- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Preditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do beta-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):119-119
Abstract
Resumos de TesesPreditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do beta-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):119-119
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200014
Views46Preditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do b-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Bacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
Abstract
Resumos de TesesBacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200013
Views55Bacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Avaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
Abstract
Resumos de TesesAvaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200012
Views51Avaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Resumos de TesesEstudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200011
Views48Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Resumos de TesesEstudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200011
Views37Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses10-10-2000
Estudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Resumos de TesesEstudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200010
Views45Estudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report10-10-2000
Takayasu’s Arteritis and Pregnancy: a Case Report
- Mônica de Souza Visniewski Ximenes,
- Sinval Ferreira de Oliveira,
- Antônio Vieira Machado,
- Mário Dias Corrêa,
- Júlio César de Faria Couto
Abstract
Case ReportTakayasu’s Arteritis and Pregnancy: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):113-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200009
- Mônica de Souza Visniewski Ximenes,
- Sinval Ferreira de Oliveira,
- Antônio Vieira Machado,
- Mário Dias Corrêa,
- Júlio César de Faria Couto
Views60See moreTakayasu’s arteritis is an idiopathic occlusive inflammation of the aorta and its major branches. The disease shows a striking predilection for young women and thus is occasionally associated with pregnancy. The authors describe a case of a pregnant patient with Takayasu’s arteritis. The pregnancy was accompanied by a multidisciplinary group in a satisfactory way. There was only one hospitalization due to an exacerbation of the symptoms during the 32nd week of gestation, controlled by medical treatment. A vaginal delivery occurred at 37 weeks. A live infant weighing 2,750 g was delivered and the patient had an uncomplicated course.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-10-2000
Effects of Domperidone on Pregnant Albino Rats Pregnancy
- Arykerne Chamon do Carmo,
- Danilo Nagib Salomão Paulo,
- Ricardo Martins Oliveira-Filho,
- Manuel de Jesus Simões,
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views97

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleEffects of Domperidone on Pregnant Albino Rats Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):107-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200008
- Arykerne Chamon do Carmo,
- Danilo Nagib Salomão Paulo,
- Ricardo Martins Oliveira-Filho,
- Manuel de Jesus Simões,
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views97See morePurpose: the aim of the present work was to study the chronic action of the antiemetic domperidone on the pregnancy of albino rats. Methods: fifty albino, pregnant Wistar rats were randomly allocated to five groups: GI (control I) = intact rats; GII (control II) = rats receiving the drug vehicle (distilled water) by gavage at the same schedule of the experimental groups; rats in groups GIII, GIV and GV were treated with domperidone by gavage, 2, 6 and 12 mg/kg per day, respectively, divided into 4 daily doses, always in 1 ml of distilled water, from time zero up to the 20th day of pregnancy. The evolution of body weight gain was followed throughout and the animals were sacrificed at term (20th day) by deep ether anesthesia. Number of fetuses, placenta and implantation sites, placenta and fetus weight, fetal malformations and maternal and fetal mortality were evaluated. Results: we observed only intrauterine fetal mortality with 14, 26 and 32 in 74, 60 and 57 newborns of the groups III, IV and V, respectively. Conclusion: though the results of animal experimentation cannot directly be transposed to human conditions, this paper calls attention to the need for a safe judgement when prescribing domperidone to a first-trimester pregnant patient in order to reduce her emetic crises.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Metformin versus insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
- Giovanna Noronha Berti
 ,
, - Igor Gutschov Oviedo Garcia
 ,
, - João Pedro Ruas Floriano de Toledo
 ,
, - Júlia Rodrigues Tatemoto
 ,
, - Lais Watanabe Marino
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Sérgio Floriano de Toledo

Abstract
Review ArticleMetformin versus insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo89
- Giovanna Noronha Berti
 ,
, - Igor Gutschov Oviedo Garcia
 ,
, - João Pedro Ruas Floriano de Toledo
 ,
, - Júlia Rodrigues Tatemoto
 ,
, - Lais Watanabe Marino
 ,
, - Mariana de Medeiros Legori
 ,
, - Sérgio Floriano de Toledo

Views312See moreAbstract
Objective:
The aim of this study is to assess the use of metformin with or without insulin for the treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus compared to insulin alone.
Data sources:
This article consists of a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. The searches were carried out on MEDLINE including 7 studies, between 2010 to 2021.
Study selection:
Randomized clinical trials comparing metformin and insulin written in English, Spanish or Portuguese, with no time limit, were included.
Data collection:
Data was extracted from all the 7 articles and compared statistically when possible. Whenever data was not available or couldn’t be statistically compared, the main results were described in detail.
Data synthesis:
Insulin alone is not superior than metformin with or without insulin on gestational diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion:
There is a potential viability of using metformin as an alternative compared to insulin alone in the treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. However, all assessed outcomes have a very low level of certainty of evidence and more studies are necessary to support these findings.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Giovanna Noronha Berti
-
Original Article01-23-2025
Comparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
- Dinç Zuhal
 ,
, - Çakar Erbil
 ,
, - Kumru Pınar
 ,
, - Erel Özcan
 ,
, - Neşelioğlu Salim
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Boz Gizem

Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
Views306See moreAbstract
Objective
Our aims to compare level of serum ischemia modified albümin(IMA) between healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies and to evaluate the relationship of IMA with preeclampsia, preeclampsia severity and perinatal outcomes.
Methods
Our study is a prospective case-control study. A total of 134 pregnant women (66 preeclamptic and 68 healthy pregnant) between 18-45 years of age and between 24- 41 gestational weeks participated. Serum IMA levels were measured by the Albumin Cobalt Binding (ACB) test.
Results
The mean IMA values were found to be significantly higher in the preeclampsia group compared to the control group (p<0,001). Patients were divided into 3 groups; severe preeclampsia(n=29), non-severe preeclampsia(n=37) and healthy pregnant(n=68). Statistically significant difference was not found between severe preeclampsia and non-severe preeclampsia (p=0.505). The performance of IMA values in predicting the development of preeclampsia among all participants was evaluated with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. According to the ROC analysis, the best cut-off value at which the maximum area under the curve (AUC) was obtained was found when IMA>0.98(AUC: 0.690 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.600-0.781 p<0.001). When IMA threshold value of >0.98 was taken to predict preeclampsia; the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated as 65.15%, 64.71%, 64.18%, and 65.67%, respectively.
Conclusion
IMA level may be a useful new marker in recognizing and predicting preeclampsia. However, despite the power of recognizing the disease, serum IMA levels do not give an idea about the severity of the disease. More comprehensive studies are needed in order to use IMA levels in the diagnosis of preeclampsia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Dinç Zuhal
-
Review Article06-03-2024
How can we reduce maternal mortality due to preeclampsia? The 4P rule
- Henri Augusto Korkes
 ,
, - Ricardo Carvalho Cavalli
 ,
, - Leandro Gustavo De Oliveira
 ,
, - José Geraldo Lopes Ramos
 ,
, - Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Maria Laura Costa

Views293

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleHow can we reduce maternal mortality due to preeclampsia? The 4P rule
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo43
- Henri Augusto Korkes
 ,
, - Ricardo Carvalho Cavalli
 ,
, - Leandro Gustavo De Oliveira
 ,
, - José Geraldo Lopes Ramos
 ,
, - Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa
 ,
, - Francisco Lázaro Pereira de Sousa
 ,
, - Edson Vieira da Cunha Filho
 ,
, - Maria Rita de Souza Mesquita
 ,
, - Mário Dias Corrêa Júnior
 ,
, - Ana Cristina Pinheiro Fernandes Araújo
 ,
, - Alberto Carlos Moreno Zaconeta
 ,
, - Carlos Henrique Esteves Freire
 ,
, - Carlos Eduardo Poli de Figueiredo
 ,
, - Edilberto Alves Pereira da Rocha Filho
 ,
, - Nelson Sass
 ,
, - José Carlos Peraçoli
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa

Views293See moreAbstract
In low and middle-income countries such as Brazil, most maternal deaths are related to hypertensive complications. Preeclampsia is the leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity. Significant proportion is associated with the following factors: lack of identification of high-risk women, lack of adequate prevention, difficulty in maintaining a high-risk prenatal follow-up, delayed diagnosis, insecurity and low use of magnesium sulphate, delayed pregnancy interruption and lack of postpartum follow-up of these high-risk cases. Four major actions are proposed to minimize this alarming clinical picture and reduce the mortality rates due to preeclampsia, called the “4 P Rule” (Adequate Prevention – Vigilant Prenatal Care – Timely Delivery (Parturition) – Safe Postpartum). From this simple “rule” we can open a range of important processes and reminders that may help in the guidance of preeclampsia management.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Henri Augusto Korkes
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Habits of Genital Hygiene and Sexual Activity among Women with Bacterial Vaginosis and/or Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Marcela Grigol Bardin
 ,
, - Paulo César Giraldo
 ,
, - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
 ,
, - José Marcos Sanches
 ,
, - Camila Carvalho de Araujo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rose Luce Gomes do Amaral

Views292

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleHabits of Genital Hygiene and Sexual Activity among Women with Bacterial Vaginosis and/or Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):169-177
- Marcela Grigol Bardin
 ,
, - Paulo César Giraldo
 ,
, - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
 ,
, - José Marcos Sanches
 ,
, - Camila Carvalho de Araujo
 ,
, - Rose Luce Gomes do Amaral

Views292See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate genital hygiene among women with and without bacterial vaginosis (BV) and/or vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).
Methods
A cross-sectional study of reproductive-aged women who underwent gynecological and laboratory tests and fulfilled a genital hygiene questionnaire.
Results
This study evaluated 166 healthy controls and 141 women diagnosed with either BV (n=72), VVC (n=61), or both (n=8). The use of intimate soap and moist wipes after urination was more frequent among healthy women (p=0.042 and 0.032, respectively). Compared to controls, bactericidal soap was more used by women with BV (p=0.05).
Conclusion
Some hygiene habits were associated to BV and/or VVC. Clinical trials should address this important issue in women’s health.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 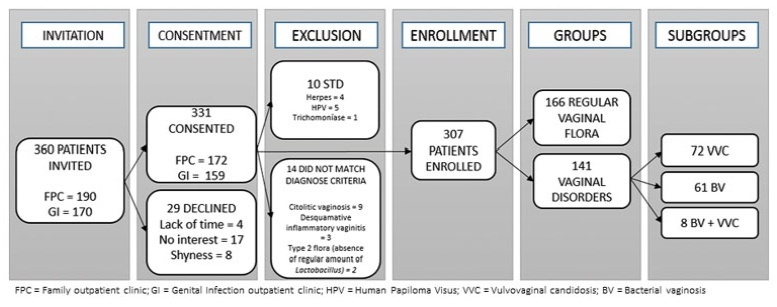
- Marcela Grigol Bardin
-
Review Article02-09-2022
Prevalence of Preeclampsia in Brazil: An Integrative Review
- José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Beatriz Gadioli de Andrade
 ,
, - Luis Gabriel Ferreira Pissinatti
 ,
, - Bruna Fagundes Rodrigues
 ,
, - Caio Augusto Hartman
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Maria Laura Costa

Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePrevalence of Preeclampsia in Brazil: An Integrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):686-691
- José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Beatriz Gadioli de Andrade
 ,
, - Luis Gabriel Ferreira Pissinatti
 ,
, - Bruna Fagundes Rodrigues
 ,
, - Caio Augusto Hartman
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa

Views291See moreAbstract
Objective
To review literature and estimate the occurrence of preeclampsia and its complications in Brazil.
Methods
We performed an integrative review of the literature, and included observational studies published until August 2021 on the SciELO and PubMed databases that evaluated preeclampsia among pregnant women in Brazil. Other variables of interests were maternal death, neonatal death, hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome, and eclampsia. Three independent reviewers evaluated all retrieved studies and selected those that met inclusion criteria. A metanalysis of the prevalence of preeclampsia and eclampsia was also performed, to estimate a pooled frequency of those conditions among the studies included.
Results
We retrieved 304 studies after the initial search; of those, 10 were included in the final analysis, with a total of 52,986 women considered. The pooled prevalence of preeclampsia was of 6.7%, with a total of 2,988 cases reported. The frequency of eclampsia ranged from 1.7% to 6.2%, while the occurrence of HELLP syndrome was underreported. Prematurity associated to hypertensive disorders ranged from 0.5% to 1.72%.
Conclusion
The frequency of preeclampsia was similar to that reported in other international studies, and it is increasing in Brazil, probably due to the adoption of new diagnostic criteria. The development of a national surveillance network would be essential to understand the problem of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in Brazil.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
-
Original Article02-15-2022
Cervical Cancer Screening with HPV Testing: Updates on the Recommendation
- Carla Fabrine Carvalho
 ,
, - Julio Cesar Teixeira
 ,
, - Joana Froes Bragança
 ,
, - Sophie Derchain
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Diama Bhadra Vale

Views285

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleCervical Cancer Screening with HPV Testing: Updates on the Recommendation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):264-271
- Carla Fabrine Carvalho
 ,
, - Julio Cesar Teixeira
 ,
, - Joana Froes Bragança
 ,
, - Sophie Derchain
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 ,
, - Diama Bhadra Vale

Views285Abstract
The present update is a reassessment of the 2018 ‘Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil’ (Zeferino et al.)9, according to the changes observed in new international guidelines and knowledge updates. The most relevant and recent guidelines were assessed. Questions regarding the clinical practice were formulated, and the answers considered the perspective of the public and private sectors of the Brazilian health system. The review addressed risk-based strategies regarding age to start and stop screening, the use of cytology and colposcopy to support management decisions, treatment, follow-up strategies, and screening in specific groups, including vaccinated women. The update aims to improve the prevention of cervical cancer and to reduce overtreatment and the misuse of HPV testing.
Key-words accessibility of health servicesearly detection of cancerhuman papillomavirus DNA testsMass screeningUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Carla Fabrine Carvalho
-
Review Article03-14-2024
Online scientific research on placentophagy: a bibliometric analysis
- Paloma Elisama de Oliveira Morais
 ,
, - Melissa Santos Nassif
 ,
, - Andreia Cristina Barbosa Costa
 ,
, - Patrícia Scotini Freitas
 ,
, - Rômulo Severo Sampaio
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Isabelle Cristinne Pinto Costa

Abstract
Review ArticleOnline scientific research on placentophagy: a bibliometric analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo4
- Paloma Elisama de Oliveira Morais
 ,
, - Melissa Santos Nassif
 ,
, - Andreia Cristina Barbosa Costa
 ,
, - Patrícia Scotini Freitas
 ,
, - Rômulo Severo Sampaio
 ,
, - Isabelle Cristinne Pinto Costa

Views285See moreAbstract
Objective:
To classify the bibliometric indicators of online scientific research on placentophagy.
Methods:
A bibliometric study was conducted to quantify the scientific production of authors and institutions with the aim of highlighting the growth and impact of these publications nationally and internationally. The Bradford Law, network maps, and textual statistics were used, with searches conducted in libraries and databases in October 2021.
Results:
The sample consisted of 64 articles, whose primary authors were associated with 49 institutions, and mostly with degrees in anthropology. The United States of America was the country that published the most papers on the theme, and most studies were reviews with individual production. Through the term analysis, it was found that the predominant themes regarding placentophagy were the following: Alternative therapy for women’s health, methodologies used for research in this area, period of placenta ingestion (postpartum period), and its benefits.
Conclusion:
The bibliometric indicators found are essential for the development of future research.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Paloma Elisama de Oliveira Morais
-
Review Article08-04-2023
Mirabegron and Anticholinergics in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-analysis
- Luisa Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Bruno Monteiro Nunes
 ,
, - Daniela Farah
 ,
, - Leticia Maria de Oliveira
 ,
, - Claudia Cristina Takano Novoa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Marcelo Cunio Machado Fonseca

Views285

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleMirabegron and Anticholinergics in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):337-346
- Luisa Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Bruno Monteiro Nunes
 ,
, - Daniela Farah
 ,
, - Leticia Maria de Oliveira
 ,
, - Claudia Cristina Takano Novoa
 ,
, - Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Marcelo Cunio Machado Fonseca

Views285See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare the use of mirabegron with anticholinergics drugs for the treatment of overactive bladder (OB).
Data Source
Systematic searches were conducted in EMBASE, PUBMED, Cochrane, and LILACS databases from inception to September 2021. We included RCTs, women with clinically proven OB symptoms, studies that compared mirabegron to antimuscarinic drugs, and that evaluated the efficacy, safety or adherence.
Data Collection
RevMan 5.4 was used to combine results across studies. We derived risk ratios (RRs) and mean differences with 95% CIs using a random-effects meta-analytic model. Cochrane Collaboration Tool and GRADE was applied for risk of bias and quality of the evidence.
Data Synthesis
We included 14 studies with a total of 10,774 patients. Fewer total adverse events was reported in mirabegron group than in antimuscarinics group [RR 0.93 (0.89–0.98)]. The risk of gastrointestinal tract disorders and dry mouth were lower with mirabegron [RR 0,58 (0.48–0.68); 9375 patients; RR 0.44 (0.35–0.56), 9375 patients, respectively]. No difference was reported between mirabegron and antimuscarinics drugs for efficacy. The adherence to treatment was 87.7% in both groups [RR 0.99 (0.98–1.00)].
Conclusion
Mirabegron and antimuscarinics have comparable efficacy and adherence rates; however, mirabegron showed fewer total and isolated adverse events.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Luisa Gracio Ferreira Sartori
-
Review Article03-24-2022
Commercial Surrogacy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Views357

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCommercial Surrogacy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Views357See moreAbstract
Objective
Surrogacy is the process in which a woman carries and delivers a baby to other person or couple, known as intended parents. When carriers are paid for surrogacy, this is known as commercial surrogacy. The objective of the present work is to review the legal, ethical, social, and cultural aspects of commercial surrogacy, as well as the current panorama worldwide.
Methods
This is a review of the literature published in the 21st century on commercial surrogacy.
Results
A total of 248 articles were included as the core of the present review. The demand for surrogate treatments by women without uterus or with important uterine disorders, single men and same-sex male couples is constantly increasing worldwide. This reproductive treatment has important ethical dilemmas. In addition, legislation defers widely worldwide and is in constant change. Therefore, patients look more and more for treatments abroad, which can lead to important legal problems between countries with different laws. Commercial surrogacy is practiced in several countries, in most of which there is no specific legislation. Some countries have taken restrictive measures against this technique because of reports of exploitation of carriers.
Conclusion
Commercial surrogacy is a common practice, despite important ethical and legal dilemmas. As a consequence of diverse national legislations, patients frequently resort to international commercial surrogacy programs. As of today, there is no standard international legal context, and this practice remains largely unregulated.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article07-30-2021
The Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

Views408

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):395-402
- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

Views408See moreAbstract
In a healthy athlete, the caloric intake is sufficient for sports energy needs and body physiological functions, allowing a balance between energy availability, bone metabolism, andmenstrual cycle.Onthe other hand, an imbalance causedby low energy availability dueto a restrictive diet, eating disorders or long periods of energy expenditure leads to multisystemic deregulation favoring the essential functions of the body. This phenomenon, described as the female athlete triad, occurs in a considerable percentage of high-performance athletes, with harmful consequences for their future. The present review was carried out based on a critical analysis of themost recent publications available and aims to provide a global perception of the topic relative energy deficit in sport (RED-S). The objective is to promote theacquisition ofmore consolidated knowledgeon an undervaluedtheme, enabling the acquisition of preventive strategies, early diagnosis and/or appropriate treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
-
Original Article03-04-2022
Screening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views411

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleScreening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):452-457
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views411See moreAbstract
Objective
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Methods
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
Results
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views314

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):133-141
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 ,
, - Marcos Pascoal Pattussi
 ,
, - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views314Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in university students, the factors associated with PMS, the most prevalent symptoms, and the interference of symptoms in academic, family, social, and work activities.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,115 university students aged ≥ 18 years from the University of Rio Verde, Goiás. Premenstrual syndrome and PMDD were identified using the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool. Associations with sociodemographic, behavioral, reproductive, nutritional, and health factors were investigated using the Poisson regression.
Results
The prevalence of PMS was 46.9% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.0-49.8), and of PMDD, 11.1% (95% CI 9.3-13.0). The most prevalent symptoms were physical, such as breast tenderness, bloating, e weight gain (73%); followed by psychological ones such as overeating/food cravings, tearful/more sensitive to rejection (> 60%). More than 30% of the patients reported that the symptoms interfered in a moderate-tosevere way in their social and academic activities. After adjusted analysis, PMS was more prevalent in those who were attending the 1st/2nd semester of college (prevalence ratio [PR] 1.44; 95% CI 1.14-1.80), those who consumed alcohol in the last 30 days (PR 1.23; 95% CI 1.04-1.47), and those who had depression (PR 1.49; 95% CI 1.30-1.71).
Conclusion
Almost half of the university students had PMS and ~ 11%, PMDD. Physical symptoms were themost common and interfered in amoderate-to-severe way in various aspects of life. Attending the first semesters, consuming alcohol, and having depression were risk factors for PMS. The identification of risk factors for PMS is essential to prevent symptoms and reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Key-words Cross-sectional studiespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeRisk factorsStudentsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
-
Review Article07-30-2021
Interventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views373

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleInterventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):403-413
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views373See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate in the literature the studies on the benefits ofmusic therapy interventions among pregnant women in the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods.
Data Sources
The search for articles was carried out in the following electronic databases: VHL, LILACS, SciELO, Portal CAPES, PsycINFO, ERIC, PubMed/Medline, and journals specialized in this field: Revista Brasileira de Musicoterapia (“Brazilian Journal of Music Therapy”) and Voices.
Study Selection
Descriptors in Portuguese (musicoterapia, gravidez, gestantes, revisão), English (music therapy, pregnancy, pregnant women, review) and Spanish (musicoterapia, embarazo, mujeres embarazadas, revisión) were used. The search was delimited between January 2009 and June 2019. The process of selection and evaluation of the articles was performed through peer review.
Data Collectio
n The following data were extracted: article title, year of publication, journal, author(s), database, country and date of collection, purpose of the study, sample size, type of care, intervention, instruments used, results, and conclusion. The data were organized in chronological order based on the year of publication of thestudy.
Summary of the Data
In total, 146 articles were identified, and only 23 studies were included in this systematic review. The articles found indicate among their results relaxation, decreased levels of anxiety, psychosocial stress and depression, decreased pain, increase in the maternal bond, improvement in the quality of sleep, control of the fetal heart rate and maternal blood pressure, and decreased intake of drugs in the postoperative period.
Conclusion
Music therapy during the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods can provide benefits to pregnant women and newborns, thus justifying its importance in this field.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views326

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views326Abstract
Introduction
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Results
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Key-words Chronic pelvic paincognitive behavioral therapyEndometriosispsychological interventionQuality of lifesystematic reviewsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-15-2022
The Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views371

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):614-620
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 ,
, - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views371Abstract
The impact of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) infection on female’s fertility is not completely established yet, since the level of evidence associating these factors is still weak. Hence, the goal of the present review is to contribute to a better elucidation of this matter. The electronic database chosen was the Medline/PubMed, with the last survey on May 11, 2021. Publication date was used as a filter, with the previous 5 years having been selected. The following describers were used: chlamydia trachomatis AND infertility; chlamydia trachomatis AND tubal alteration AND infertility; chlamydia AND low pregnancy rates. From the 322 studies screened, 293 that failed to meet our eligibility criteria were excluded. Subsequently, we removed seven studies for not having the possible correlation between CT infections and female infertility as its main focus, and three for being about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in general. Moreover, two studies designed as reviews were also excluded. Ergo, we included 17 studies in our qualitative analysis. The authors conducted research individually and analyzed carefully the studies selected. As we retrieved the information needed for our study through reading the texts, no contact was made with the authors of the studies selected. This systematic review corroborates the hypothesis that CT infection potentiates female infertility, as 76.47% of the included studies found a positive correlation between them. We conclude that there is an important association between CT infection and female infertility. Ergo, making CT screening part of the infertility investigation routine is relevant and has a reasonable justification.
Key-words Chlamydia trachomatishuman reproductionInfertilitySexually transmitted diseasestubal factor infertilitySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Laura Gazal Passos
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Views339

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePolycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Views339See moreAbstract
Diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) during adolescence is challenging since normal pubertal development overlap typical features of this syndrome. The authors aim to summarize the existing evidence concerning PCOS in adolescence, particularly its diagnostic criteria and therapeutic options. A search throughout medical databases such as PubMed and MedScape was performed. Diagnostic criteria include irregular menstrual cycles according to time postmenarche and evidence of clinical hyperandrogenism and/or biochemical hyperandrogenism, provided other causes have been excluded. Polycystic ovarianmorphology ought not to be used as a diagnostic criterion. Treatment should targetmanifestations and/or comorbidities, even in the absence of a definite diagnosis. Lifestyle interventions are the first-line treatment. Combined oral contraceptives, metformin or antiandrogens may also be considered as adjuvants. Screening for PCOS in adolescence is crucial as it allows an early intervention on the symptoms and comorbidities presented leading to better long-term reproductive and metabolic outcomes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
