- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Female genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views242

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleFemale genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views242Abstract
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) has been evolving since 1978, with the number of techniques performed increasing over the years. Despite continued advances, some couples continue to have difficulties getting pregnant, and it has recently been considered that the microbiome of the female genital tract (FGT) may influence embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. This review aims to evaluate the role of probiotics on reproductive outcomes in infertile women on ART. A search throughout medical databases was performed, and six articles met the criteria. Five studies showed improvements in pregnancy rates, with only one demonstrating statistical significance. One article showed no improvement but reported a statistically significant reduction in the miscarriage rate in the probiotic group. Further research is needed to evaluate the true potential of probiotics, namely to assess whether they effectively modulate the FGT microbiome and if these changes are maintained over time.
Key-words Abortion, spontaneousEmbryo implantationGenitalia, femaleInfertility, femalePregnancy outcomePregnancy rateProbioticsReproductive techniques, assisted, MicrobiotaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article12-04-2024
Prevalence and factors associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among women with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Maria Elisa Franciscatto
 ,
, - Juliana Bosso Taniguchi
 ,
, - Raquel Wohlenberg
 ,
, - Isadora Luísa Riedi
 ,
, - Karen Oppermann

Views286

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence and factors associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo81
- Maria Elisa Franciscatto
 ,
, - Juliana Bosso Taniguchi
 ,
, - Raquel Wohlenberg
 ,
, - Isadora Luísa Riedi
 ,
, - Karen Oppermann

Views286Abstract
Objective:
To verify the prevalence and factors associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) among women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 53 patients with PCOS. The diagnosis of PCOS followed the Rotterdam criteria. The diagnosis of NAFLD was made through US showing hepatic steatosis, excluding significant alcohol consumption and chronic liver disease. The following variables were compared between the groups of women with and without NAFLD: age, race, anthropometric data, blood pressure levels, liver enzymes, glycemic and lipid profiles, total testosterone, presence of hirsutism, and metabolic syndrome (MS). Variables were compared between the groups using T-test, Mann-Whitney, and Chi-square tests.
Results:
Among 53 patients with PCOS, 50.9% had NAFLD. The NAFLD group had higher weight (p=0.003), BMI (p=0.001), waist circumference (p≤0.001), fasting glucose (p=0.021), HbA1C% (p=0.028), triglycerides (p=0.023), AST (p=0.004), ALT (p=0.001), higher prevalence of MS (p=0.004), and lower levels of HDL cholesterol (p=0.043). The other variables did not differ between the groups. Both groups were predominantly of caucasian race, and there was no significant difference in age.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of NAFLD among patients with PCOS was 50.9%. Metabolic and hepatic enzyme abnormalities were more prevalent in this group compared to the group without the disease. Obesity tripled the prevalence of NAFLD.
Key-words Alcohol drinkingHyperandrogenismmetabolic syndromenon-alcoholic fatty liver diseaseObesityPolycystic ovary syndromeWaist circumferenceSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Maria Elisa Franciscatto
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Zuranolone for postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized studies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo79
Abstract
Review ArticleZuranolone for postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized studies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo79
Views303See moreAbstract
Objective:
To evaluate the maternal outcomes in women with postpartum depression using zuranolone, the first oral medication indicated to treat postpartum depression.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic search in September 2023, on Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane Trials. We included randomized controlled trials comparing the effectiveness and safety of zuranolone versus placebo in women with postpartum depression. No time or language restrictions were applied. 297 results were retrieved, of which 11 papers were selected and fully reviewed by two authors. Review Manager 5 was used for statistical analysis and Cochrane Risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials was applied for quality assessment.
Results:
We included 2 studies, with 346 women, of whom 174 (50.2%) were treated with zuranolone. Zuranolone was significantly associated to an improvement of Clinical Global Impression response rate; Hamilton Depression Rating Scale 15 days and 45-day remission, 3-day, 15-day, and 45-day symptom remission, and reduction in the dose of antidepressants. As for safety outcomes, it was noticed that zuranolone increases sedation risk, which can be dose related. No significant differences were found for other adverse events.
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that zuranolone might present a safe and effective medication for out-of-hospital treatment of PPD. Sedation effects need to be further assessed.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-04-2024
Self-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Abstract
Review ArticleSelf-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo77
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 ,
, - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Views295Abstract
Objective:
An in-depth evaluation of the published evidence is needed on self-medication, specifically the evidence focusing on vulnerable groups, such as pregnant women. This scoping review aims to provide an overview of the differences in self-medication prevalence and study characteristics among different groups, while identifying gaps in the literature.
Methods:
A literature search was performed in PubMed and Web of Science, including articles published in the last 10 years for the pregnant women group (PWG) and the general population group (GPG). Data on study design, self-medication prevalence, medications used, and other variables were collected, tabulated, and summarized.
Results:
From 2888 screened articles, 75 were considered including 108,559 individuals. The self-medication (SM) in the PWG ranged from 2.6 to 72.4% and most studies had an SM prevalence between 21 and 50% and in the GPG, 32 from 50 studies had a SM prevalence higher than 50%. The reviewed studies varied considerably in methodology, requiring careful interpretation. While most of the studies assessed self-medication during the entire pregnancy, self-medication definition was often inconsistent between studies. Acetaminophen was the most used medication and headache was the most frequent symptom leading to self-medication initiation in the PWG.
Conclusions:
Self-medication among pregnant women showed a lower prevalence when compared to the general population. The medications used and symptoms reported were similar between groups. However, methodological differences must be carefully considered. Pregnant women should carefully follow their physicians’ advice before initiating self-medication to avoid preventable maternal and fetal adverse effects.
Key-words drug-related side effects and adverse reactionsMedication usePregnant womenSelf-medicationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gabriela Pereira
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT11-25-2024
Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in women: diagnosis and treatment: Number 11 – 2024
- Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Sá Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - José Maria Soares Júnior
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto

Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTNonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in women: diagnosis and treatment: Number 11 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS11
- Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Sá Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - José Maria Soares Júnior
 ,
, - Gabriela Pravatta Rezende Antoniassi
 ,
, - Lia Cruz da Costa Damásio
 ,
, - Técia Maria de Oliveira Maranhão
 ,
, - Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel
 ,
, - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto



This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Andrea Prestes Nácul
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT11-14-2024
Challenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTChallenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Letter to the Editor10-23-2024
The gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
Views164

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Letter to the EditorThe gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
Views164Cervical cancer continues to claim an alarming number of victims around the world, especially among poor women. In Brazil, in 2022, an incidence of 16.3/100,000 women was recorded,() with a projection for 2023 of 17,010 new cases, corresponding to a rate of 15.38/100,000, representing 7% of tumors in women.In the Brazilian reality, where there is […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-23-2024
Nipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
- Antônio Luiz Frasson
 ,
, - Isabela Miranda
 ,
, - Betina Vollbrecht
 ,
, - Carolina Malhone
 ,
, - Ana Beatriz Falcone
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Martina Lichtenfels

Abstract
Original ArticleNipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
- Antônio Luiz Frasson
 ,
, - Isabela Miranda
 ,
, - Betina Vollbrecht
 ,
, - Carolina Malhone
 ,
, - Ana Beatriz Falcone
 ,
, - Fernanda Barbosa
 ,
, - Francisco Pimentel Cavalcante
 ,
, - Martina Lichtenfels

Views176See moreAbstract
Objective:
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Methods:
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
Results:
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Conclusion:
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Antônio Luiz Frasson
-
Original Article07-20-2004
Search for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
- Edison Natal Fedrizzi,
- Newton Sérgio de Carvalho,
- Luisa Lina Villa,
- Irene Vieira de Souza,
- Ana Paula Martins Sebastião
Views125830

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSearch for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400003
- Edison Natal Fedrizzi,
- Newton Sérgio de Carvalho,
- Luisa Lina Villa,
- Irene Vieira de Souza,
- Ana Paula Martins Sebastião
Views125830See moreOBJECTIVE: to compare the prevalence of DNA of human papillomavirus (HPV), in samples of normal endometrial tissue, and tissue with endometrial carcinoma of women submitted to surgical treatment (hysterectomy), or between endometrial carcinoma and benign disease, through the PCR technique. METHODS: this is an observational control-case study where 100 women (50 with endometrial carcinoma and 50 with normal endometrial tissue) were analyzed for the detection of HPV DNA in samples of endometrial tissue kept in paraffin blocks by the PCR technique. The cases of endometrial carcinoma with uncertain primary site of the lesion as well as the cases with previous or current history of pre-neoplasic lesions or carcinoma of the lower genital tract were excluded. Variables as age, smoking habit, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation were also evaluated. RESULTS: the estimated relative risk of the presence of HPV in the endometrial carcinoma and in the normal endometrial tissue was the same. HPV was detected in 8% of the cases of carcinoma and 10% in the normal endometrial tissue. In spite of HPV having been 3.5 times more detected in women with smoking habit in the group without carcinoma, there was no statistical difference. The presence of HPV was also not correlated with the women’s age, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation. The HPV types 16 (5 cases) and 18 (4 cases) were the viruses most frequently found both in the normal endometrial tissue or in the tissue with carcinoma. No oncogenic low risk virus was detected in the samples. CONCLUSION: The same proportion of HPV is present in the endometrial tissue of women with endometrial cancer and with normal endometrium. It could not be demonstrated a possible correlation of DNA of HPV with the development of endometrial carcinoma.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
 ,
, - Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel
 ,
, - Vania dos Santos Nunes Nogueira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Glezer

Views1199

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 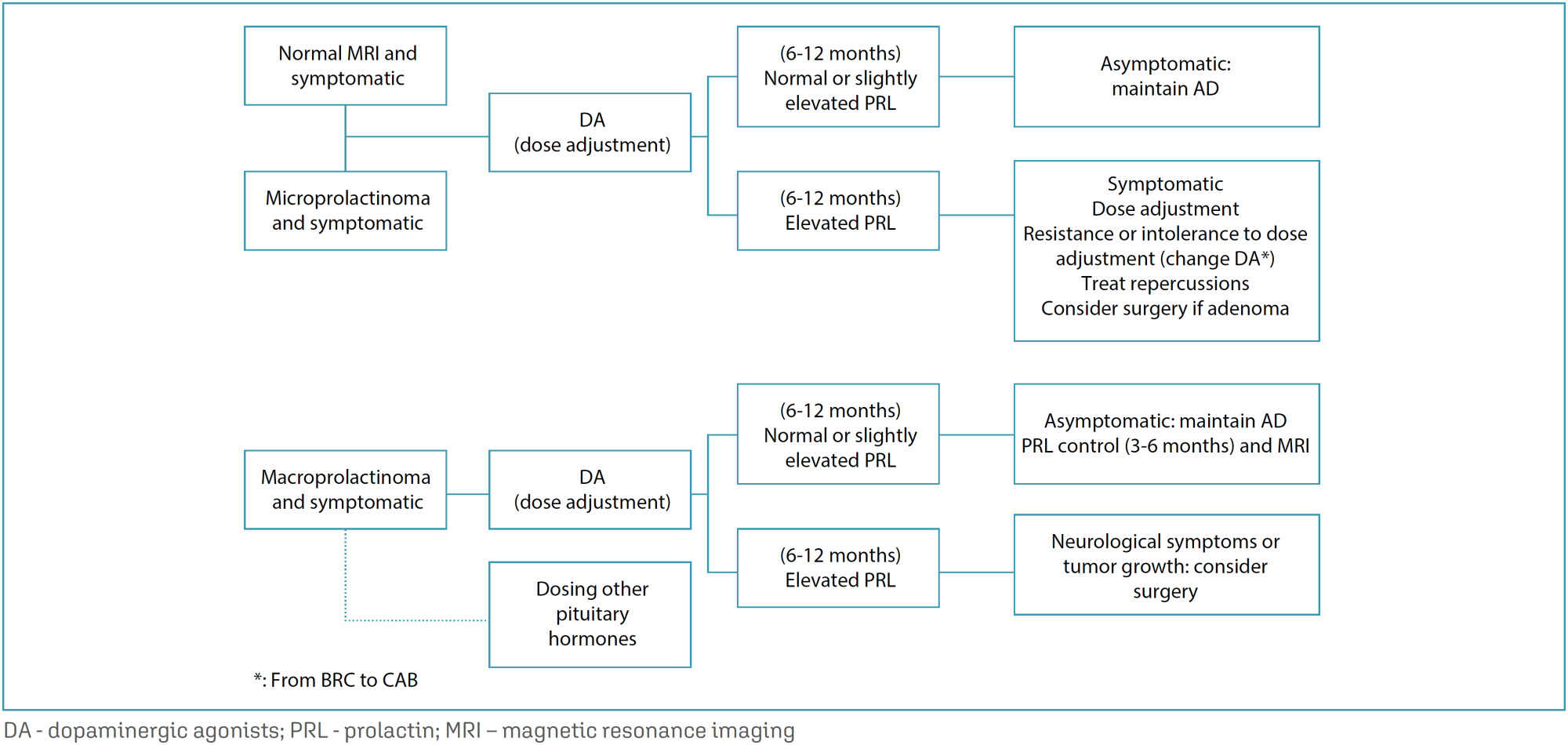
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
- Andrea Glezer
 ,
, - Heraldo Mendes Garmes
 ,
, - Leandro Kasuki
 ,
, - Manoel Martins
 ,
, - Paula Condé Lamparelli Elias
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Prestes Nácul

Views1200

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 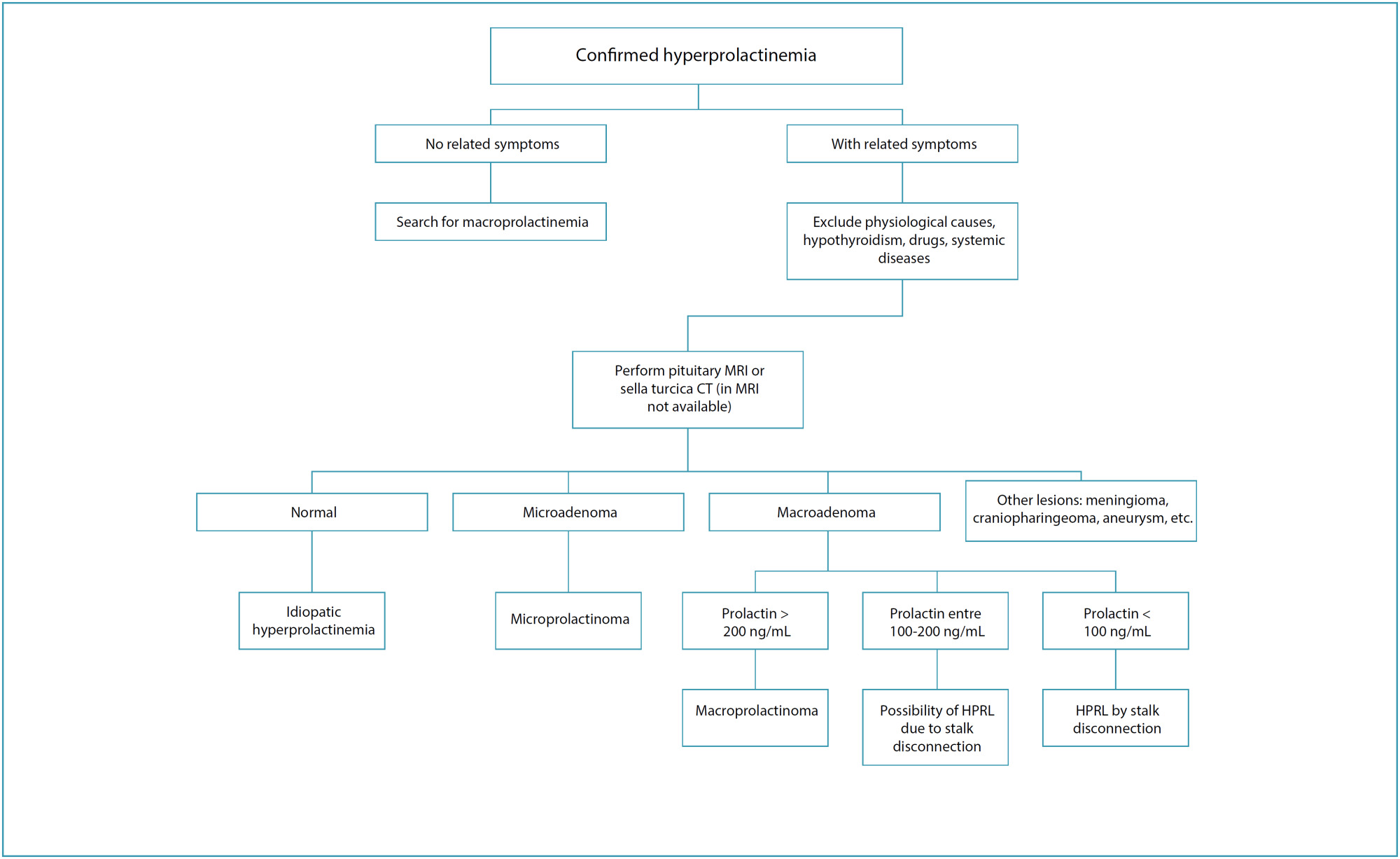
- Andrea Glezer
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT00-00-2024
Breech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
- Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
 ,
, - Alexandre Massao Nozaki
 ,
, - Carla Betina Andreucci Polido
 ,
, - Lucas Barbosa da Silva
 ,
, - Roxana Knobel

Views1004

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTBreech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
- Gustavo Romero-Velez
 ,
, - Guillermo Ponce de Leon-Ballesteros
 ,
, - Juan Barajas-Gamboa
 ,
, - Jerry Dang
 ,
, - Andrew Strong
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Mathew Kroh

Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gustavo Romero-Velez
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Use of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views829

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 ,
, - Marcos Arêas Marques
 ,
, - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views829See moreKey points
•The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is not increased in women using long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARCs) with progestogens.
•Oral contraceptives with levonorgestrel or norgestimate confer half the risk of VTE compared to oral contraceptives containing desogestrel, gestodene or drospirenone.
•Progestogen-only pills do not confer an increased risk of VTE.
•Women using transdermal contraceptive patches and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are at an approximately eight times greater risk of VTE than non-users of hormonal contraceptives (HCs), corresponding to 9.7 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Vaginal rings increase the risk of VTE by 6.5 times compared to not using HC, corresponding to 7.8 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of VTE in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy (HT).
•Hormone therapy during menopause increases the risk of VTE by approximately two times, and this risk is increased by obesity, thrombophilia, age over 60 years, surgery and immobilization.
•The route of estrogen administration, the dosage and type of progestogen associated with estrogen may affect the risk of VTE in the climacteric.
•Combined estrogen-progesterone therapy increases the risk of VTE compared to estrogen monotherapy.
•Postmenopausal HT increases the risk of thrombosis at atypical sites.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
-
Editorial00-00-2024
The path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
- Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
 ,
, - Cecilia Maria Roteli-Martins
 ,
, - Neila Maria de Góis Speck
 ,
, - Newton Sérgio de Carvalho
 ,
, - Eduardo Batista Cândido
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Júlio César Teixeira

Views819

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialThe path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgoedt2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views781

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTVulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 ,
, - Ivete Canti
 ,
, - Marcos Takimura
 ,
, - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views781See moreKey points
• The balanced vaginal microbiome is the main factor defending the vaginal environment against infections. Lactobacilli play a key role in this regard, maintaining the vaginal pH within the normal range (3.8 to 4.5).
•Hormonal and immune adaptations resulting from pregnancy influence changes in the vaginal microbiome during pregnancy.
•An altered vaginal microbiome predisposes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
•Bacterial vaginosis is the main clinical expression of an imbalanced vaginal microbiome.
•Vulvovaginal candidiasis depends more on the host’s conditions than on the etiological agent.
•Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan transmitted during sexual intercourse.
•The use of probiotics is not approved for use in pregnant women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Geraldo Duarte
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci, [ … ],
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci,
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial09-01-2018
Maternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra, [ … ],
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views222

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):501-506
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra,
- Carmen Simone Grilo Diniz,
- Brenno Belazi Nery de Souza Campos,
- Eliana Martorano Amaral,
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views222Maternal mortality is one of the health indicators that most reflect the social conditions of women. The inequities observed in this indicator between high- and low-income countries and among regions in the same country are explained by differences in the provision, in the access, and in the quality of obstetric care and of family planning. […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-27-2019
Quality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva, [ … ],
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):312-317
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva,
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the quality of life among university students with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Methods
The cross-sectional study was conducted at the Faculdade Pernambucana de Saúde, in Recife, Brazil, between August 2016 and July 2017. Sociodemographic, gynecological, and lifestyle variables, and PMS occurrence, were investigated among 642 students. The short form of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL Bref) questionnaire was used to evaluate four domains of the quality of life of the students: physical, mental, social relationships, and environmental. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ criteria were used to define PMS.
Results
Of the 642 students, 49.9% had PMS, 23.3% had mild PMS and 26.6% had premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Most of the students were between 18 and 24 years old, had regular menstrual cycles, and practiced physical activity. Regarding the physical and mental domains of the WHOQOL-Bref questionnaire, a statisticallysignificant difference was observed between the students who did not have and those who had mild or PMDD (p < 0.001). A difference was also found between the students who did not have PMS and those who had mild PMS in the social relationships (p = 0.001) and environmental domains (p = 0.009).
Conclusion
Mild PMS and PMDD are prevalent among university students on healthrelated courses, and the syndrome can affect the students’ self-assessment of all the domains of quality of life.
Key-words medical studentMenstruation disturbancespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuality of lifeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article06-01-2016
Selective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views197

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSelective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views197See moreAbstract
Introduction
Episiotomy is a controversial procedure, especially because the discussion that surrounds it has gone beyond the field of scientific debate, being adopted as an indicator of the “humanization of childbirth”. The scientific literature indicates that episiotomy should not be performed routinely, but selectively.
Objectives
To review the literature in order to assess whether the implementation of selective episiotomy protects against severe perineal lacerations, the indications for the procedure, and the best technique to perform it.
Methods
A literature search was performed in PubMed using the terms episiotomy or perineal lacerations, and the filter clinical trial. The articles concerning the risk of severe perineal lacerations with or without episiotomy, perineal protection, or episiotomy techniques were selected.
Results
A total of 141 articles were identified, and 24 of them were included in the review. Out of the 13 studies that evaluated the risk of severe lacerations with and without episiotomy, 5 demonstrated a protective role of selective episiotomy, and 4 showed no significant differences between the groups. Three small studies confirmed the finding that episiotomy should be performed selectively and not routinely, and one study showed that midline episiotomy increased the risk of severe lacerations. The most cited indications were primiparity, fetal weight greater than 4 kg, prolonged second stage, operative delivery, and shoulder dystocia. As for the surgical technique, episiotomies performed with wider angles (> 40°) and earlier in the second stage (before “crowning “) appeared to be more protective.
Conclusions
Selective episiotomy decreases the risk of severe lacerations when compared with the non-performance or the performance of routine episiotomy. The use of a proper surgical technique is fundamental to obtain better results, especially in relation to the angle of incision, the distance from the vaginal introitus, and the correct timing for performing the procedure. Not performing the episiotomy when indicated or not applying the correct technique may increase the risk of severe perineal lacerations.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 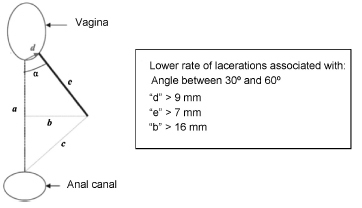
-
Review Article08-01-2017
Physical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views236

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePhysical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views236See moreAbstract
The literature that supports and recommends the practice of exercise during pregnancy is extensive.However, although a more complete research on ways to evaluate the physical activity performedby pregnant women has been perfomed, it is found that there is no gold standard and that the articles in the area are inconclusive. Thus, the objective of the present article is to review relevant aspects, such as, technique and applicability of the different methods for the assessment of physical activity during pregnancy to providemore reliable and safe information for health professionals to encourage their pregnant patients to engage in the practice of physical activity. This review concluded that all tools for the analysis of physical activity have limitations. Thus, it is necessary to establish the objectives of evaluation in an appropriate manner, as well as to determine their viability and costeffectiveness for the population under study.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article02-01-2017
Predictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePredictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232See moreAbstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate which risk factors may lead patients with gestational diabetes mellitus to cesarean delivery.
Methods
This was a retrospective, descriptive study. The subjects of the study were pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus attending a public maternity hospital in the south of Brazil. The primary outcomes assessed were based on maternal and fetal characteristics. The data were correlated using an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), calculated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 392 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were analyzed, and 57.4% of them had cesarean deliveries. Among the maternal characteristics, the mean age of the patients and the pregestational body mass index were greater when a cesarean delivery was performed (p = 0.029 and p < 0.01 respectively). Gestational age at birth, newborn weight, weight class according to gestational age, and Apgar score were not significant. The analysis of the OR showed that the chance of cesarean delivery was 2.25 times (95%CI = 1.49-2.39) greater if the pregnant woman was obese, 4.6 times (95%CI = 3.017-7.150) greater if she was a primigravida, and 5.2 times (95% CI = 2.702-10.003) greater if she had a previous cesarean delivery. The other parameters analyzed showed no differences.
Conclusion
The factors that led to an increase in the occurrence of cesarean deliveries included history of a prior cesarean section, first pregnancy, and obesity.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial12-01-2015
Maternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551
Views104

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article08-21-2015
Increased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu, [ … ],
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleIncreased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):411-416
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005397
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu,
- Fatma Meriç Yılmaz,
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91See morePURPOSE:
The aim of this study was to evaluate serum levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (INOS), myeloperoxidase (MPO), total antioxidant status (TAS), and total oxidative status (TOS) in women with primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) and to compare them with healthy fertile women. We also examined the possible risk factors associated with POI.
METHODS:
This cross-sectional case control study was conducted in Zekai Tahir Burak Women’s Health Education and Research Hospital. The study population consisted of 44 women with POI (study group) and 36 healthy fertile women (control group). In all patients, serum levels of INOS, MPO, TAS, and TOS were determined. INOS and MPO levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay whereas colorimetric method was used for evaluating TAS and TOS levels. Age, body mass index (BMI), obstetric history, smoking status, family history, comorbidities, sonographic findings, complete blood count values, C-reactive protein and baseline hormone levels were also analyzed. Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables between the groups; categorical data were evaluated by using Pearson χ2 or Fisher exact test, when appropriate. Binary logistic regression method was used to identify risk factors for POI.
RESULTS:
We found significantly elevated levels of INOS (234.1±749.5 versus133.8±143.0; p=0.005), MPO (3,438.7±1,228.6 versus 2,481.9±1,230.1; p=0.001), and TOS (4.3±1.4 versus 3.6±1.4; p=0.02) in the sera of the study group when compared to the BMI-age matched control group. However, difference in serum levels of TAS were not significant between the 2 groups (1.7±0.2 versus 1.6±0.2; p=0.15). Logistic regression method demonstrated that BMI <25 kg/m2, nulliparity, family history of POI, smoking, and elevated serum levels of INOS, MPO, and TOS were independent risk factors for POI.
CONCLUSION:
We found an increase in INOS, MPO, and TOS in women with POI. These serum markers may be promising in early diagnosis of POI. Further large-scale studies are required to determine whether oxidative stress markers have a role in diagnosing POI.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)

