-
Original Article10-23-2024
Validation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
Views306ABSTRACT
Objective:
To traslate and validate of the Brazilian version of the SDI-2.
Methods:
This was a cross-sectional study. The cultural adaptation considered the stages of initial translation, synthesis of translations, evaluation by a committee of experts from different regions of Brazil, back-translation, and pre-test. The content validity and psychometric proprieties was assessed.
Results:
Ten specialists participated in the cultural adaptation of the SDI-2. The content validity showed a Content Validity Ratio (CVR) ≥ 0.75 (p = 0.05). A total of 674 subjects participated in the field study. The Exploratory Factorial Analysis (EFA) presented factor loads ≥ 0.445, and commonalities ≥ 0.40; and two dimensions represented 77% of the total variance explained. The Confirmatory Factorial Analysis CFA presented X2/df = 4.265; the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation RMSEA = 0.110; the Non-Normed Fit Index NNFI = 0.946; the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.963; the Goodness of Fit Index GFI = 0.986; and the Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index AGFI = 0.979 for a two-factor model. The coefficient values for the total SDI-2 score were 0.91 for Cronbach’s alpha, 0.91 for McDonald’s Omega, and 0.97 for the Greatest Lower Bound GLB coefficients. The invariance between sexes was 0.01 for the ΔCFI and ΔRMSEA, showing model stability for these two populations.
Conclusion:
The Brazilian version of the SDI-2 is self-report, valid, reliable and invariant across sex.
Key-words cross cultural comparisonLibidoPsychometricsSexual behaviorSexual desiresurveys and questionnairesSee more -
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT10-15-2024
Immunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTImmunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
Views380See moreKey points
•The negative impact of infectious diseases and their immunoprevention during the different stages of a woman’s life requires a broad approach including adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy and the postmenopausal phase.
•Immunization of pregnant women should be a priority for the protection of the maternal-fetal dyad, especially in regions with high rates of infections preventable by immunization.
•Brazil has one of the most comprehensive vaccination programs in the world – the National Immunization Program (Programa Nacional de Imunizações, PNI) – that serves all age groups: newborns, children, adolescents, adults, pregnant women and older adults, as well as groups with special needs, such as adolescents, pregnant and older adult women.
•However, vaccination coverage remains below ideal for all available vaccines, especially among adolescents and pregnant women, and Febrasgo is committed to collaborating with the PNI to combat vaccine hesitancy.
•The gynecologist/obstetrician is the reference physician for women, therefore the access to information and updates regarding all vaccines recommended for their patients is extremely important for this professional, aiming at the greatest possible protection.
•The objective of this Febrasgo Position Statement is to bring an update to women’s vaccination schedule, covering some vaccines that are available, including new approved vaccines and those in the commercialization phase.
•This work is a compilation of the First Febrasgo Scientific Immunization Forum held in the city of São Paulo in October 2023 with the objective to update recommendations for vaccines in use and new innovative vaccines soon to be available.
-
GUIDELINES10-07-2024
Brazilian Guideline on Menopausal Cardiovascular Health – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo100
Abstract
GUIDELINESBrazilian Guideline on Menopausal Cardiovascular Health – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo100
Views3701. IntroductionAfter the publication of the results from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) clinical trial in 2002 showing more risks than benefits to female health with estrogen (alone or combined with progestin) use to control menopausal signs and symptoms, there has been a progressive and sustained decline in the prescription of those drugs.–In the United […]See more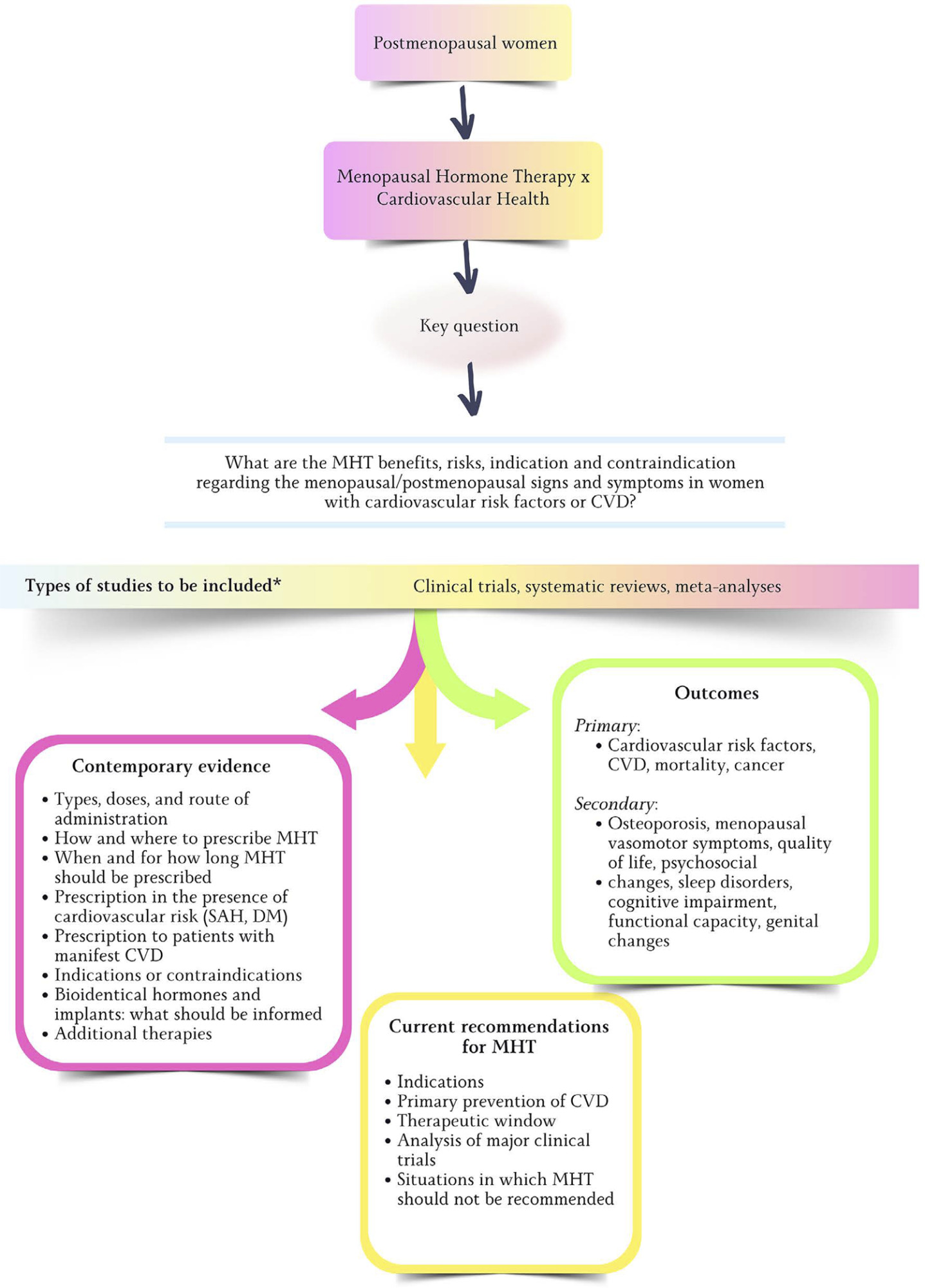
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT09-23-2024
Syphilis and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS09
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTSyphilis and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS09
Views429See moreKey points
•Although congenital syphilis has a known etiological agent, accessible diagnosis and low-cost, effective treatment with low fetal toxicity, it continues to challenge obstetric and antenatal care services.
•The increasing rates of syphilis in the general population have direct repercussions on the increase in cases of congenital syphilis, a situation of objective interest for public health.
•Although transforming the recording of syphilis and congenital syphilis into notifiable diseases improved the records and has made it possible to measure the occurrence of these diseases and create solutions, no effects on reducing their frequency have been reached yet.
•The failure to control syphilis/congenital syphilis is multifactorial, and associates variables that range from the deficiency in teaching about these diseases in schools and in the training system of the various health professional segments, as well as the lack of rigid policies for quality control from antenatal care until the clinical follow-up of children exposed to Treponema pallidum during pregnancy.
•To date, benzathine penicillin is the only antimicrobial accepted as effective by the main health authorities on the planet for the treatment of syphilis in pregnant women.
•The fear of anaphylaxis in response to the treatment of syphilis with benzathine penicillin is an important factor hindering the prompt and correct treatment of pregnant women with syphilis, even though health authorities have made efforts to face the problem with solid arguments, still insufficient to resolve the question.
•Although specific protocols are published, the failure to control the treatment of syphilis in pregnant women is still observed with high frequency, indicating and reinforcing a failure in the quality control of these care principles.
The National Specialized Commission on Infectious Diseases of the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (Febrasgo) endorses this document. Content production is based on scientific evidence on the proposed topic and the results presented contribute to clinical practice.
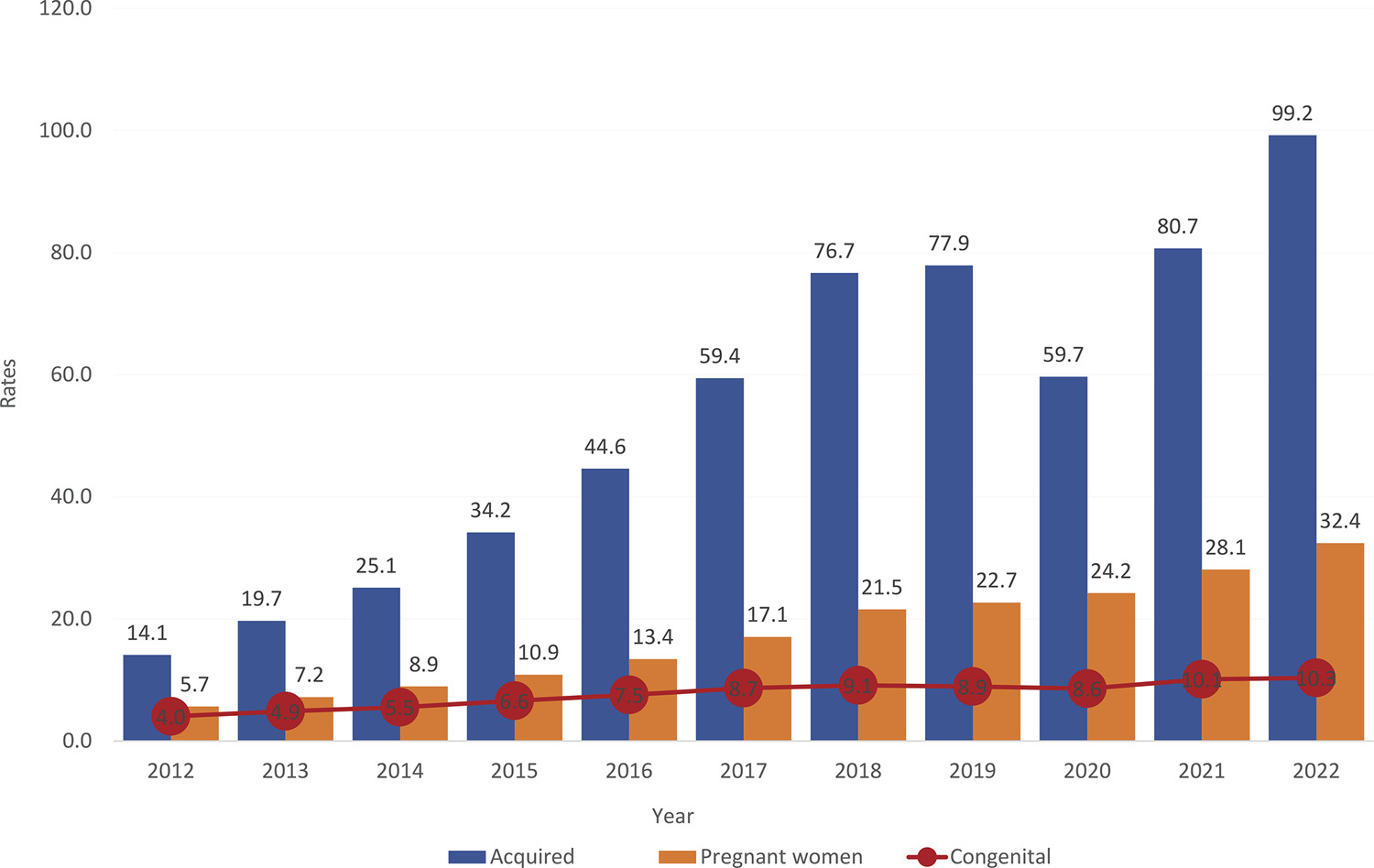
-
Review Article09-18-2024
Immunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Abstract
Review ArticleImmunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Views339Abstract
Objective
To compare outcomes in patients with repeated implantation failure undergoing Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection/In vitro fertilization (IVF/ICSI) plus immunosuppressants such as prednisolone, prednisone, or cyclosporine A versus the use of IVF/ICSI alone.
Data source
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase databases in September 2023.
Study Selection
Randomized clinical trials and observational studies with the outcomes of interest were included.
Data collect
We computed odds ratios (ORs) for binary endpoints, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics. Data were analyzed using Review Manager 5.4.The main outcomes were live birth, miscarriage, implantation rate, clinical pregnancy, and biochemical pregnancy.
Data synthesis
Seven studies with 2,829 patients were included. Immunosuppressive treatments were used in 1,312 (46.37%). Cyclosporine A improved implantation rate (OR 1.48; 95% CI 1.01-2.18) and clinical pregnancy (1.89, 95% CI 1.14-3.14). Compared to non-immunosuppressive treatment, prednisolone and prednisone did not improve live birth (OR 1.13, 95% CI 0.88-1.46) and miscarriage (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.07-2.09). Prednisolone showed no significant effect in patients undergoing IVF/ICSI, clinical pregnancy (OR 1.34; 95% CI 0.76-2.36), or implantation rate (OR 1.36; 95% CI 0.76-2.42).
Conclusion
Cyclosporine A may promote implantation and clinical pregnancy rates. However, given the limited sample size, it is important to approach these findings with caution. Our results indicate that prednisolone and prednisone do not have any beneficial effects on clinical outcomes of IVF/ICSI patients with repeated implantation failure.
PROSPERO
CRD42023449655
Key-words Cyclosporine APrednisolone Immunosupressive agentsPrednisoneRepeated implantation failureReproductionReproductive techniques, assistedSee more -
Review Article09-18-2024
Neonatal and maternal outcomes of mRNA versus Non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo69
Abstract
Review ArticleNeonatal and maternal outcomes of mRNA versus Non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo69
Views332Abstract
Objective
To compare the effectiveness and safety of non-mRNA versus mRNA COVID-19 vaccines on pregnant women and their newborns in a systematic review with meta-analysis.
Data sources
We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central in May 2023.
Study selection
The search strategy yielded 4451 results, 16 studies were fully reviewed. We selected case-control studies analysing non-mRNA versus mRNA vaccines. Data collection and analysis: we assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool. Standardised mean differences were pooled using random-effect models.
Data synthesis
We identified 8 prospective and retrospective studies with a total of 32,153 patients. Non-mRNA vaccines were associated with a higher incidence of fever (OR 2.67; 95% CI 2.08-3.43; p<0.001), and a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death (OR 0.16; 95% CI 0.08-0.33; p<0.001). In subgroup analyses, the Jansen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) was found to have a higher rate of premature labor/delivery (OR 4.48; 95% CI 1.45-13.83; p=0.009) and missed/spontaneous abortion (OR 1.90; 95% CI 1.09-3.30; p=0.02), as compared with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) vaccine.
Conclusion
non-mRNA vaccines are associated with a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death among pregnant women who receive a Covid19 vaccine, although at an increased rate of pyrexia compared with mRNA vaccines. Other studies are required for better assessment.
PROSPERO
CRD42023421814
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19COVID-19 vaccinesInfant, newbornmRNA vaccinesPregnancy complicationsPregnant womenSARS-CoV-2See more -
Original Article09-18-2024
Multidisciplinary team training in postpartum hemorrhage: impact on the use of blood products
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo67
Abstract
Original ArticleMultidisciplinary team training in postpartum hemorrhage: impact on the use of blood products
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo67
Views340See moreAbstract
Objective
Compare the number of puerperal women submitted to blood transfusion before and after the implementation of a care protocol for postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) with multidisciplinary team training.
Methods
Cross-sectional study in a university hospital, analyzing births from 2015 to 2019, compared the use of blood products before and after the adoption of a PPH protocol with multidisciplinary training.
Results
Between 2015 and 2019, there were 17,731 births, with 299 (1.7%) postpartum women receiving blood products and 278 postpartum women were considered for this analysis, 128 (0.7%) at Time 1 and 150 (0.8%) at Time 2. After the multiprofessional team training (T2), there was a difference in the complete use of the PPH protocol (use of oxytocin, misoprostol and tranexamic acid) (T1 = 5.1% x T2 = 49.5%, p≤0.0001). An individual categorized analysis revealed that, in the T2 period, there was lower use of blood component units per patient compared to T1 (Mann-Whitney, p=0.006). It should be noted that at T1 and T2, 54% and 24% respectively received two units of blood products. It is important to highlight that after the multidisciplinary team training for the PPH protocol, the goal of zero maternal death due to hemorrhage was reached.
Conclusion
The adoption of a specific protocol for PPH, combined with the training of a multidisciplinary team, had an impact on the ability to identify women at high risk of hemorrhage, resulting in a decrease in the use of blood components.
-
Original Article09-06-2024
Immediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
Abstract
Original ArticleImmediate prepectoral versus submuscular breast reconstruction in nipple-sparing mastectomy: a retrospective cohort analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo76
Views334Abstract
Objective
To evaluate early complications in prepectoral breast reconstruction.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study including 180 consecutive cases of nipple-sparing mastectomy, comparing immediate breast reconstruction with subpectoral to prepectoral mammary implants in 2012-2022. Clinical and demographic characteristics and complications in the first three months following surgery were compared between the two techniques.
Results
The prepectoral technique was used in 22 cases (12.2%) and the subpectoral in 158 (87.8%). Median age was higher in the prepectoral group (47 versus 43.8 years; p=0.038), as was body mass index (25.1 versus 23.8; p=0.002) and implant volume (447.5 versus 409 cc; p=0.001). The prepectoral technique was more associated with an inframammary fold (IMF) incision (19 cases, 86.4% versus 85, 53.8%) than with periareolar incisions (3 cases, 13.6% versus 73, 46.2%); (p=0.004). All cases in the prepectoral group underwent direct-to-implant reconstruction compared to 54 cases (34.2%) in the subpectoral group. Thirty-eight complications were recorded: 36 (22.8%) in the subpectoral group and 2 (9.1%) in the prepectoral group (p=0.24). Necrosis of the nipple-areola complex/skin flap occurred in 27 patients (17.1%) in the subpectoral group (prepectoral group: no cases; p=0.04). The groups were comparable regarding dehiscence, seroma, infection, and hematoma. Reconstruction failed in one case per group (p=0.230). In the multivariate analysis, IMF incision was associated with the prepectoral group (aOR: 34.72; 95%CI: 2.84-424.63).
Conclusion
The incidence of early complications was comparable between the two techniques and compatible with previous reports. The clinical and demographic characteristics differed between the techniques. Randomized clinical trials are required.
Key-words Breast implantationBreast implantsBreast neoplasmsMammaplastyMastectomyNipplesPectoralis musclesSurgical procedures, operativeSee more
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)