- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article06-27-2002
The Trial of Labor After one Cesarean Section
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon,
- Jacqueline Leite Frade,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Carolina Prado Diniz,
- Ivete Dalben, [ … ],
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views61

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleThe Trial of Labor After one Cesarean Section
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(3):161-166
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000300003
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon,
- Jacqueline Leite Frade,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Carolina Prado Diniz,
- Ivete Dalben,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views61See morePurpose: to study trial of labor (TOL) for vaginal birth after one previous cesarean section. Methods: this is a retrospective cohort study that included 438 pregnant women with one previous cesarean section and their 450 newborns. They were divided into two groups – with and without TOL. The minimum sample size was 121 pregnant mothers per group. TOL was considered as an independent variable and vaginal birth and maternal and perinatal complication frequency as dependent variables. Both univariate and multivariate analyses were performed. The comparison of observed frequencies (%) was analyzed by the chi-squared test (chi²) with 5% significance, and linear regression from the odds ratio (OR) and confidence interval of 95% (CI95%). Results: TOL was used in 59.2% of vaginal deliveries. It was less used in women over 40 years (2.7% vs 6.7%) and in those with clinical or obstetrical diseases such as arterial hypertension (7.0%) and bleeding in the third trimester (0.3%). There was a higher risk for puerperal complications with cesarean deliveries (OR = 3.53, CI 95% = 1.57-7.93), independent of TOL. Perinatal mortality was dependent on neonatal weight and fetal malformations, not on TOL. Newborns from mothers not submitted to TOL were at a higher risk for developing breathing complications (OR = 1.92 CI 95% = 1.20-3.07). Conclusions: The results confirm that trial of labor after a previous cesarean section is a safe method – assisting vaginal delivery in 59.2% of births and not interfering with maternal and perinatal mortality. It is a treatment that should be stimulated.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
DECLARAÇÃO DE BARCELONA
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(3):151-151
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
A Grande Vitória
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):07-07
Views60

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-20-2002
Microinvasive Carcinoma in the Cone Specimen in Women With Colposcopically Directed Biopsy Suggesting CIN 3
- Priscila Garcia Figueiredo,
- Renata Clementino Gontijo,
- Sophie Françoise Mauricette Derchain,
- Fabiana Yumi Nakano,
- Julio César Teixeira, [ … ],
- Edson Zangiacomi Martinez
Views52

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleMicroinvasive Carcinoma in the Cone Specimen in Women With Colposcopically Directed Biopsy Suggesting CIN 3
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):37-43
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100006
- Priscila Garcia Figueiredo,
- Renata Clementino Gontijo,
- Sophie Françoise Mauricette Derchain,
- Fabiana Yumi Nakano,
- Julio César Teixeira,
- Edson Zangiacomi Martinez
Views52See morePurpose: to determine the factors associated with the detection of a microinvasive carcinoma in the cervical cone of women with a previous colposcopically directed biopsy compatible with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 3 and to evaluate the proportion of involved margins. Patients and methods: we reviewed the medical records of 385 women (mean age: 39 years) submitted to cold conization or conization by high frequency surgery (HFS) with a loop during the period from January 1993 to July 2000. These procedures were indicated on the basis of a biopsy compatible with (CIN) 3. Results: the diagnosis of the cone was compatible with (CIN) 3 in 243 (63%) women and with (CIN) 2 in 13 (3%). Only 10 presented HPV/CIN 1 (3%) and eight had no residual disease in the cone. However, 101 (26%) women presented a microinvasive carcinoma in the cone and 10 (3%) presented a frankly invasive carcinoma. Age, menstrual status and number of deliveries were not related to the severity of the cone lesion. Women with oncologic colpocytology changes suggestive of invasion presented a significantly higher risk of having a microinvasive or invasive carcinoma as determined by final histology (p<0.01), although 52 of the 243 women with CIN 2 or CIN 3 in the cone also showed a suggestion of invasion at colpocytology. Among the women with CIN 2 or 3, the epithelium was white in 44%, dotted in 21%, and mosaic-like in 17%. This proportion was similar for women with a microinvasive or invasive carcinoma, with these images being detected in 37%, 23% and 21% of the cases, respectively. Involvement of the cone margins was significantly higher among women submitted to HFS (49%) than among those submitted to cold conization (29%). Conclusion: the absence of independent clinical and colposcopic factors associated with the detection of a microinvasive carcinoma in women submitted to conization on the basis of a biopsy compatible with (CIN) 3 justifies the conical excision of the squamocolumnar junction in high grade cervical lesions.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Erratum06-19-2002Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1)
Abstract
ErratumRevista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1)
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100018
Views27Associação entre a incisura Diastólica das artérias uterinas e a histologia do leito placentário em grávidas com pré-eclâmpsia […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Contribuição ao Estudo do Laser de Vapor de Cobre no Tratamento da Endometriose Induzida Cirurgicamente em Coelhas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):71-71
Abstract
Resumos de TesesContribuição ao Estudo do Laser de Vapor de Cobre no Tratamento da Endometriose Induzida Cirurgicamente em Coelhas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):71-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100017
Views49Contribuição ao Estudo do Laser de Vapor de Cobre no Tratamento da Endometriose Induzida Cirurgicamente em Coelhas […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Avaliação do Potencial de Peroxidação Lipídica no Fluido Peritoneal de Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose Pélvica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):70-70
Abstract
Resumos de TesesAvaliação do Potencial de Peroxidação Lipídica no Fluido Peritoneal de Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose Pélvica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):70-70
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100016
Views56Avaliação do Potencial de Peroxidação Lipídica no Fluido Peritoneal de Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose Pélvica […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Prevalência das Neoplasias Intra-epiteliais Cervicais e Lesões Induzidas pelo HPV nas Mulheres Soropositivas/AIDS
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):70-70
Abstract
Resumos de TesesPrevalência das Neoplasias Intra-epiteliais Cervicais e Lesões Induzidas pelo HPV nas Mulheres Soropositivas/AIDS
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):70-70
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100015
Views42Prevalência das Neoplasias Intra-epiteliais Cervicais e Lesões Induzidas pelo HPV nas Mulheres Soropositivas/AIDS […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Nominata 202412-31-2024
Nominata 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:eRBGO20242024
Abstract
Nominata 2024Nominata 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:eRBGO20242024
DOI 10.61622/rbgo/2024nominata02024
Views191We wish to thank everyone who contributed to the edition of the Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia – RBGO volume 46, year 2024, especially the authors and reviewers whose work and opinions were essential to maintain the scientific and methodological rigor of the published articles.A. Seval Ozgu-Erdinc, University of Health Sciences, Ankara Eğitim ve […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-04-2024
Self-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Abstract
Review ArticleSelf-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo77
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 ,
, - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Views249Abstract
Objective:
An in-depth evaluation of the published evidence is needed on self-medication, specifically the evidence focusing on vulnerable groups, such as pregnant women. This scoping review aims to provide an overview of the differences in self-medication prevalence and study characteristics among different groups, while identifying gaps in the literature.
Methods:
A literature search was performed in PubMed and Web of Science, including articles published in the last 10 years for the pregnant women group (PWG) and the general population group (GPG). Data on study design, self-medication prevalence, medications used, and other variables were collected, tabulated, and summarized.
Results:
From 2888 screened articles, 75 were considered including 108,559 individuals. The self-medication (SM) in the PWG ranged from 2.6 to 72.4% and most studies had an SM prevalence between 21 and 50% and in the GPG, 32 from 50 studies had a SM prevalence higher than 50%. The reviewed studies varied considerably in methodology, requiring careful interpretation. While most of the studies assessed self-medication during the entire pregnancy, self-medication definition was often inconsistent between studies. Acetaminophen was the most used medication and headache was the most frequent symptom leading to self-medication initiation in the PWG.
Conclusions:
Self-medication among pregnant women showed a lower prevalence when compared to the general population. The medications used and symptoms reported were similar between groups. However, methodological differences must be carefully considered. Pregnant women should carefully follow their physicians’ advice before initiating self-medication to avoid preventable maternal and fetal adverse effects.
Key-words drug-related side effects and adverse reactionsMedication usePregnant womenSelf-medicationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gabriela Pereira
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Metformin versus insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
- Giovanna Noronha Berti
 ,
, - Igor Gutschov Oviedo Garcia
 ,
, - João Pedro Ruas Floriano de Toledo
 ,
, - Júlia Rodrigues Tatemoto
 ,
, - Lais Watanabe Marino
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Sérgio Floriano de Toledo

Abstract
Review ArticleMetformin versus insulin in gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo89
- Giovanna Noronha Berti
 ,
, - Igor Gutschov Oviedo Garcia
 ,
, - João Pedro Ruas Floriano de Toledo
 ,
, - Júlia Rodrigues Tatemoto
 ,
, - Lais Watanabe Marino
 ,
, - Mariana de Medeiros Legori
 ,
, - Sérgio Floriano de Toledo

Views318See moreAbstract
Objective:
The aim of this study is to assess the use of metformin with or without insulin for the treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus compared to insulin alone.
Data sources:
This article consists of a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. The searches were carried out on MEDLINE including 7 studies, between 2010 to 2021.
Study selection:
Randomized clinical trials comparing metformin and insulin written in English, Spanish or Portuguese, with no time limit, were included.
Data collection:
Data was extracted from all the 7 articles and compared statistically when possible. Whenever data was not available or couldn’t be statistically compared, the main results were described in detail.
Data synthesis:
Insulin alone is not superior than metformin with or without insulin on gestational diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion:
There is a potential viability of using metformin as an alternative compared to insulin alone in the treatment of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. However, all assessed outcomes have a very low level of certainty of evidence and more studies are necessary to support these findings.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Giovanna Noronha Berti
-
Letter to the Editor12-04-2024
Comment on: Effects of COVID-19 on human placentas in the second and third trimester
- Nayara Ribeiro Máximo de Almeida
 ,
, - Mateus Augusto Felix de Melo
 ,
, - Pâmela Marillac Rodrigues Feijó de Melo
 ,
, - Julio Martinez Santos
 ,
, - Johnnatas Mikael Lopes

Abstract
Letter to the EditorComment on: Effects of COVID-19 on human placentas in the second and third trimester
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo88
- Nayara Ribeiro Máximo de Almeida
 ,
, - Mateus Augusto Felix de Melo
 ,
, - Pâmela Marillac Rodrigues Feijó de Melo
 ,
, - Julio Martinez Santos
 ,
, - Johnnatas Mikael Lopes

Views141Recent evidence demonstrates na increase in negative maternal and neonatal outcomes in cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection, such as greater severity of the disease, need for mechanical ventilation and longer hospitalization in intensive care units.(,) The greater severity of infectious diseases in pregnancy occurs due to anatomical and immunological changes, such as a change in the […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Nayara Ribeiro Máximo de Almeida
-
Original Article12-04-2024
Analysis of vaginal microbiota before and after treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix
- Patrícia Mendonça Ventura
 ,
, - Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val Guimarães
 ,
, - Luis Guillermo Coca Velarde
 ,
, - Susana Cristina Aidé Viviani Fialho
 ,
, - Douglas Guedes Ferreira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rafael Augusto Chaves Machado

Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of vaginal microbiota before and after treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo86
- Patrícia Mendonça Ventura
 ,
, - Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val Guimarães
 ,
, - Luis Guillermo Coca Velarde
 ,
, - Susana Cristina Aidé Viviani Fialho
 ,
, - Douglas Guedes Ferreira
 ,
, - Matheus Madureira Fernandes
 ,
, - Rafael Augusto Chaves Machado

Views207Abstract
Objective:
HPV infection is considered the most common sexually transmitted virus today. The persistence of HPV is the main cause for the development of precursor lesions and cervical cancer. There are environmental and non-environmental factors that contribute to the persistence of the virus. Studies indicate a possible relationship between the vaginal microbiota (environmental factor) and the risk of high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer. This study evaluates the association between the type of vaginal microbiota and the occurrence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix.
Methods:
Observational, longitudinal, prospective, and analytical studies carried out between 2019 and 2021, which evaluated the vaginal microbiota of patients diagnosed with high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion before and after treatment in two collections with an interval of 6 months, using scrapings and vaginal swabs.
Results:
In Group I (with lesions) 28 women participated and 29 in Group II (without lesions). According to Nugent, in the initial collection of Group I, 16 women (57%) had lactobacillary microbiota, eight (28%) intermediate, and four (14%) coccus. In Group II, twenty-one (75%) were lactobacillary, one (3%) was intermediate, and seven (24%) werecoccus. With p=0.03.
Conclusion:
According to Nugent’s criteria, there was an association between the type of vaginal microbiota and the occurrence of high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. The same was not observed in the Donders classification. Studies with a larger sample are needed to confirm our results.
Key-words CervixuterimicrobiotaPapillomavirus infectionssquamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervixUterine cervical neoplasmsVaginosis, bacterialSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Patrícia Mendonça Ventura
-
Original Article12-04-2024
Systemic inflammatory indices as a non-invasive grading modality for endometriosis: a comparative study versus exploratory laparoscopy
- Ahmed Sabra Ibrahim Mohammed Sabra
 ,
, - Shreen Naguib Aboelezz Moselhy
 ,
, - Ahmed Kasem Mohamed Zain Eldin

Views207

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSystemic inflammatory indices as a non-invasive grading modality for endometriosis: a comparative study versus exploratory laparoscopy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo84
- Ahmed Sabra Ibrahim Mohammed Sabra
 ,
, - Shreen Naguib Aboelezz Moselhy
 ,
, - Ahmed Kasem Mohamed Zain Eldin

Views207See moreAbstract
Objective:
Included evaluation of the possibility of using the systemic inflammatory indices for preoperative screening for the presence and severity of endometriosis (EM) in comparison to the findings of the exploratory laparoscopy
Methods:
88 women with clinical manifestations suggestive of EM were evaluated clinically and by US and gave blood samples for estimation of serum cancer antigen-125 (CA125), platelet and total and differential leucocytic counts for calculation of inflammatory indices; the Systemic Immune-Inflammation index, the Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the Neutrophil-Monocyte ratio, the Neutrophil-Platelet ratio and the Platelet-Lymphocyte ratio. Then, patients were prepared to undergo laparoscopy for diagnosis and staging.
Results:
Laparoscopy detected EM lesions in 63 patients; 27 of stage I-II and 36 of stage III-IV. Positive laparoscopy showed significant relation with US grading, high serum CA125 levels, platelet and inflammatory cell counts and indices. Statistical analyses defined high SIRI and NLR as the significant predictors for positive laparoscopy and high serum CA125 and NLR as the most significant predictors for severe EM (stage III-IV) on laparoscopy
Conclusion:
The intimate relation between EM and inflammation was reflected systematically as high levels of blood cellular components, but indices related to neutrophil especially NLR and SIRI showed highly significant relation to the presence and severity of EM and might be used as routine, cheap and non-invasive screening test before exploratory laparoscopy to guide the decision-making.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ahmed Sabra Ibrahim Mohammed Sabra
-
Letter to the Editor12-04-2024
Comment on: Effect of combined training on body image, body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer: controlled clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo96
Abstract
Letter to the EditorComment on: Effect of combined training on body image, body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer: controlled clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo96
Views193Dear Editor,I am writing to express my appreciation for the recent article titled “Effect of Combined Training on Body Image, Body Composition, and Functional Capacity in Patients with Breast Cancer: Controlled Clinical Trial,” published online on June 20, 2023. The study provides crucial insights into the benefits of combined training for breast cancer patients, highlighting […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-04-2024
Female genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views214

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleFemale genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views214Abstract
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) has been evolving since 1978, with the number of techniques performed increasing over the years. Despite continued advances, some couples continue to have difficulties getting pregnant, and it has recently been considered that the microbiome of the female genital tract (FGT) may influence embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. This review aims to evaluate the role of probiotics on reproductive outcomes in infertile women on ART. A search throughout medical databases was performed, and six articles met the criteria. Five studies showed improvements in pregnancy rates, with only one demonstrating statistical significance. One article showed no improvement but reported a statistically significant reduction in the miscarriage rate in the probiotic group. Further research is needed to evaluate the true potential of probiotics, namely to assess whether they effectively modulate the FGT microbiome and if these changes are maintained over time.
Key-words Abortion, spontaneousEmbryo implantationGenitalia, femaleInfertility, femalePregnancy outcomePregnancy rateProbioticsReproductive techniques, assisted, MicrobiotaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Review Article03-18-2025
Short cervix and use of cervical pessary for preventing preterm birth in singleton and twin pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ana Clara Felix de Farias Santos
 ,
, - Nicole dos Santos Pimenta
 ,
, - Ana Gabriela Alves Pereira
 ,
, - Gabriela Oliveira Gonçalves Molino
 ,
, - Maírla Marina Ferreira Dias
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Pedro Henrique Costa Matos da Silva

Abstract
Review ArticleShort cervix and use of cervical pessary for preventing preterm birth in singleton and twin pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo10
- Ana Clara Felix de Farias Santos
 ,
, - Nicole dos Santos Pimenta
 ,
, - Ana Gabriela Alves Pereira
 ,
, - Gabriela Oliveira Gonçalves Molino
 ,
, - Maírla Marina Ferreira Dias
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Costa Matos da Silva

Views172See moreAbstract
Objective:
Preterm birth remains a significant contributor to neonatal morbidity and mortality. The use of cervical pessaries as an intervention for preventing preterm delivery in women with a short cervix has been a subject of interest. We evaluated the effectiveness of cervical pessary compared to standard care in preventing preterm delivery in women with a short cervix.
Data source:
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase databases in December 2023.
Study selection:
Randomized clinical trials with the outcomes of interest were included.
Data collect:
We computed risk ratios for binary endpoints, with 95% confidence intervals. Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics. Data were analyzed using R software (version 4.3.0). The primary outcomes of interest were preterm delivery before 37 weeks, and preterm delivery before 34 weeks.
Data synthesis:
Seventeen studies with 5,704 patients were included. The use of cervical pessary was associated with a decreased risk of preterm delivery before 37 (RR 0.88; 95% CI 0.81-0.96) and 34 weeks (RR 0.79; 95% CI 0.63-0.99) of gestation in twin pregnancies as compared to standard care without progesterone. There were no significant differences in preterm delivery in singleton pregnancy, neonatal outcomes, preterm premature rupture of the membranes or chorioamnionitis.
Conclusion:
The use of cervical pessary was associated with a significant reduction in preterm delivery at 34 and 37 weeks of gestation in twin pregnancies among patients with a short cervix compared to no treatment. No significant difference was found in singleton pregnancies or maternal outcomes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 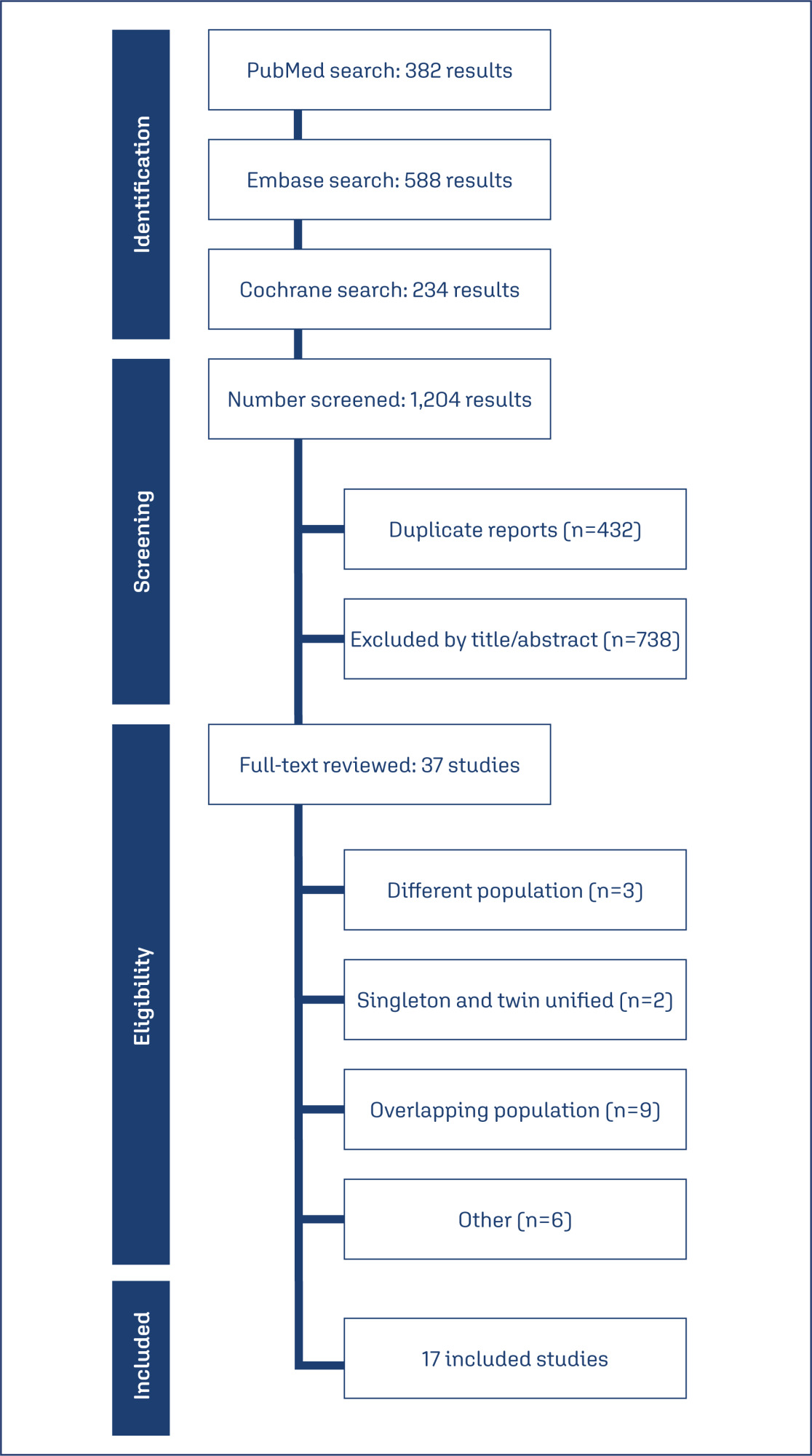
- Ana Clara Felix de Farias Santos
-
Short Communication03-18-2025
Contraception in adolescents with mental disorders: adherence and satisfaction in the use of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo9
Abstract
Short CommunicationContraception in adolescents with mental disorders: adherence and satisfaction in the use of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo9
Views172See moreAbstract
Objective:
To evaluate the continuation rate, satisfaction, and reasons for discontinuation of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) in adolescents treated in a mental health service.
Methods:
Prospective cohort study conducted in a reference unit for the care of adolescents with mental disorders (MDs) and intellectual disabilities (IDs). All patients received a gynecological consultation and an educational group on contraceptive methods. Sociodemographic data on age, education and gynecological data (menarche, coitarche, regularity of menstrual cycles and presence of symptoms) were collected. Follow-up was quarterly for 12 months, during which symptoms, desire to continue, and satisfaction with the use of the quarterly injectable were assessed.
Results:
Eight hundred and sixty-two sexually active adolescents were supported, 532 adolescents chose to use the quarterly injectable, and 69 of these agreed to participate in the study. The mean age of users was 15.5 years (SD=0.91). After 12 months of follow-up, 34 (49.3%) of the 69 adolescents continued to use the method and 36 (52.3%) were satisfied. Among the 33 (47.8%) who discontinued use, the most common reasons were irregular bleeding and weight gain.
Conclusions:
Adolescents with intellectual disabilities and/or other mental disorders showed a significant rate of continuation and satisfaction with the use of the depot medroxyprogesterone acetate at 12 months, and the most common reasons for discontinuation were irregular uterine bleeding and weight gain.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 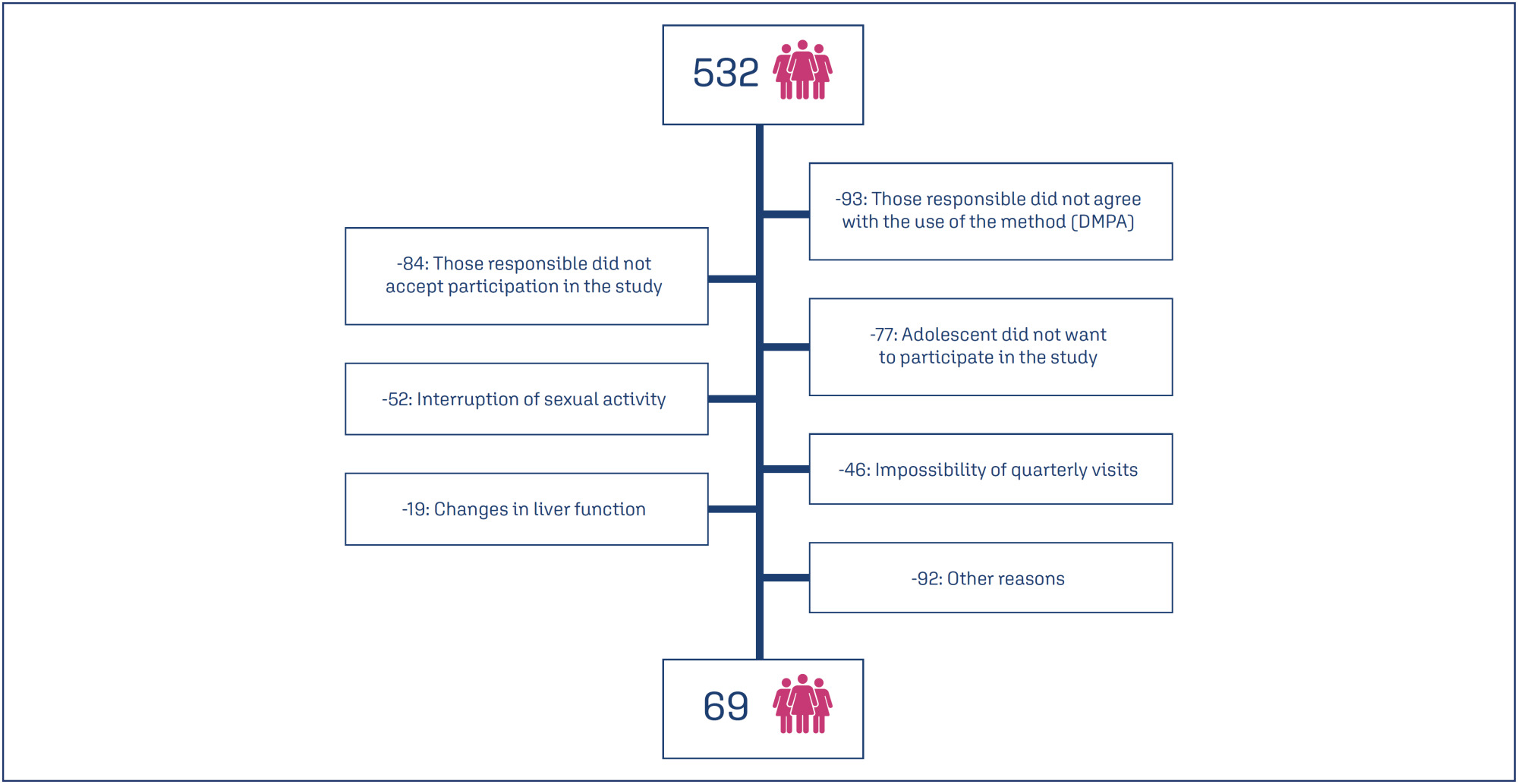
-
Original Article03-18-2025
The experience of pregnancy in the COVID-19 pandemic
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
 ,
, - Cheryl Tatano Beck
 ,
, - Zelina Hilária de Souza Rosa
 ,
, - Erika de Sá Vieira Abuchaim

Abstract
Original ArticleThe experience of pregnancy in the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo8
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
 ,
, - Cheryl Tatano Beck
 ,
, - Zelina Hilária de Souza Rosa
 ,
, - Erika de Sá Vieira Abuchaim

Views187See moreAbstract
Objective:
To describe women’s experience of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods:
A qualitative study conducted in a private maternity hospital, from May, 2020 to November, 2021, with women aged ≥ 18 years, gestational age ≥ 36 weeks at birth and ≥ 24 hours post-partum. Data collected through semi-structured interviews, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed adopting Krippendorff’s Content Analysis as theoretical-methodological framework.
Results:
Four main themes emerged: Fear, Taking care and celebrating pregnancy: adjusting to the new reality, Harms of Isolation, and Benefits of Isolation. The fear of contamination and its impact on the health of mother and child resulted in the adoption of severe social isolation, including from those considered sources of support by the expecting mother. Overwhelmed, some of the participants reported loneliness and psychic suffering. The opportunity to focus on the pregnancy, the preparations for the arrival of the child, and the family made isolation a beneficial and positive period for other women.
Conclusion:
The experience of pregnancy in the Pandemic was an event outside of the ordinary and common. The expecting mother faced her worst fears on a daily basis and attended prenatal care, in order to ensure her child would be born healthy. The celebration of the baby’s life, amid so many deaths, had to be adjusted to the virtual environment. It was a tense, solitary, and ambiguous period, which demanded a lot from the mental health of some participants, but to others, brought advantages that would not have been possible in different times.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 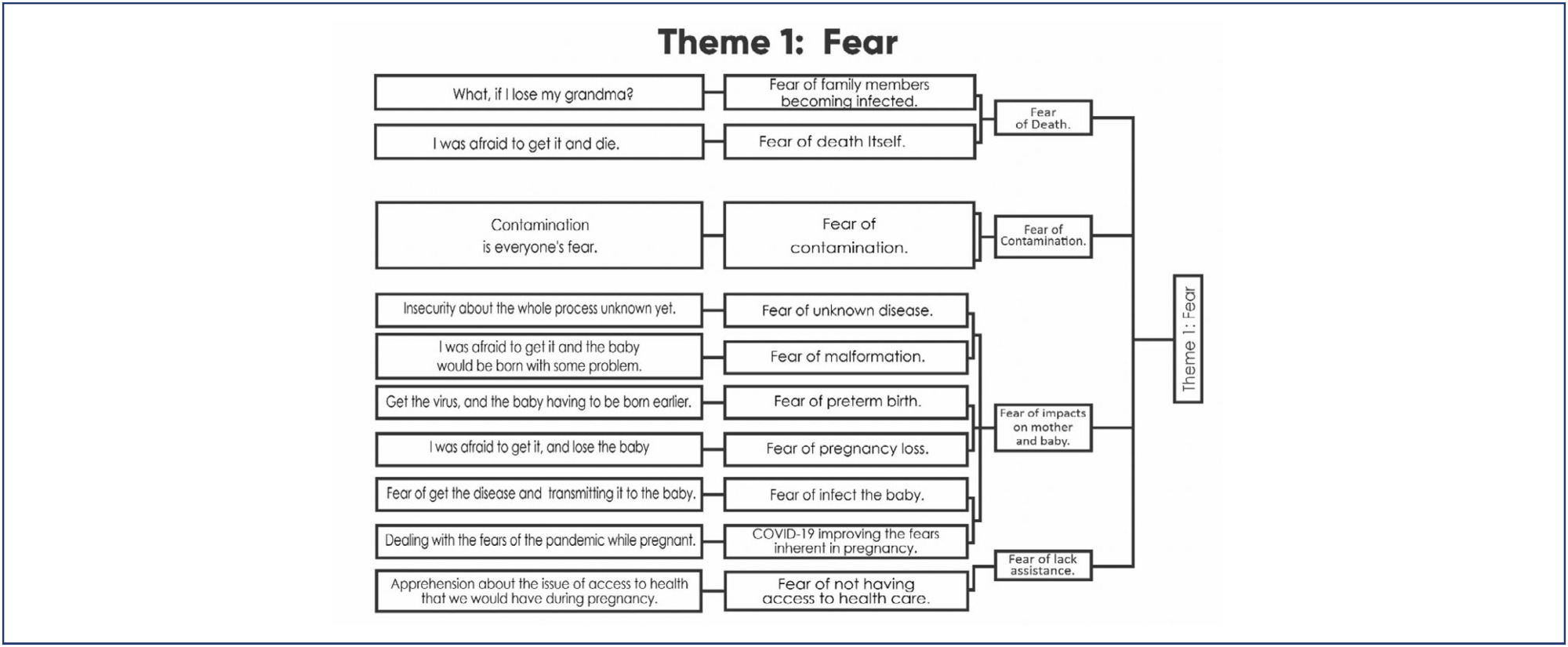
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
-
Original Article03-18-2025
Effect of COVID-19 on Brazilian cesarean and prematurity rates: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo6
Abstract
Original ArticleEffect of COVID-19 on Brazilian cesarean and prematurity rates: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo6
Views166See moreAbstract
Objective:
To investigate the relationship between prematurity and cesarean section rate in Brazil during the beginning of COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods:
Utilizing the Robson Classification, this study analyzed data from the Brazilian Ministry of Health’s Live Births Panel, comparing CSR) and group 10 (preterm deliveries) between 2019 (pre-pandemic) and 2021 (pandemic) in each of Brazilian states and the overall country. The prematurity and CSR were compared using prevalence ratio and confidence interval, and p-value was obtained. The variation of prematurity and CSR were compared through the coefficient of determination (R2).
Results:
A total of 5,522,910 deliveries were evaluated during the period. The CSR increased from 56.34% to 57.05% (p<0.01), and the frequency of preterm deliveries rose from 8.99% to 9.13% (p<0.01). The CSR increased in 23 States and decreased in 4 States, while the prematurity rate increased in 16 States and decreased in 10 States. A positive relationship between the increase of CSR and prematurity was observed during COVID-19, with an R2 value of 0.3121, suggesting a moderate association between these two variables.
Conclusion:
Between 2019 (pre-COVID-19 pandemic) and 2021 (the first full year of the COVID-19 pandemic), there was an increase in prematurity and CSR in Brazil. These increases were observed in most Brazilian states and may be correlated. However, it is impossible to establish a cause-effect relationship given the design of this study.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 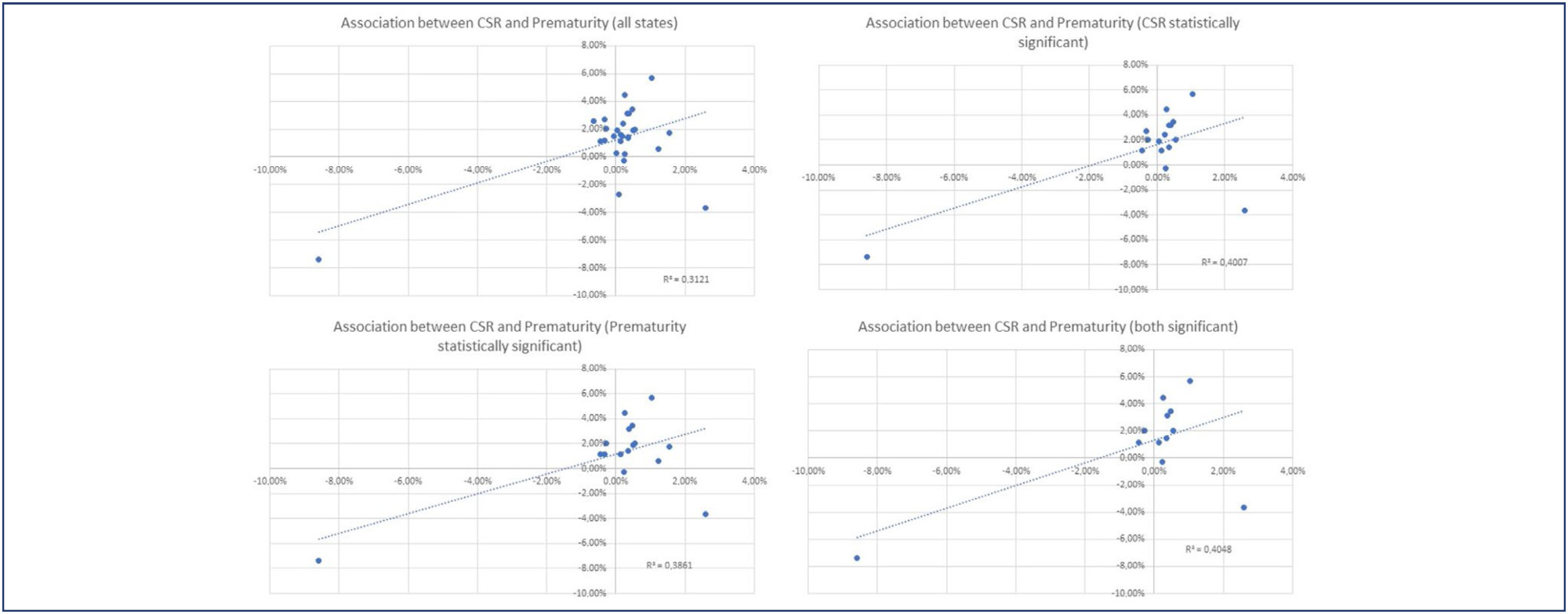
-
Original Article03-18-2025
Accurate evaluation of mode of delivery and labor progression with angle of progression: a prospective cross-sectional
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo5
Abstract
Original ArticleAccurate evaluation of mode of delivery and labor progression with angle of progression: a prospective cross-sectional
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo5
Views156See moreAbstract
Objective:
To determine the validity of the angle of progression (AoP) in predicting delivery mode among women in the second stage of labor.
Designs:
This prospective cohort study was conducted at the Obstetrics and Gynecology unit (OBGYN) of two hospitals in Vietnam. Transperineal ultrasound was performed for each woman to measure the progression angle in the second phase of labor.
Participants:
A total of 725 women with singleton pregnancies with cephalic presentation at term
Methods:
Transperineal ultrasound was used to measure the angle of progression in the second labor phase and to identify the delivery method.
Results:
The rate of vaginal birth in women with an AoP ≥ 120° on transperineal ultrasound was 70.2%. The optimal cutoff point of AOP ≥122° with sensitivity and specificity for vaginal birth were 87.8% and 80.7%, respectively the area under the ROC curve of 0.887 (p<0.0001). The study's sample size was restricted owing to deficiencies in resources and time.
Conclusion:
The likelihood of achieving spontaneous vaginal delivery can be predicted by the angle of progression measured with transperineal intrapartum ultrasonography during the second stage of labor in women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 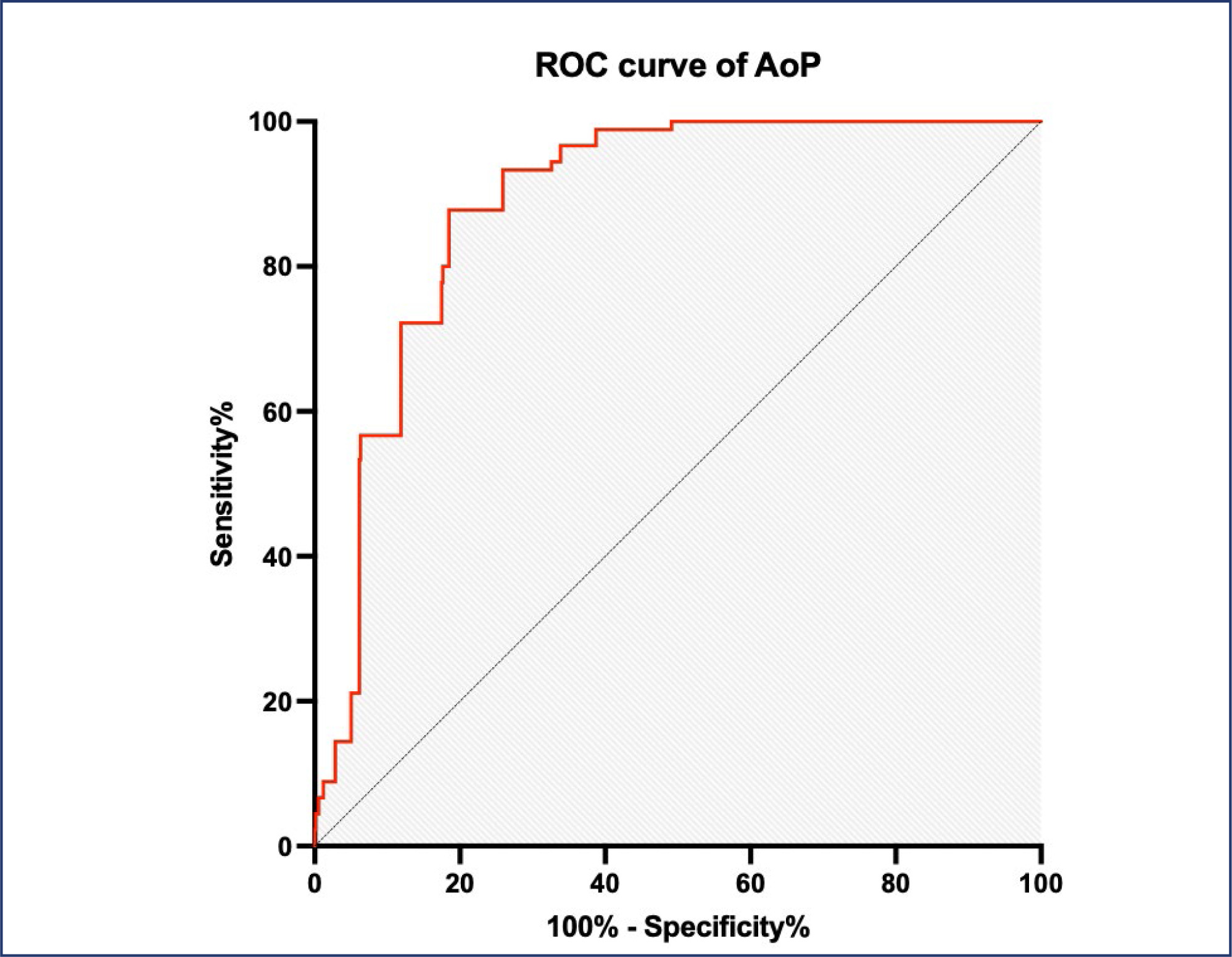
-
Original Article03-18-2025
Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
- Martina Lichtenfels
 ,
, - Rafaella Almeida Lima Nunes
 ,
, - Rossana Veronica Mendoza López
 ,
, - Camila Alves da Silva
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Lara Termini

Views137

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleGastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
- Martina Lichtenfels
 ,
, - Rafaella Almeida Lima Nunes
 ,
, - Rossana Veronica Mendoza López
 ,
, - Camila Alves da Silva
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 ,
, - Vanesca de Souza Lino
 ,
, - Adhemar Longatto-Filho
 ,
, - Louise De Brot
 ,
, - Silvia Helena Rabelo-Santos
 ,
, - Daniela Baumann Cornelio
 ,
, - Enrique Boccardo
 ,
, - Caroline Brunetto de Farias
 ,
, - Lara Termini

Views137Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to verify the relation between gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR), oncogenic Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical lesions severity.
Methods:
GRPR mRNA levels were evaluated in cervical cancer-derived cell lines and in primary keratinocytes expressing HPV16 oncogenes by RT-PCR. GRPR protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry in organotypic cell cultures derived from keratinocytes transduced with HPV16 oncogenes and in 208 cervical samples, including 59 non-neoplastic tissue, 28 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3), 44 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and 77 adenocarcinomas (ADC). Generic primers (GP5+/GP6+) were used to identify HPV infection in tissue samples. Experiments involving cell lines were analyzed through non-parametric tests (Kruskal Wallis), and Fisher’s Exact Test for human tissues samples. All statistical tests were considered significant at p <0.05. Immunohistochemical evaluation was conducted independently and blindly by two observers (AD- LO). Any discordant findings were resolved through discussion to reach a consensus score.
Results:
GRPR mRNA levels were not increased in cells expressing HPV16 or HPV18 oncogenes. However, at the protein level, GRPR was upregulated in organotypic cell cultures containing HPV oncogenes. Besides, it was identified an association between GRPR expression and cervical lesion severity (p < 0.0001). The detection rate of high-risk HPV DNA was directly correlated with cervical disease. Nonetheless, HPV infection was not directly associated with GRPR in cervical samples.
Conclusion:
GRPR expression is highly predictive of cervical lesion severity, irrespective of HPV infection and might contribute to improving patient’s therapeutic management as well as being used a marker of disease progression.
Key-words AdenocarcinomaCarcinoma, squamous cellGastrin-releasing peptide receptorHuman papillomavirusOncogenesPapillomavirus infectionsUterine cervical dysplasiaUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 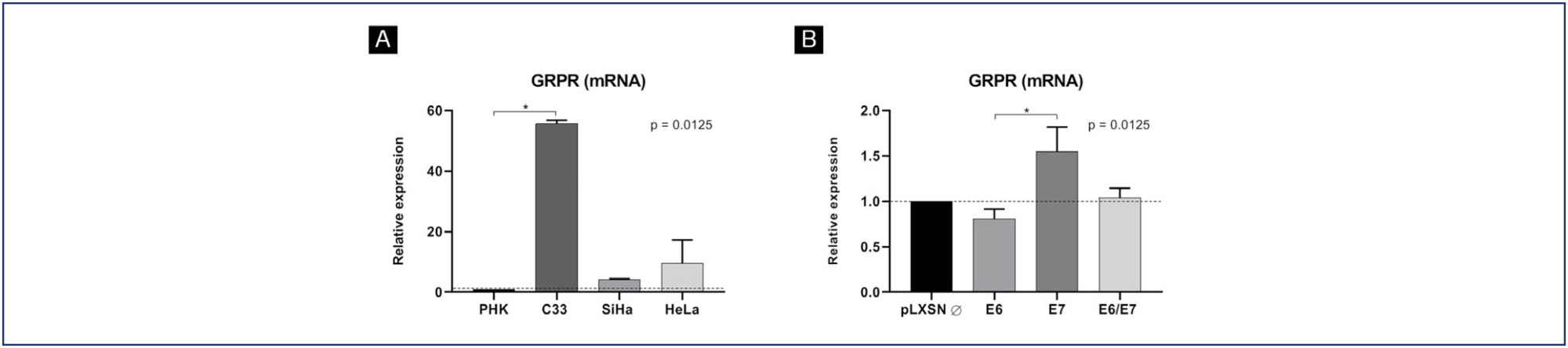
- Martina Lichtenfels
-
Review Article03-18-2025
Low-level laser therapy for nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maria Victória Candida Gaitero
 ,
, - Ticiana Aparecida Alves de Mira
 ,
, - Edna Jéssica Lima Gondim
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita

Abstract
Review ArticleLow-level laser therapy for nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding: systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo3
- Maria Victória Candida Gaitero
 ,
, - Ticiana Aparecida Alves de Mira
 ,
, - Edna Jéssica Lima Gondim
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita

Views147Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to investigate the effect of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) on nipple trauma and pain during breastfeeding through a systematic review with a meta-analysis of selected studies.
Source of the data:
A thorough search was conducted on March 22, 2022, using the databases PubMed, SciELO, LILACS, PEDro, CINAHL, EMBASE, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Google Scholar, MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, Web of Science, TRIP, DARE, and ProQuest. The search terms included various combinations of low-level laser therapy, nipple pain, nipple trauma, and breastfeeding.
Studies selection:
Out of 107 articles identified, only three controlled and randomized clinical trials was included. The extracted data encompassed breast and trauma characteristics, treatment types, outcomes (pain and healing process), evaluation tools, LLLT usage, laser brand, and parameters.
Data collection:
Data extraction was performed using RAYYAN for systematic reviews. The risk of bias in the studies was evaluated.
Data synthesis:
Pain was measured using the visual analog scale (VAS). The included studies did not use validated tools for assessing physical conditions. All studies employed LLLT with a 660-nm wavelength, though there were variations in equipment power, energy dose, and application methods. The meta-analysis revealed an average difference of −0.60 points (95% CI: −1.52 to 0.31) in the VAS pain scores between the LLLT and control groups. No heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2=0%), indicating no significant difference in pain relief between LLLT (red light) and control groups.
Conclusion:
LLLT may offer a promising option for managing breastfeeding-related complications, though further research is required.
Key-words Breast feedingLaser therapyLow level light therapyLow-level laserNipple painNipple traumaNipplesSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Maria Victória Candida Gaitero
-
Review Article03-18-2025
Clinical repercussions of statin use during pregnancy: a review of the literature
- Joan Lins Serafim
 ,
, - Pedro Lucas Santos de Menezes Teles
 ,
, - Amanda Katharinne Souza Lima
 ,
, - Jéssica dos Santos Coelho
 ,
, - Paloma Luna Maranhão Conrado
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - George Alessandro Maranhão Conrado

Abstract
Review ArticleClinical repercussions of statin use during pregnancy: a review of the literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo2
- Joan Lins Serafim
 ,
, - Pedro Lucas Santos de Menezes Teles
 ,
, - Amanda Katharinne Souza Lima
 ,
, - Jéssica dos Santos Coelho
 ,
, - Paloma Luna Maranhão Conrado
 ,
, - Valda Lúcia Moreira Luna
 ,
, - Pauliana Valéria Machado Galvão
 ,
, - George Alessandro Maranhão Conrado

Views126Abstract
Statins are the most widely used pharmacological class for treating hyperlipidemia, although they are contraindicated during pregnancy. This study aims to demonstrate the clinical effects of statins in pregnant women through an interactive review. Fifteen original articles were selected, in English or Portuguese, within of five years. Statins have not been associated with the development of fetal malformations and their use may be useful in preventing unfavorable cardiovascular outcomes, with the potential to reduce oxidative stress and angiogenic dysfunction. However, the use of statins to prevent pre-eclampsia in humans has not been properly clarified and further studies are needed. Pravastatin is considered safer than statins for use during pregnancy.
Key-words Antihypertensive agentsHydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitorsPravastatinPre-eclampsiaPregnancyPregnant womanSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Joan Lins Serafim
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
