Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):225-231
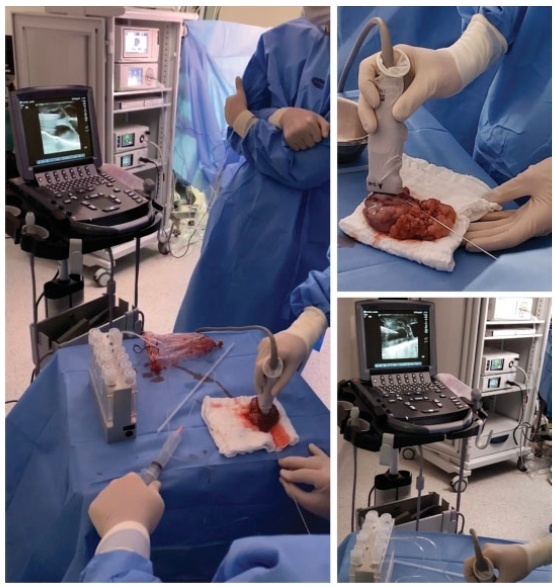
We report a case of ultrasound-guided ex vivo oocyte retrieval for fertility preservation in a woman with bilateral borderline ovarian tumor, for whom conventional transvaginal oocyte retrieval was deemed unsafe because of the increased risk of malignant cell spillage. Ovarian stimulation with gonadotropins was performed. Surgery was scheduled according to the ovarian response to exogenous gonadotropic stimulation; oophorectomized specimens were obtained by laparoscopy, and oocyte retrieval was performed ~ 37 hours after the ovulatory trigger. The sum of 20 ovarian follicles were aspirated, and 16 oocytes were obtained.We performed vitrification of 12 metaphase II oocytes and 3 oocytes matured in vitro. Our result emphasizes the viability of ex vivo mature oocyte retrieval after controlled ovarian stimulation for those with high risk of malignant dissemination by conventional approach.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):614-621
The present study aimed to evaluate the impact of vitrification on the viability of follicles using a three-dimensional (3D) in vitro culture.
Bovine ovarian tissue samples (n = 5) obtained from slaughterhouses were utilized. The cortex was cut into small fragments of 2 x 3 x 0.5 mm using a tissue slicer. From these fragments, secondary follicles were first isolated by mechanical and enzymatic methods, then encapsulated in alginate gel and individually cultured for 20 days. Additional fragments of the same ovarian tissue were vitrified in a solution containing 25% glycerol and 25% ethylene glycol. After warming, the follicles underwent the same follicular isolation process that was performed for the fresh follicles.
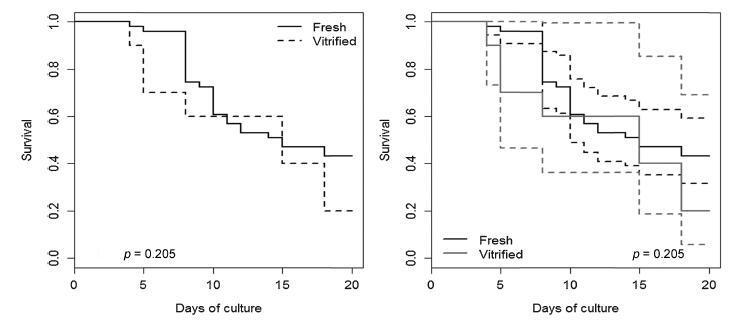
A total of 61 follicles were isolated, 51 from fresh ovarian tissue, and 10 from vitrified tissue. After the culture, the vitrified and fresh follicles showed 20% and 43.1% survival rates respectively (p = 0.290),with no significant differences. At the end of the culture, therewere no significant differences in follicular diameter between the vitrified (422.93 ± 85.05 μm) and fresh (412.99 ± 102.55 μm) groups (p = 0.725). Fresh follicles showed higher mean rate of antrum formation when compared with vitrified follicles (47.1% and 20.0% respectively), but without significant difference (p = 0.167).
The follicles were able to develop, grow and form antrum in the 3D system after vitrification, despite the lower results obtained with the fresh tissue.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):333-339
To assess the viability of bovine ovarian tissue after cryopreservation through either slow freezing or vitrification, and to compare it to that of control tissue by performing morphological analyses.
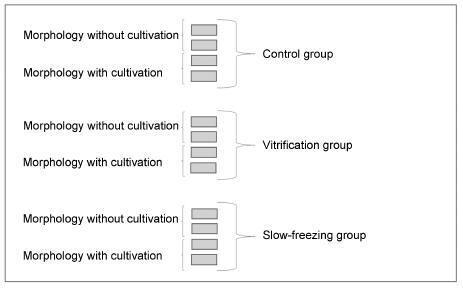
The study included 20 bovine ovarian cortex fragments that were divided into control, vitrification, and slow freezing groups. Each group consisted of four fragments of the same ovary, two fixed without cultivation, and two fixed with cultivation. Tissues were evaluated based on follicular morphology immediately after heating and after 7 days of culture, and compared with the control group.
A total of 240 fragments were analyzed, generating a sample of 1,344 follicles without cultivation and 552 with cultivation. When the non-cultivated samples were classified as non-atretic follicles, 572 were found in the control group, 289 in the vitrification group, and 373 in the slow freezing group, showing no significant differences. When classified as atretic, 46 follicles were found in the control group, 23 in the vitrification group, and 41 in the slow freezing group, also showing no statistical difference. In the post-culture sample, an evolution of the follicular stages could be observed. This finding was important to support that the follicles considered non-atretic in the non-cultivated group were actually viable in the morphological evaluation.
With no differences between the protocols, vitrification was shown to be an advanced and alternative method for patients who will undergo treatments that
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):553-559
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800003
PURPOSE: to verify vitrification techniques using 6 M DMSO to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes, and to assess the effects of the time of exposure to vitrification solutions (VS). METHODS: dilutions of VS were prepared from the stock VS (VS 100%) consisting of 6 M DMSO to give 25 and 65% DMSO solutions. Bovine oocytes were in vitro matured for 18-22 h. Matured oocytes were placed first into 25% VS, at room temperature for 5 min, then transferred to 65% VS, before being pipetted into the 100% VS in plastic straws. Three experimental groups were formed: in the first group, time of pipetting through 65% VS and loading the straw took up to 60 s, in the second group it did not exceed 30 s. For thawing, straws were held in air for 10 s and then in a water bath for 10 s. The contents of each straw were expelled in sucrose solution and held for 5 min. In the third experimental group, oocytes went through all VS, but were not vitrified. All retrieved oocytes were inseminated. For control, fresh, in vitro matured oocytes were inseminated. RESULTS: after vitrification, 69.1 and 59.8% of the oocytes were retrieved from the 30 s and 60 s groups, respectively, and 93 and 89% of these oocytes appeared morphologically normal 24 h after insemination, respectively. In the group of oocytes exposed without vitrification, 75.6% were retrieved and 84.7% were morphologically viable, 24 h after insemination. No fertilization was observed in the experimental groups. Among controls, 65.4% were fertilized. CONCLUSIONS: the vitrification technique using 6 M DMSO is not a feasible approach to cryopreserve in vitro matured bovine oocytes. Decreasing the time of exposure to VS did not overcome deleterious effects of the procedure on the fertilizability of oocytes. Improvements in the technique are needed to protect the zona pellucida and oolemma.