-
Original Article07-26-2024
Validation and cultural translation for the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Estro-Androgenic- Symptom Questionnaire in Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo56
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation and cultural translation for the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Estro-Androgenic- Symptom Questionnaire in Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo56
Views167Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to translate and validate the Estro-Androgenic-Symptom Questionnaire in Women (EASQ-W) into Brazilian Portuguese language, as we hypothesized that this tool would be consistent for addressing the specific context of hormonal symptoms in menopause.
Methods
In a cross-sectional study, a total of 119 women with Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) and 119 climacteric women without GSM were included. The EASQ-W was translated, and its psychometric properties were rigorously examined. Participants completed questionnaires covering sociodemographic details, the EASQ-W, and the Menopause Rating Scale (MRS). A subgroup of 173 women was re-invited after 4 weeks for test-retest analysis of the EASQ-W. Additionally, the responsiveness of the questionnaire was evaluated in 30 women who underwent oral hormonal treatment.
Results
The internal consistency of the EASQ-W was found to be satisfactory in both GSM and control groups (Cronbach’s alpha ≥ 0.70). Notably, a floor effect was observed in both groups; however, a ceiling effect was only evident in the sexual domain of the GSM group. Construct validity was established by comparing the EASQ-W with the MRS, yielding statistically significant correlations (0.33831-0.64580, p < 0.001). The test-retest reliability over a 4-week period was demonstrated to be satisfactory in both the GSM and control groups (ICC 0.787-0.977). Furthermore, the EASQ-W exhibited appropriate responsiveness to oral hormonal treatment (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study successfully translated and validated the Estro-Androgenic-Symptom Questionnaire in Women (EASQ-W) into Brazilian Portuguese, with satisfactory internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and construct validity.
Key-words AndrogenEASQ-WEstrogenMenopauseSigns and symptomssurveys and questionnairesValidation studiesSee more -
Original Article07-10-2023
Analysis of the Measurement Properties of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) in a Postpartum Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):089-095
Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of the Measurement Properties of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) in a Postpartum Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):089-095
Views167See moreAbstract
Objective
We evaluated internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and criterion validity of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) for postpartum women.
Methods
Therefore, questionnaires were applied to 100 sexually active women in the postpartum period. The Cronbach α coefficient was used to evaluate the internal consistency. Test-retest reliability was analyzed by Kappa for each item of the questionnaire and by the Wilcoxon parametric test, comparing the total scores of each evaluation. For the assessment of criterion validity, the FSFI was used as the gold standard and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). It was found that the internal consistency of the FSFI-6 questionnaire was considerably high (0.839).
Results
The test-retest reliability results were satisfactory. It can also be stated that the FSFI-6 questionnaire presented excellent discriminant validity (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.926). Women may be considered as having sexual dysfunction if the overall FSFI-6 score is < 21, with 85.5% sensitivity, 82.2% specificity, positive likelihood ratio of 4.81 and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18.
Conclusion
We conclude that the Brazilian Portuguese version of FSFI-6 is valid for use in postpartum women.

-
Original Article07-22-2019
Content and Face Validity of the Mackey Childbirth Satisfaction Rating Scale Questionnaire Crossculturally Adapted to Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(6):371-378
Abstract
Original ArticleContent and Face Validity of the Mackey Childbirth Satisfaction Rating Scale Questionnaire Crossculturally Adapted to Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(6):371-378
Views143See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to determine the content and face validity of the Mackey Childbirth Satisfaction Rating Scale (MCSRS) questionnaire cross-culturally adapted to Brazilian Portuguese.
Methods
The MCSRS is a questionnaire with 34 items related to childbirth satisfaction. The forward- and back-translated versions were compared with the original material, and 10 experts analyzed each item according to the following criteria: clarity, semantic equivalence, appropriateness, and cultural relevance. The final version was presented to 10 mothers for face validation to ensure the questionnaire would suit the target population.
Results
The total of 34 items assessed by experts for clarity, semantic equivalence, appropriateness, and relevance showed positive agreement of 0.85, 0.92, 0.97 and 0.97; negative agreement of 0.13, 0.09, 0.04 and 0.04; and total agreement of 0.75; 0.85, 0.94 and 0.94, respectively. Multilevel linear modeling was applied with crossed random effects and with nested random effects for each judge. The intercept of each criterion was as follows: clarity, 0.87; semantic equivalence, 0.92; appropriateness, 0.96; and cultural relevance, 0.96. The overall mean of agreement was 92.8%. The face validity measurement yielded 80% of agreement on the items, all of them clearly understood.
Conclusion
The final version of the Brazilian Portuguese MCSRS questionnaire had face and content validity confirmed. This instrument of evaluation of maternal satisfaction during childbirth was validated to be applied in the Brazilian female population.
-
Review Article03-01-2019
Quality of Life in Women with Defecatory Dysfunctions: Systematic Review of Questionnaires Validated in the Portuguese Language
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):191-198
Abstract
Review ArticleQuality of Life in Women with Defecatory Dysfunctions: Systematic Review of Questionnaires Validated in the Portuguese Language
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):191-198
Views233See moreAbstract
Objective
To identify the quality of life (QoL) assessment instruments related to the health of women with fecal incontinence (FI) or anal incontinence (AI).
Data Sources
Systematic review conducted in the Virtual Health Library (VHL), PubMed and Cochrane Library databases. The descriptors used were: Questionnaire, Questionnaires, Quality of life, validation, validation Studies, anal incontinence, fecal incontinence and constipation. The search was performed between December 26, 2017 and the beginning of January 2018. The limits used were female gender.
Selection of Studies
Initially, 5,143 articles were obtained in the search. The articles of validation for Portuguese of questionnaires for the evaluation of the impact of FI/AI on the QoL of women were considered eligible.
Data Collection
The article search was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes (PRISMA) guidelines.
Data Synthesis
Of the 5,143 articles, only 2 fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria: Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life (FIQL) and the Wexner scale (WS). The FIQL evaluates the QoL related to FI, not covering flatus incontinence. The WS assesses flatus incontinence and the severity of the AI. The WS obtained an interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.932 and a Cronbach α coefficient > 0.90. The FIQL obtained intraexaminer and interexaminer reproducibility ranging from 0.929 to 0.957 and from 0.944 to 0.969, respectively.
Conclusions
The WS and the FIQL have satisfactory reliability and validity for use during gynecological consultations.
-
Original Article06-01-2018
Translation and Cultural Adaptation of the Short-Form Food Frequency Questionnaire for Pregnancy into Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):313-321
Abstract
Original ArticleTranslation and Cultural Adaptation of the Short-Form Food Frequency Questionnaire for Pregnancy into Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):313-321
Views197See moreAbstract
Objective
To translate and culturally adapt the short-formFood Frequency Questionnaire (SFFFQ) for pregnant women, which contains 24 questions, into Brazilian Portuguese.
Methods
Description of the process of translation and cultural adaptation of the SFFFQ into Brazilian Portuguese. The present study followed the recommendation of the International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research for translation and cultural adaptation with the following steps: 1) preparation; 2) first translation; 3) reconciliation; 4) back translation; 5) revision of back translation; 6) harmonization; 7) cognitive debriefing; 8) revision of debriefing results; 9) syntax and orthographic revision; and 10) final report. Five obstetricians, five dietitians and five pregnant women were interviewed to contribute with the language content of the SFFFQ.
Results
Few changes were made to the SFFFQ compared with the original version. These changes were discussed with the research team, and differences in language were adapted to suit all regions of Brazil.
Conclusion
The SFFFQ translated to Brazilian Portuguese can now be validated for use in the Brazilian population.
-
Original Article02-01-2017
Validation of the 36-item version of the WHO Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 (WHODAS 2.0) for assessing women’s disability and functioning associated with maternal morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):44-53
Abstract
Original ArticleValidation of the 36-item version of the WHO Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 (WHODAS 2.0) for assessing women’s disability and functioning associated with maternal morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):44-53
Views247Abstract
Objective
To validate the translation and adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese of 36 items from the World Health Organizaton Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 (WHODAS 2.0), regarding their content and structure (construct), in a female population after pregnancy.
Methods
This is a validation of an instrument for the evaluation of disability and functioning and an assessment of its psychometric properties, performed in a tertiary maternity and a referral center specialized in high-risk pregnancies in Brazil. A sample of 638 women in different postpartum periods who had either a normal or a complicated pregnancy was included. The structure was evaluated by exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), while the content and relationships among the domains were assessed through Pearson's correlation coefficient. The sociodemographic characteristics were identified, and the mean scores with their standard deviations for the 36 questions of the WHODAS 2.0 were calculated. The internal consistency was evaluated byCronbach's α.
Results
Cronbach's α was higher than 0.79 for both sets of questons of the questionnaire. The EFA and CFA for the main 32 questions exhibited a total variance of 54.7% (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin [KMO] measure of sampling adequacy = 0.934; p < 0.001) and 53.47% (KMO = 0.934; p < 0.001) respectively. There was a significant correlation among the 6 domains (r = 0.571-0.876), and a moderate correlation among all domains (r = 0.476-0.694).
Conclusion
The version of the WHODAS 2.0 instrument adapted to Brazilian Portuguese showed good psychometric properties in this sample, and therefore could be applied to populations of women regarding their reproductive history.
Key-words Disability and Health (ICF)international classification of functioningMaternal and child healthPregnancy complicationsValidation studiesSee more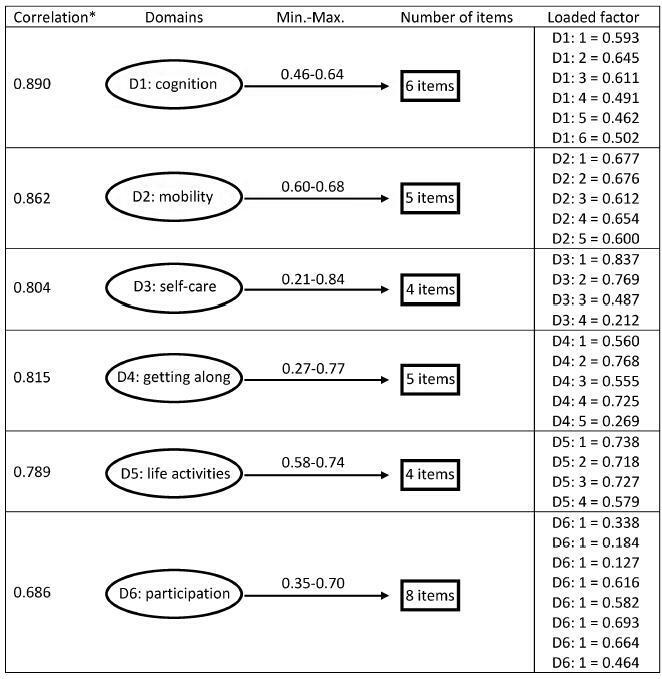
-
Original Article10-01-2016
Uterine Fibroid Symptom – Quality of Life questionnaire translation and validation into Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):518-523
Abstract
Original ArticleUterine Fibroid Symptom – Quality of Life questionnaire translation and validation into Brazilian Portuguese
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(10):518-523
Views188See moreAbstract
Purpose
To translate into Portuguese, culturally adapt and validate the Uterine Fibroid Symptom - Quality of Life (UFS-QoL) questionnaire for Brazilian women with uterine leiomyoma.
Methods
Initially, the UFS-QoL questionnaire was translated into Brazilian Portuguese in accordance with international standards, with subsequent cultural, structural, conceptual and semantic adaptations, so that patients were able to properly answer the questionnaire. Fifty patients with uterine leiomyoma and 19 patients without the disease, confirmed by abdominal pelvic examination and/or transvaginal ultrasound, were selected at the outpatient clinics of the Department of Gynecology of the Universidade Federal de São Paulo (Unifesp). The UFS-QoL questionnaire was administered to all women twice on the same day, with two different interviewers, with an interval of 15 minutes between interviews. After 15 days, the questionnaire was readministered by the first interviewer. Reliability (internal consistency and test-retest), construct and discriminative validity were tested to ratify the questionnaire.
Results
The reliability of the instrument was assessed by Cronbach’s α coefficient with an overall result of 0.97, indicating high reliability. The survey results showed a high correlation (p= 0.94; p 0.001).
Conclusion
The UFS-QoL questionnaire was successfully adapted to the Brazilian Portuguese language and Brazilian culture, showing reliability and validity.
-
Original Article11-01-2015
Translation, adaptation and validation of the Brazilian version of the Utian Quality of Life for evaluation of quality of life in the climacteric
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(11):520-525
Abstract
Original ArticleTranslation, adaptation and validation of the Brazilian version of the Utian Quality of Life for evaluation of quality of life in the climacteric
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(11):520-525
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005438
Views114See morePURPOSE
To translate, to adapt and to validate the Utian Quality of Life (UQOL) for the Brazilian population.
METHODS
Women in the climacteric phase, residents in the city of Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, located in the Brazilian Northeast, were randomly selected. UQOL and SF-36 questionnaires were used, and the translation from English to Portuguese was made by three teachers, while the adaptation stage of the translated version was made by applying the questionnaire to 35 women, which could mark the answer choice "I did not understand the question"; reproducibility measurements (test-retest) and construct validity were used to validate, following international methodological standards.
RESULTS
The Brazilian version was fully recognized by the target population, which was comprised of 151 women, as no question showed a percentage of "non-understanding" equal to or greater than 20%. The results for intra and interobserver reproducibility demonstrated significant agreement on all the questionnaire items. This version showed consistency above the required criteria (>70), demonstrating its accuracy, while the construct validity was obtained by statistically significant correlations between the domains occupation, health and emotional of UQOL and the SF-36 domains. The Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the whole instrument was 0.82, representing good accuracy. Item-total correlation analysis showed the scale homogeneity
CONCLUSION
From the steps taken, the UQOL questionnaire was translated and adapted for its use in Brazil, with high reproducibility and validity. Thus, it can be included and used in Brazilian studies that aim at evaluating the quality of life of women during the peri- and postmenopausal.


