Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(9):428-435
This study was done to evaluate the normal fetal cerebral lateral ventricle dimensions with transabdominal ultrasonography. The atrial width (AW), ventricle-tochoroid measurement (V-C), ventricle-to-hemisphere ratio (VHR), and combined anterior horn measurement (CAHM) were taken.
This was a cross-sectional study involving 400 normal singleton pregnant subjects whose gestational ages were between 14 and 40 weeks. Transabdominal sonography was performed to obtain the values of the fetal cerebral lateral ventricle (FCLV) parameters. Data were reported as mean standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables. The degrees of correlation between FCLV parameters and the estimated gestational age (EGA) were obtained using Pearson's correlation. Regression equations were used to generate the reference limits for the FCLV measurements.
The values of AW, V-C measurements and CAHM increased with advancing gestation. The mean values of the AW, V-C and CAHM from 14 to 40 weeks increased from 6.60 0.94 mm to 9.75 0.07 mm (R2 = 0.114), 0.80 0.00 mm to 1.90 0.14 mm (R2= 0.266), and 6.95 0.06 mm to 23.07 4.02 mm (R2= 0.692) respectively, while the mean VHR decreased from 61.20 1.60% to 42.84 2.91% (R2 = 0.706) over the same period.
The AW, V-C, and CAHM increase, while VHR decreases with advancing gestation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(9):436-442
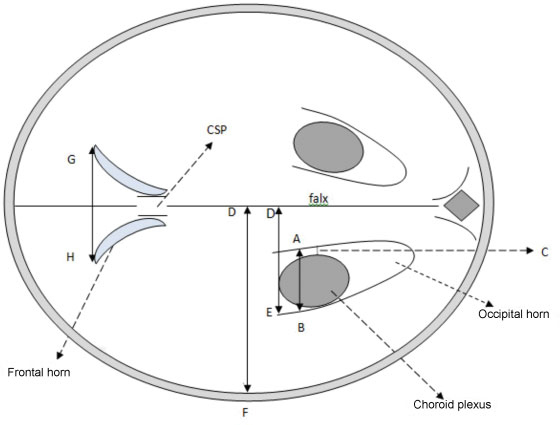
Ventriculomegaly (VM) is one the most frequent anomalies detected on prenatal ultrasound. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may enhance diagnostic accuracy and prediction of developmental outcome in newborns.
The aim of this study was to assess the correlation between ultrasound and MRI in fetuses with isolated mild and moderate VM. The secondary aim was to report the neurodevelopmental outcome at 4 years of age.
Fetuses with a prenatal ultrasound (brain scan) diagnosis of VM were identified over a 4-year period. Ventriculomegaly was defined as an atrial width of 10- 15 mm that was further divided as mild (10.1-12.0 mm) and moderate (12.1-15.0 mm). Fetuses with VM underwent antenatal as well as postnatal follow-ups by brain scan and MRI. Neurodevelopmental outcome was performed using the Griffiths Mental Development Scales and conducted, where indicated, until 4 years into the postnatal period.
Sixty-two fetuses were identified. Ventriculomegaly was bilateral in 58% of cases. A stable dilatation was seen in 45% of cases, progression was seen in 13%, and regression of VM was seen in 4.5% respectively. Fetal MRI was performed in 54 fetuses and was concordant with brain scan findings in 85% of cases. Abnormal neurodevelopmental outcomes were seen in 9.6% of cases.
Fetuses in whom a progression of VM is seen are at a higher risk of developing an abnormal neurodevelopmental outcome. Although brain scan and MRI are substantially in agreement in defining the grade of ventricular dilatation, a low correlation was seen in the evaluation of VM associated with central nervous system (CNS) or non-CNS abnormalities.