Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):683-688
12-05-2023
It is well known that female infertility is multifactorial. Therefore, we aimed to compare the effects of thyroid dysfunction, vitamin deficiency, and microelement deficiency in fertile and infertile patients.
Between May 1st, 2017, and April 1st, 2019, we conducted a retrospective case-control study with of 380 infertile and 346 pregnant patients (who normally fertile and able to conceive spontaneously). The fertile patients were selected among those who got pregnant spontaneously without treatment, had a term birth, and did not have systemic or obstetric diseases. The levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO), vitamin D, vitamin B12, folic acid, ferritin, and zinc of both groups were compared.
There was no difference between patients in the infertile and pregnant groups in terms of low normal and high serum T3 and T4 levels (p = 0.938; p > 0.05) respectively, nor in terms of normal and high anti-TPO levels (p = 0.182; p > 0.05) respectively. There was no significant difference regarding patients with low, insufficient, and sufficient vitamin D levels in the infertile and pregnant groups (p = 0.160; p >0.05) respectively. The levels of folic acid, ferritin, and zinc of the infertile group were significantly lower than those of the pregnant group.
The serum levels of folic acid, ferritin, and zinc in infertile patients presenting to our outpatient clinic were lower than those o the fertile patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):743-748
12-17-2021
To assess maternal serum levels of vitamin D in fetuses appropriate for gestational age (AGA), small for gestational age (SGA), and with fetal growth restriction (FGR) according to estimated fetal weight (EFW).
This cross-sectional study included 87 pregnant women between 26 and 36 weeks of gestation: 38 in the AGA group, 24 in the SGA group, and 25 in the FGR group. Maternal serum vitamin D levels were assessed using the chemiluminescence method. The Fisher exact test was used to compare the results between the groups.
The mean ± standard deviation (SD) of maternal age (years) and body mass index (kg/m2) in the AGA, SGA, and FGR groups were 25.26 8.40 / 26.57 ± 4.37; 25.04 ± 8.44 / 26.09 ± 3.94; and 25.48 ± 7.52 / 26.24 ± 4.66, respectively (p > 0.05). The maternal serum vitamin D levels (mean ± SD) of the AGA, SGA, and FGR groups were 22.47 ± 8.35 ng/mL, 24.80 ± 10.76 ng/mL, and 23.61 ± 9.98 ng/mL, respectively, but without significant differences between the groups (p = 0.672).
Maternal serum vitamin D levels did not present significant differences among pregnant women with AGA, SGA, or FGR fetuses between 26 and 36 weeks of gestation according to EFW.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(7):425-431
08-15-2019
To evaluate the relationship between vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism (FokI [rs10735810]) and serum vitamin D concentration in gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
A prospective case-control study that recruited healthy pregnant women (control group) (n = 78) and women with GDM (GDM group) (n = 79), with no other comorbidities. Peripheral blood samples were collected in the 3rd trimester of gestation, and all of the pregnant women were followed-up until the end of the pregnancy and the postpartum period. Serum vitamin D concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). For genomic polymorphism analysis, the genomic DNA was extracted by the dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide/ cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB/CTAB) method, and genotyping was performed by the polymerase chain reaction - restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technique, using the restriction enzyme FokI. The Student-t, Mann- Whitney, chi-squared, and Fischer exact tests were used for the analysis of the results.
There was no significant difference between the pregnant women in the control and GDM groups regarding serumvitamin D levels (17.60 ± 8.89 ng/mL versus 23.60 ± 10.68 ng/mL; p = 0.1). Also, no significant difference was detected between the FokI genotypic frequency when the 2 groups were compared with each other (p = 0.41).
There was no association between the FokI polymorphism and the development of GDM, nor was there any change in serum vitamin D levels in patients with GDM.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):337-343
07-01-2017
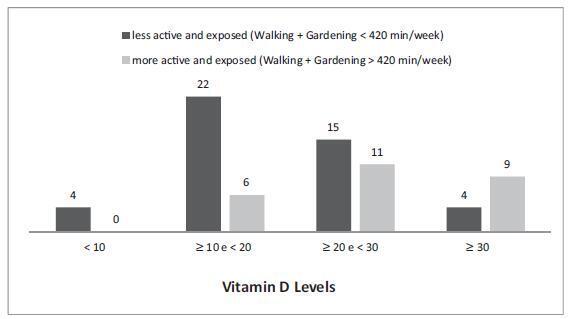
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with various diseases. Prevalent in Brazil, it can result from inadequate lifestyle habits.
To demonstrate that postmenopausal women with vitamin D deficiency have worse quality of health, expressed as worse quality of life, lower levels of physical activity, and worse nutritional profile.
Postmenopausal women answered questionnaires about physical activity and quality of life, provided a 24-hour food record, and had serum vitamin D levels measured.
Among the more active women, those who perform a daily average of one hour of physical activity had vitamin D levels above 20 ng/mL (76.9%), and those, which expose themselves to sunlight, had vitamin D levels above 30 ng/mL (34.6%). Meanwhile the percentages for the women who are less physically active and less exposed to sunlight were 42.2% and 8.9% respectively. Being more active and more exposed to sunlight resulted in a lower fat percentage. Serum vitamin D levels were not correlated with quality of life.
Walking and gardening increased serum vitamin D levels and decreased the percentage of body fat. The limitations of the study prevented the impact of 25hidroxyvitamin D on the quality of life and nutritional aspects of the women from being evaluated.