Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):194-200
04-08-2022
To analyze the existing scientific literature to find out if the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has an effect on gynecological health.
We performed an integrative review of articles published between April 2020 and April 2021 on the PubMed, SciELO, and LILACS databases, using COVID-19 and the following relevant terms: Menstrual change; Ovarian function; Violence against women; Contraception; HPV; Mental health; and Urogynecology.
Among the eligible studies found, editorials and primary research articles, which describe the dynamics between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection (the cause of the COVID-19 pandemic) and gynecological health, were included.
Through qualitative synthesis, data were extracted from the included publications and from guidelines of national and international societies of gynecology.
The 34 publications included in the present study showed that some factors of the SARS-CoV-2 infection, and, consequently, the COVID-19 pandemic, might be associated with menstrual abnormalities, effects on contraception, alterations in steroid hormones, changes in urogynecological care, effects on women’s mental health, and negative impact on violence against women.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the health of women. The scientific community encourages the development of recommendations for specialized care for women and strategies to prevent and respond to violence during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):47-54
02-28-2022
To evaluate the assistance provided to women victims of sexual violence and their participation in the follow-up treatment after the traumatic event, presenting a sociodemographic profile, gynecological background, and circumstances of the event, and reporting the results, acceptance, and side effects of prophylaxis for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and pregnancy.
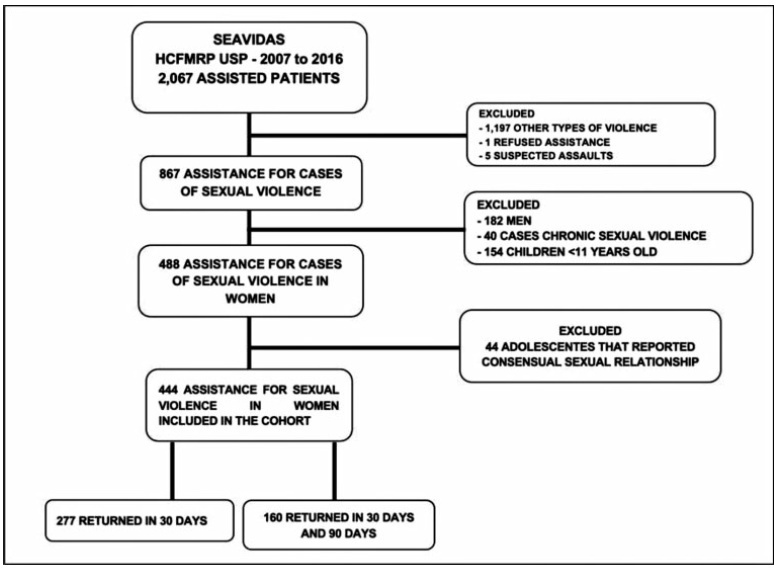
A retrospective cohort study comprising the period between 2007 and 2016. All women receiving medical care and clinical follow-up after a severe episode of sexual violence were included. Records of domestic violence, male victims, children, and adolescents who reported consensual sexual activity were excluded. The present study included descriptive statistics as frequencies and percentages.
A total of 867medical records were reviewed and 444 cases of sexual violence were included. The age of the victims ranged from10 to 77 years old, most of them selfdeclared white, with between 4 and 8 years of education, and denying having a sexual partner. Sexual violence occurred predominantly at night, on public thoroughfare, being committed by an unknown offender. Most victims were assisted at the referral service center within 72 hours after the violence, enabling the recommended prophylaxis. There was high acceptance of antiretroviral therapy (ART), although half of the users reported side effects. Seroconversion to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or to hepatitis B virus (HBV) was not detected in women undergoing prophylaxis.
In the present cohort, the profile of victims of sexual violence was loweducated, young, white women. The traumatic event occurred predominantly at night, on public thoroughfare, being committed by an unknown offender. Assistance within the first 72 hours after sexual violence enables the healthcare center to provide prophylactic interventions against STIs and unwanted pregnancies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):547-554
10-23-2020
To characterize the sociodemographic profile of women victims of sexual violence treated at a university hospital in southern Brazil.
The present cross-sectional study included all female victims of sexual violence who attended the sexual violence unit at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA, in the Portuguese acronym) from April 18, 2000 to December 31, 2017.Data were extracted from the electronic record of the patients and stored in a standardized questionnaire database with epidemiological aspects of the victim, the perpetrators and the type of aggression. Statistical analysis was performed using the chi-squared test for trend and descriptive statistics with 95% confidence interval (CI).
During the length of the study, 711 women victims of sexual violence were treated. The mean age of the patients was 24.4 (±10) years old (range from 11 to 69 years old) and most of the victims were white (77.4%), single (75.9%) and sought care at the unit within 72 hours after the occurrence (80.7%). In most cases, violence was exerted by a single perpetrator (87.1%), who was unknown in 67.2% of cases. Victims < 19 years old showed a higher risk of not using contraception (relative risk [RR] = 2.7; 95% CI = 1.9-3.6).
Most victims of sexual violence were treated within 72 hours of the occurrence. The majority of these victims were white and young, and those < 19 years old had a higher risk of not using contraception and to know the sexual perpetrator.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(12):609-614
12-01-2016
To assess depression, domestic violence and the use of substances in women with recurrent miscarriages.
The Abuse Assessment Screen (AAS), the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) and the Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) were used to assess violence, depression and the use of substances among women with recurrent miscarriages. The population corresponded to patients receiv-ing prenatal care from June to August 2014. Multiple logistic regression was used to assess the multivariable relationship between depression and sociodemographic, psychosocial and medical characteristics (p < 0,10).
The prevalence of depression was of 41.3% (95% confidence interval [CI] 1/4 28.3-55.7%). One third of the pregnant women (32.6%) reported emotional or physical violence, and 13% were classified as abusing or addicted to tobacco according to ASSIST. History of psychiatric diseases was associated with depression (p 1/4 0.005). Violence during life demonstrated a modest association (p 1/4 0.073) with depression, as well as the number of miscarriages (p 1/4 0.071).
Depression is a frequent disease among pregnant women with recurrent miscarriages. The results of this investigation suggest that a systematic assessment of depression and its associated conditions, such as domestic violence and the use of substances, should be part of the prenatal follow-up visits for women with recurrent miscarriages.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):309-316
09-05-2003
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500002
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of domestic physical violence among women who delivered at a tertiary center in the Northeast of Brazil, to study the main risk factors associated with domestic violence, and to determine perinatal outcome. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted, enrolling 420 women who delivered at a tertiary center in Recife (Brazil) with fetuses weighing more than 500 g. They were submitted to interviews with open and closed questions. The prevalence of domestic physical violence was determined. Statistical analysis was performed using c² and Fisher's exact tests at a 5% level of significance. The prevalence ratio was determined as measurement of relative risk of violence. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed and the adjusted risk was calculated. RESULTS: the prevalence of domestic physical violence was 13.1% (95% CI = 10.1-16.6) and 7.4% (95% CI = 5.2-10.2) before and during pregnancy, respectively. The pattern of violence has changed during pregnancy: stopped in 43.6%, was reduced in 27.3% and increased in 11% of the victims. After multivariate analysis the variables that persisted strongly associated with violence were low female educational level, history of violence in the women´s family, partner's use of alcohol and unemployment. Perinatal outcome was studied and a significantly higher frequency of neonatal death was observed among victims of domestic violence. CONCLUSIONS: a high prevalence of domestic physical violence was observed (about 13%) in women who delivered at a tertiary center in Northeast of Brazil. The main risk factors were low educational level and previous familiar history of violence in the women's family, alcohol use by and unemployment of their partners. Neonatal mortality was increased in victims of violence.