Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):373-379
To investigate the patterns of hospital births in the state of Rio de Janeiro (RJ), Brazil, between 2015 and 2016; considering the classification of obstetric characteristics proposed by Robson and the prenatal care index proposed by Kotelchuck.
Data obtained from the Information System on Live Births of the Informatics Department of the Brazilian Unified Health System (SINASC/DATASUS, in the Portuguese acronym) databases were used to group pregnant women relatively to the Robson classification. A descriptive analysis was performed for each Robson group, considering the variables: maternal age, marital status, schooling, parity, Kotelchuck prenatal adequacy index and gestational age. A logistic model estimated odds ratios (ORs) for cesarean sections (C-sections), considering the aforementioned variables.
Out of the 456,089 live births in Rio de Janeiro state between 2015 and 2016, 391,961 records were retained, 60.3% of which were C-sections. Most pregnant women (58.6%) were classified in groups 5, 2 or 3. The percentage of C-sections in the Robson groups 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 8 was much higher than expected. Prenatal care proved to be inadequate for women who subsequently had a vaginal delivery, had an unfavorable family structure and a lower socioeconomic status (mothers without partners and with lower schooling), compared with those undergoing cesarean delivery. For a sameRobson group, the chance of C-section increases when maternal age rises (OR = 3.33 for 41-45 years old), there is the presence of a partner (OR = 1.81) and prenatal care improves (OR = 3.19 for “adequate plus”).
There are indications that in the state of RJ, from 2015 to 2016, many cesarean deliveries were performed due to nonclinical factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):53-59
To evaluate blood loss during misoprostol-induced vaginal births and during cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction.
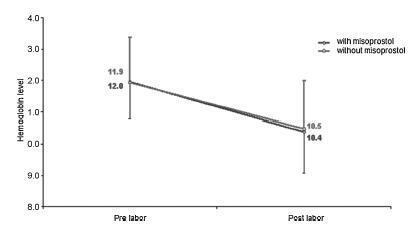
We conducted a prospective observational study in 101 pregnant women indicated for labor induction; pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were measured to estimate blood loss during delivery. Labor was induced by administering 25 μg vaginal misoprostol every 6 hours (with a maximum of 6 doses). The control group included 30 patients who spontaneously entered labor, and 30 patients who underwent elective cesarean section. Pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels were evaluated using the analysis of variance for repeated measurements, showing the effects of time (pre- and postpartum) and of the group (with and withoutmisoprostol administration).
Therewere significant differences between pre- and postpartum hemoglobin levels (p < 0.0001) with regard to misoprostol-induced vaginal deliveries (1.6 ± 1.4 mg/dL), non-induced vaginal deliveries (1.4 ± 1.0 mg/dL), cesarean sections after attempted misoprostol induction (1.5 ± 1.0 mg/dL), and elective cesarean deliveries (1.8 ± 1.1 mg/dL). However, the differences were proportional between the groups with and without misoprostol administration, for both cesarean (p = 0.6845) and vaginal deliveries (p = 0.2694).
Labor induction using misoprostol did not affect blood loss during delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):175-179
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300009
Purpose: to evaluate the route of delivery in a group of low-income primipara pregnant women with a previous cesarean section, and the factors associated with the repetition of the cesarean section on the second delivery. Patients and Methods: it was a case-control study including 356 women who were assisted at the Maternity of CAISM/UNICAMP during the period between January 1993 and January 1996. The cases were 153 women whose second delivery was through a cesarean section and the controls were 203 women whose second delivery was vaginal. For analysis, means, standard deviation, Student's t-test, Mann-Whitney test, chi² test and odds ratio (OR) with 95% CI for each factor possibly associated with cesarean section on the second delivery were used. Results: the route of the second delivery was vaginal for 57% of the women. Among the several variables studied, those which showed to be significantly associated with a cesarean section on the second delivery were: higher maternal age (for women over 35 years, OR = 16.4), previous abortions (OR = 2.09), induced labor (OR = 3,83), premature rupture of membranes (OR = 2.83), not having an epidural analgesia performed during labor (OR = 5.3), the finding of some alteration in fetal well-being (OR = 2.7) and the delivery occurring during the afternoon (OR = 1.92). Conclusions: these results indicate that the factors associated with the repetition of cesarean section in women with a previous scar of cesarean section in this population are predominantly medical; however, there is still the possibility of proposing interventions directed to decreasing the rates of repeated cesarean sections.