-
Case Report
Does Big Mean Evil? Giant, but Benign Uterine Leiomyoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):66-71
03-08-2021
Summary
Case ReportDoes Big Mean Evil? Giant, but Benign Uterine Leiomyoma: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):66-71
03-08-2021Views155See moreAbstract
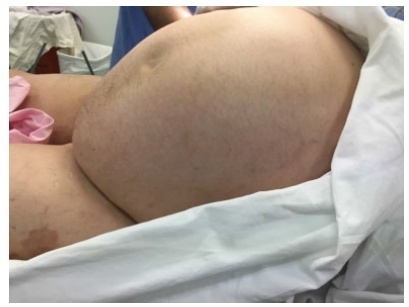
Uterine leiomyoma is themost prevalent benign type of gynecological tumor. It affects more than 80% of women worldwide and, within this group, more than 50% may be asymptomatic. However, large fibroid volumes may be associated with symptoms of extrinsic compression, and most of the cases do not present atypical cells. We present the case of a 49-year-old woman who underwent a total abdominal hysterectomy of a 13.5-kg uterine leiomyoma with no malignancies at histopathology and review the literature about giant uterine leiomyomas and their clinical repercussion. We concluded that large volumes do not always pose a threat regarding malignancy; however, future molecular studies are needed to investigate giant uterine fibroids.
-
Case Report
Pelvic Intravenous Leiomyomatosis – Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):412-415
08-01-2016
Summary
Case ReportPelvic Intravenous Leiomyomatosis – Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):412-415
08-01-2016Views130See moreAbstract
Introduction
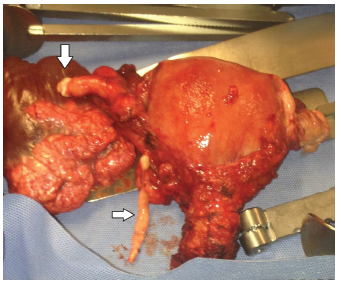
Intravenous leiomyomatosis is a benign and rare condition that can result in cardiac events with fatal outcomes when left untreated. Intravenous leiomyomatosis is probably underestimated because the diagnosis is easily missed. We present a case of an intravenous leiomyomatosis without extra-pelvic involvement, with a brief review of this pathology.
Case Report
46-year-old woman submitted to hysterectomy and bilateral adnexectomy because of a pelvic mass detected in ultrasound. During the surgery, intravenous leiomyomatosis diagnosis was suspected. Pathological analysis confirmed this suspicion. Further imaging exams were performed without detecting any anomalies related to this condition. The patient remained with no evidence of disease after one year of follow-up.
Conclusion
Intravenous leiomyomatosis is a rare condition that can lead to serious complications. Early diagnosis followed by an appropriate treatment is very important to patient outcome, and underdiagnoses can be counteracted if the gynecologist is aware of this entity.
-
Artigos Originais
Uterine leiomyomas and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):80-85
07-06-2005
Summary
Artigos OriginaisUterine leiomyomas and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):80-85
07-06-2005DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000200007
Views142See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the evolution of pregnancy and the maternofetal prognosis in women with uterine leiomyomas. METHODS: a descriptive retrospective analysis of the medical records of 75 pregnant women with leiomyomas attended at the University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo, from January 1992 to January 2002. RESULTS: seventy-five pregnant women with leiomyomas were identified in a population of 34,467 pregnant women attended during this period (incidence of 0.2%). The diagnosis was made before pregnancy in 18 patients (24%), during the current pregnancy in 41 (54.6%), and during cesarean section in 16 (21.3%), of whom only six were not submitted to ultrasound scan during the prenatal period. Ten deliveries with preterm fetuses and five cases of premature rupture of the amniotic membranes were observed. Forty-seven patients (75.8%) were submitted to cesarean section, with the indication being directly related to the leiomyomas in 38.3% of them (anomalous presentation, obstruction of the birth canal, or uterine scar due to a previous myomectomy). Four cases of central necrosis, two cases of hyaline degeneration and one case of malignant potential of the leiomyoma were identified in patients submitted to postpartum myomectomy or hysterectomy. Sixty-one newborns (98.4%) had an Apgar score above 7 at the fifth minute of life, and surgery did not lead to a worse maternofetal prognosis when performed during pregnancy. CONCLUSIONS: the incidence of leiomyomas during pregnancy was 0.2% during the study period, with ultrasonography failing to diagnose 10 patients. Cesarean section was frequently indicated for this group of patients, but the presence of leiomyomas during pregnancy did not compromise the Apgar score of the newborns.


