed higher sensitivity and specificity (71.4 and 98.9%, respectively), ruling out the possibility that errors related to collection methods and staining would explain the low performance of the laboratory.
A low diagnostic accuracy of cervicovaginal cytology can be a barrier against the control of cervical cancer in Roraima. We emphasize the need for professional training and internal and external monitoring in Brazilian states with a high incidence of cervical cancer.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):315-319
DOI 10.159/S0100-720320140004977
To analyze associations between mammographic arterial mammary calcifications in menopausal women and risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
This was a cross-sectional retrospective study, in which we analyzed the mammograms and medical records of 197 patients treated between 2004 and 2005. Study variables were: breast arterial calcifications, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, age, obesity, diabetes mellitus, smoking, and hypertension. For statistical analysis, we used the Mann-Whitney, χ2 and Cochran-Armitage tests, and also evaluated the prevalence ratios between these variables and mammary artery calcifications. Data were analyzed with the SAS version 9.1 software.
In the group of 197 women, there was a prevalence of 36.6% of arterial calcifications on mammograms. Among the risk factors analyzed, the most frequent were hypertension (56.4%), obesity (31.9%), smoking (15.2%), and diabetes (14.7%). Acute coronary syndrome and stroke presented 5.6 and 2.0% of prevalence, respectively. Among the mammograms of women with diabetes, the odds ratio of mammary artery calcifications was 2.1 (95%CI 1.0-4.1), with p-value of 0.02. On the other hand, the mammograms of smokers showed the low occurrence of breast arterial calcification, with an odds ratio of 0.3 (95%CI 0.1-0.8). Hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, stroke and acute coronary syndrome were not significantly associated with breast arterial calcification.
The occurrence of breast arterial calcification was associated with diabetes mellitus and was negatively associated with smoking. The presence of calcification was independent of the other risk factors for cardiovascular disease analyzed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):290-295
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004892
To identify the major causes of maternal death in the State of Pará, Brazil.
A descriptive, observational and retrospective study was conducted using data from the Mortality Information System (SIM) of the State Department of Public Health of Pará. SIM information was obtained using the TabWin 3.2 software and recorded in a research protocol developed by the investigators. The sample included 383 maternal deaths of 10-49-year-old women, which occurred from 2006 to 2010. Data were analyzed using non-parametric tests (χ2 and G-tests). The BioStat(r) 5.0 software was used for statistical analysis and Microsoft(r) Excel 2007 for the preparation of database and tables.
The Maternal Mortality Ratio was 51.9 and did not decrease significantly during the period. Most deaths occurred during the postpartum period (up to 42 days) (51.7%), and some diagnostic confirmation was used. Direct obstetric causes were dominant (90.6%), mainly hypertension (34.6%), with emphasis on eclampsia (70%), and hemorrhage (22.2%). All of these maternal deaths were avoidable (100%).
Maternal death in Pará is characterized by occurring during the puerperium (up to 42 days), due mainly to direct obstetric causes, such as hypertension, with emphasis on eclampsia, and hemorrhage. This evidences the need for complete attention with good quality for pregnant women, from prenatal care to puerperium, in the state of Pará.