-
Original Article01-04-2000
Stress Urinary Incontinence Correction with Sling: First Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):301-305
Abstract
Original ArticleStress Urinary Incontinence Correction with Sling: First Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):301-305
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500008
Views141See morePurpose: to analyze the surgical results after slings with vaginal wall, performed by the Urogynecology and Vaginal Surgery Sector of UNIFESP/EPM, for the treatment of incontinent women with hypermobility of the bladder neck, who show great risk of surgery failure with other techniques or in those with intrinsic sphincteric deficiency (ISD) and, also, surgery recurrence. Methods: we studied 21 patients submitted to surgery in order to correct urinary incontinence by the vaginal wall sling technique, in the period from December 1997 to February 1999, with postoperative follow-up which varied between 1 and 14 months (average 8.2). The mean age of patients was 56 years (39 to 77 years), 15 (71.4%) were in menopause and 6 (28.6%) in menacme. All patients were evaluated before the surgery through medical interview, physical examination, ultrasound and urodynamic study, the grade of urinary loss being high in 66.7% and moderate in 33.3% of the patients. All patients showed hypermobility of the bladder neck (more than 10 mm) and 12 patients had previous surgery to correct the urinary incontinence. Regarding the urodinamic study, the patients manifested urinary loss with maximum pressure of urethral closure (MPUC) varying from 20 to 124 cmH2O (average 55.2) and Valsalva leak point pressure (VLPP) varying from 18 to 128 cmH2O (average 60.3). The indications of surgery were: ISD (11 patients — 52.4%), obesity (5 patients — 23.8%), ISD and obesity (2 patients — 9.5%), surgery recurrence (2 patients — 9.5) and ISD and first grade womb prolapse (1 patient — 4.8%). Results: as complications, 6 patients (28.6%) showed temporary urinary retention after surgery, 1 patient (4.8%) infection in the urinary tract, 1 patient (4.8%) presence of polypropylene suture in the vagina, 1 patient (4.8%) infection of the surgery wound, 4 patients (19%) developed urgency/incontinence, 1 (4.8%) urgency and 1 (4.8%) difficulty in urinating (high postvoiding residue). The grade of the patients’ satisfaction was satisfactory, with 15 patients (71.4%) referring cure, 3 patients (14.3%) improvement, in 2 patients (9.5%) the urinary loss remained unchanged and in 1 patient (4.8%) the urinary loss got worse. Conclusions: the vaginal wall sling surgery is efficient for the treatment of specific cases of stress urinary incontinence, emphasizing intrinsic urethral sphincteric incompetence, surgery recurrence and predisposing factors to failure of other techniques.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Role of Sonohysterography in the Evaluation of the Uterine Cavity in Patients with Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):293-299
Abstract
Original ArticleRole of Sonohysterography in the Evaluation of the Uterine Cavity in Patients with Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):293-299
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500007
Views121See morePurpose: to determine the role of sonohysterography in the evaluation of abnormalities in the uterine cavity in patients presenting abnormal uterine bleeding, who had previously been selected by transvaginal ultrasonography. Methods: forty-eight patients presenting abnormal uterine bleeding and changes in the uterine cavity seen by transvaginal ultrasonography were selected, and they were in the menacme or postmenopause period. All patients underwent a sonohysterography, and later a hysteroscopy and/or a hysterectomy. The sonohysterographies were evaluated by two different physicians, and the diagnoses were compared. Results: the sonohysterography method showed high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of benign pathologies in the uterine cavity. First, in the presence of polyps the sensitivity and specificity rates were 100 and 97%, respectively, second, in the presence of submucous myoma, they were 83 and 100%, and finally, concerning endometrial hyperplasia and normal endometrium, they were 100%. We diagnosed thirty-three cases of polyps, thirteen cases of submucous myoma, four cases of endometrial hyperplasia and three normal cases. The correlation between the diagnoses provided by the two physicians was high. Conclusions: sonohysterography is a safe and fast method which is very well tolerated by the patient, and has low levels of complications. Its high sensitivity and specificity allow this method to be used for routine diagnosis concerning benign pathologies in the uterine cavity of patients presenting abnormal uterine bleeding.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Variation of Blood Pressure in Users of Hormone Replacement Therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):287-292
Abstract
Original ArticleVariation of Blood Pressure in Users of Hormone Replacement Therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):287-292
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500006
Views143See morePurpose: to evaluate the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on the systolic and diastolic blood pressure of postmenopausal women. Methods: a total of 166 users and 136 non-users of hormone replacement were evaluated retrospectively during a period of three years. All women were assisted at the Menopause Outpatient Clinic of CAISM — Unicamp, where the variations of these parameters were evaluated at the end of each year in relation to the initial parameters. The data analysis was performed through Student’s t test, Mann-Whitney test, and the Wilcoxon nonparametric test. Results: we observed that the systolic blood pressure of HRT users was statistically lower at the end of the third year of use, compared to the initial values (p = 0.01). There was no significant difference in the diastolic blood pressure between users and non-users. Conclusion: hormone replacement therapy did not produce changes in the parameters studied in women properly assisted during the use of HRT.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Fetal Growth with the use of the Transverse Cerebellar Diameter
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):281-286
Abstract
Original ArticleUltrasonographic Evaluation of Fetal Growth with the use of the Transverse Cerebellar Diameter
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):281-286
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500005
Views132See morePurpose: to evaluate the effectiveness of the transverse cerebellar diameter (TCD), by ultrasonography, in the evolution of the fetal growth, and to relate it to gestational age, biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur length (FL). Method: a prospective and longitudinal study was performed on 254 pregnant women considered of low risk, with a gestational age from 20 to 40 weeks. Only 55 pregnant women were included in the study, according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. All the examinations, 217 ultrasonographic evaluations, were done by the author (LN), at least three and at most six examinations for each pregnant woman being accomplished at an interval of one to five weeks. Normality patterns were established between the 10 and 90 percentiles for each gestational age and confirmed postnatally. Results: the transverse cerebellar diameter presented a good correlation with the gestational age either as a dependent variable (R² = 0.90) or as an independent variable (R² = 0.92). A significant relationship was found in the evaluation of the fetal growth between the TCD and the several fetal parameters: BPD and HC (R² = 0.92), FL (R² = 0.90) and AC (R² = 0.89). Conclusions: the transverse cerebellar diameter is a parameter that should be used in the follow-up of development and of fetal growth because of the ascending pattern of its growth curve. Any up- or downward alteration in the growth curve can be useful for the detection of deviations of fetal growth.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Ultrasound Findings in First-trimester Threatened Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):275-279
Abstract
Original ArticleUltrasound Findings in First-trimester Threatened Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):275-279
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500004
Views97See moreObjective: to evaluate ultrasound findings in pregnant women with threatened abortion in the first trimester of pregnancy. Methods: transabdominal and transvaginal ultrasound scans were performed in patients with vaginal bleeding with previous positive pregnancy test. Patients with 6-14-week gestation (by the last menstrual period or ultrasound scan), with closed cervix on clinical evaluation were included. Multiple pregnancies and those patients who have tried abortion by using abortive drugs or manipulation were excluded. Results: in 132 of 247 (53.4%) the pregnancy was viable and in 46.6% (115/247) the pregnancy was nonviable. Incomplete miscarriage was found in 19% (47/247), complete miscarriage in 8.5% (21/247), missed abortion in 7.7% (19/247), anembryonic pregnancy in 6.1% (15/247), ectopic pregnancy in 4.5% (11/247) and hydatidiform mole in 0.8% (2/247). Conclusion: almost half (46.6%) of the pregnancies with threatened abortion in the first trimester were diagnosed as a nonviable pregnancy. The ultrasound scan can help to define this condition and the management of the pregnancy.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Use of Verapamil in Chronic Hypertensive Pregnant Women: flow Analysis of Uterine Arteries and Umbilical Artery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):265-274
Abstract
Original ArticleUse of Verapamil in Chronic Hypertensive Pregnant Women: flow Analysis of Uterine Arteries and Umbilical Artery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):265-274
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500003
Views141See morePurpose: this study, using verapamil, a slow calcium channel blocker, was a randomized, clinical, double blind and placebo controlled trial, whose objective was to observe if there was a uteroplacental and fetoplacental flow variation during its chronic oral use. Methods: 123 patients were accompanied: study group (n = 61), submitted to verapamil 240 mg/day and control group (n = 62), submitted to placebo. These patients were randomized into groups of four women and treatment or placebo was given for thirty days. A flow examination of the uterine arteries and umbilical artery through doppler-velocimetry was recorded. The values of resistance (RI) and pulsatility index (PI) and of the systole/diastole ratio (S/D) of the arteries were compared after the drug administration calculating means and standard deviations. Results: the verapamil group showed RI = 0.82 (0.28), PI = 1.06 (0.12) and S/D = 2.42 (0.51) in the uterine arteries. The placebo group showed RI = 0.75 (0.35), PI = 1.00 (0.18) and S/D = 2.30 (0.38). When we analyzed the umbilical artery, the verapamil group showed RI = 0.73 (0.12), PI = 1.04 (0.13) and S/D = 2.94 (0.32). The placebo group showed RI = 0.70 (0.14), PI = 1.03 (0.07) and S/D = 3.02 (0.78). The statistical analysis of the differences of the means by the F ratio showed that there was no difference between these two groups. Conclusion: this study indicates the use of verapamil for chronic hypertensive pregnants since it does not provoke damage to the uterine and fetal blood flow.
-
Original Article01-04-2000
Comparative Study of Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes among Patients with Pregestational Type I and Type II Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):257-263
Abstract
Original ArticleComparative Study of Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes among Patients with Pregestational Type I and Type II Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):257-263
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000500002
Views127See morePurpose: to evaluate the evolution of gestation, metabolic control and perinatal outcome of pregestational diabetic patients and to perform a comparative study of the results of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes (type I) and non-insulin-dependent diabetes (type II). Methods: retrospective analysis of 57 pregestational diabetic woman charts who began a prenatal follow-up in the Service of Maternofetal Medicine of the Maternidade-Escola Assis Chateaubriand of the Universidade Federal do Ceará, in the period from January 1995 to December 1998. The 57 pregnant women included in the study were divided into groups: the first, composed of 28 patients with insulin-dependent diabetes (type I), and the second with 29 pregnant women with non-insulin-dependent diabetes (type II), controlled with diet or with oral hypoglycemics before pregnancy. Results: there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in relation to the need of hospitalization for glycemia control (39.2% x 27.5%) and maternal complications, such as: chronic arterial hypertension (14.2% x 27.5%), pregnancy-induced hypertension (14.2% x 17.2%), premature rupture of membranes (3.5% x 10.3%), urinary tract infection (10.7% x 6.8%), and preterm labor (3.5% x 6.8%). However, episodes of maternal hypoglycemia were more frequent among insulin-dependent patients (35.7% x 3.4%). The perinatal results were similar. We observed a great number of congenital anomalies and increased perinatal morbidity and mortality. Conclusion: there was no difference in the incidence of obstetric and clinical complications between insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent patients, except for maternal hypoglycemia.
-
01-04-2000
Gravidez na Adolescência
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(5):256-256
-
Case Report04-01-2016
Prenatal Diagnosis of Lissencephaly Type 2 using Three-dimensional Ultrasound and Fetal MRI: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):201-206
Abstract
Case ReportPrenatal Diagnosis of Lissencephaly Type 2 using Three-dimensional Ultrasound and Fetal MRI: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):201-206
Views209Abstract
Lissencephaly is a genetic heterogeneous autosomal recessive disorder characterized by the classical triad: brain malformations, eye anomalies, and congenital muscular dystrophy. Prenatal diagnosis is feasible by demonstrating abnormal development of sulci and gyri. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may enhance detection of developmental cortical disorders as well as ocular anomalies. We describe a case of early diagnosis of lissencephaly type 2 detected at the time of routine second trimester scan by three-dimensional ultrasound and fetal MRI. Gross pathology confirmed the accuracy of the prenatal diagnosis while histology showed the typical feature of cobblestone cortex. As the disease is associated with poor perinatal prognosis, early and accurate prenatal diagnosis is important for genetic counseling and antenatal care.
Key-words cobblestone cortexGenetic counselinglissencephalyMagnetic resonance ImagingPathologyprenatal diagnosisthree-dimensional ultrasoundSee more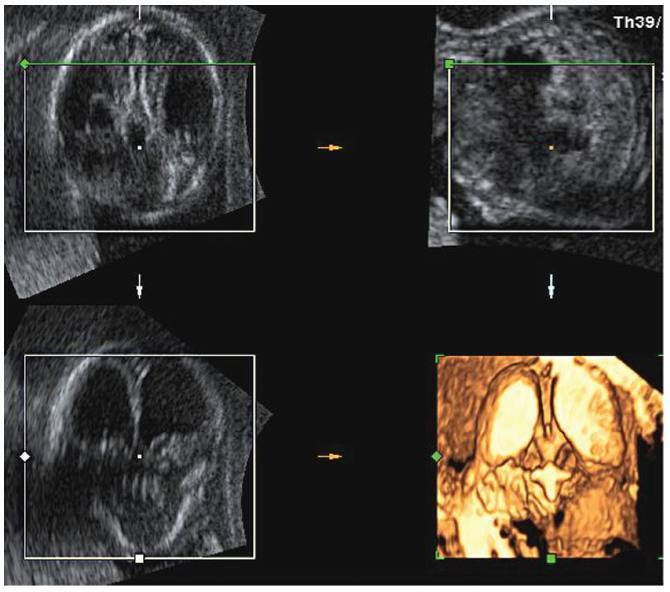
-
Short Communication12-01-2017
Nutritional Counseling Promotes Changes in the Dietary Habits of Overweight and Obese Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):692-696
Abstract
Short CommunicationNutritional Counseling Promotes Changes in the Dietary Habits of Overweight and Obese Adolescents with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):692-696
Views208See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the effects of nutritional counseling on the dietary habits and anthropometric parameters of overweight and obese adolescentswith polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Methods
This was a prospective, longitudinal and auto-controlled study. Thirty adolescents aged 13-19 years-old, diagnosed with PCOS received nutritional counseling and were followed-up for 6 months. After the follow-up period, the results were evaluated through body weight, body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC).
Results
Sixty-percent of the adolescents adhered to the nutritional counseling and, of these, 50% lost weight. Adolescents who lost weight changed their dietary habits by adopting hypocaloric diets and eating more meals per day, as per nutritional counseling. The waist circumference (WC) decreased significantly, although the body weight decreased non-significantly after adoption of a hypocaloric diet.
Conclusion
Although there was no significant weight loss, there was a considerable reduction in theWCassociated with hypocaloric diets and with eating a greater number of meals per day.
-
Original Article04-15-2019
The Influence of Light Exposure in Ambiance during Pregnancy inMaternal and Fetal Outcomes: An Experimental Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):24-30
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Influence of Light Exposure in Ambiance during Pregnancy inMaternal and Fetal Outcomes: An Experimental Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(1):24-30
Views208See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate whether exposure to different environmental lighting conditions affects the reproductive parameters of pregnant mice and the development of their offspring.
Methods
Fifteen pregnant albino mice were divided into three groups: light/dark, light, and dark. The animalswere euthanized on day 18 of pregnancy following the Brazilian Good Practice Guide for Euthanasia of Animals.Maternal and fetal specimens weremeasured and collected for histological evaluation. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used for comparison of the groups considering p ≤ 0.05 to be statistically significant.
Results
There was no significant difference in the maternal variables between the three groups. Regarding fetal variables, significant differences were observed in the anthropometric measures between the groups exposed to different environmental lighting conditions, with the highest mean values in the light group. The histological evaluation showed the same structural pattern of the placenta in all groups, which was within the normal range. However, evaluation of the uterus revealed a discrete to moderate number of endometrial glands in the light/dark and light groups, which were poorly developed in most animals. In the fetuses, pulmonary analysis revealed morphological features consistent with the transition from the canalicular to the saccular phase in all groups.
Conclusion
Exposure to different environmental lighting conditions had no influence on the reproductive parameters of female mice, while the offspring of mothers exposed to light for 24 hours exhibited better morphometric features.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT12-17-2021
Fertility preservation in women with endometriosis Number 10 – October 2021
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):796-801
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTFertility preservation in women with endometriosis Number 10 – October 2021
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):796-801
-
Original Article01-24-2021
Overview of the Effect of Complementary Medicine on Treating or Mitigating the Risk of Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):919-925
Abstract
Original ArticleOverview of the Effect of Complementary Medicine on Treating or Mitigating the Risk of Endometriosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):919-925
Views194See moreAbstract
Objective
Endometriosis is a hormone-dependent chronic inflammatory disease with symptoms such as pelvic pain, which affect the physical, emotional, and social health of women in reproductive age. The current overview article aims to explore the effect of complementary medicine on the treatment or in mitigating the risk of endometriosis.
Methods
This is an overview article done in Iran. Two separate researchers systematically searched 3 databases (Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane Central Register Trials) until September 2020. The methodological quality of each study was assessed using the assessment of multiple systematic reviews (AMSTAR) tool.
Results
The results of two reviews suggested that physical activity, tobacco smoking, diet, coffee and caffeine intake had no effect on mitigating the risk of endometriosis or improving its treatment, but acupuncture successfully reduced pain and related marker (serum CA-125) levels.
Conclusion
As endometriosis is an annoying disease with many complications and is hard to diagnose and treat, related studies in complementary medicine can help patients with endometriosis. Based on the relevant literature review, among the complementary medicine available for the treatment or to mitigate the risk of endometriosis, only acupuncture seems to alleviate the pain of endometriosis.
-
Original Article07-07-2022
Increment of Maternal Mortality Among Admissions for Childbirth in Low-risk Pregnant Women in Brazil: Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):740-745
Abstract
Original ArticleIncrement of Maternal Mortality Among Admissions for Childbirth in Low-risk Pregnant Women in Brazil: Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):740-745
Views205See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the possible impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth in 2020 in relation of the last 10 years.
Methods
An ecological study with pregnant women who underwent hospital births at the Brazilian unified public health service (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym) in Brazil from 2010 to 2020. The mortality among admissions for childbirth was obtained based on the number of admissions for childbirth with reported death as outcome divided by the total number of admissions. The underlying gestational risk and route of delivery were considered based on the national surveillance system. The average mortality for the period between 2010 and 2019 (baseline) was compared with the rate of deaths in 2020 (1st pandemic year); the rate ratio was interpreted as the risk of death in 2020 in relation to the average of the previous period (RR), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
In 2020, the 1st year of the COVID-19 pandemic, 1,821,775 pregnant women were hospitalized for childbirth and 651 deaths were reported, which represents 8.7% of the total hospitalizations and 11.3% of maternal deaths between 2010 and 2020. There was an increase in maternal mortality after births in 2020 compared with the average for the period between 2010 and 2019, specially in low-risk pregnancies, both in vaginal (RR = 1.60; 95%CI:1.39–1.85) and cesarean births (RR = 1.18; 95%CI:1.04–1.34).
Conclusion
Maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth according to SUS data increased in 2020 compared with the average between 2010 and 2019, with an increment of 40% in low-risk pregnancies. The increase was of 18% after cesarean section and of 60% after vaginal delivery.
-
Original Article02-17-2022
Quality of Life of Pregnant Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):475-482
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life of Pregnant Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):475-482
Views205See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the quality of life (QoL) of pregnant women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated at a high-risk prenatal outpatient clinic during the third trimester of gestation.
Methods
An observational descriptive study was performed in a high-risk prenatal outpatient clinic. Women in the third trimester of pregnancy and undergoing antenatal care between July 2017 and July 2019 answered the abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL-BREF) questionnaire, consisting of 26 questions divided into 4 domains (physical, psychological, social and environmental).
Results
We interviewed 50 pregnant women with a mean gestational age of 30 weeks (standard deviation [SD]: 10 weeks) who were diagnosed with SLE. The average age of the participants was 30 years (SD: 14.85), and the average time since the diagnosis of SLE was of 9.06 years (SD: 6.8 years). Most participants had a partner, did not plan their pregnancy (76%), and did not use contraception prior to pregnancy (80%). The score of each domain ranges from 0 (the worst score) to 100 (the best score). The means ± SDs of the scores of the participants on each domain were: physical – 52.21 ± 18.44); psychological – 64.17 ± 18.56); social – 66.33 ± 27.09); and environmental – 64.56 (18.53). The means ± SDs of the general QoL, and health-related QoL items were of 70.50 ± 24.06 and 70.00 ± 30.72 respectively.
Conclusion
The physical domain presented the lowest scores compared with the other three domains. Pregnant women with SLE had high overall QoL scores, and their health-related QoL scores were also relatively high.
-
Systematic Review12-01-2017
Is Pethidine Safe during Labor? Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):686-691
Abstract
Systematic ReviewIs Pethidine Safe during Labor? Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):686-691
Views174See moreAbstract
Purpose
To verify if pethidine is safe for the conceptus when used during labor.
Methods
Systematic review in the Capes Periodicals/PubMed and MEDLINE/Virtual Health Library (BVS, in the Portuguese acronym) databases.
Results
A total of 17 studies published from January 1st, 2000, to September 2nd, 2016, with a total of 1,688 participants involved were included in the present review. There was no record of conceptus vitality decrease associated with low doses of pethidine being administered to mothers during labor.
Conclusions
Intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) pethidine at low doses, of up to 50 mg, is safe to administer during labor.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)


