Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):726-730
The objective of the present study is to observe the frequency and severity of urinary symptoms in women with breast cancer (BC) being treated with oral hormone therapy, associating them to drug adherence.
The participants were interviewed once from June to October 2016. The evaluation of urinary symptoms was performed by two questionnaires: International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire - Short Form (ICIQ-SF) and International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Overactive Bladder Module (ICIQ-OAB). Adherence was evaluated by the Morisky-Green method. Statistical analysis was performed by the Mann-Whitney test, linear regression, and Spearman correlation.
Fifty-eight women were interviewed: 42 treated with tamoxifen and 16 with aromatase inhibitor. Twenty-seven women (46.5%) presented urinary incontinence symptoms and 15 (25.8%) presented stress urinary incontinence (SUI). Fourteen (24.1%) women had symptoms of overactive bladder (OAB). There was no statistical difference in symptoms between both treatments and duration of treatments. Higher scores in the ICIQ-SF questionnaire were associated with low/medium adherence and advanced age. Higher scores in the ICIQ-OAB questionnaire were associated with low/medium adherence.
The present study showed a high prevalence of urinary symptoms, such as urinary incontinence and OAB, associated with low/medium adherence and older age in women with BC being treated with oral hormone therapy. Health professionals should be alert to these symptoms since it could influence life quality and adherence to treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):769-771
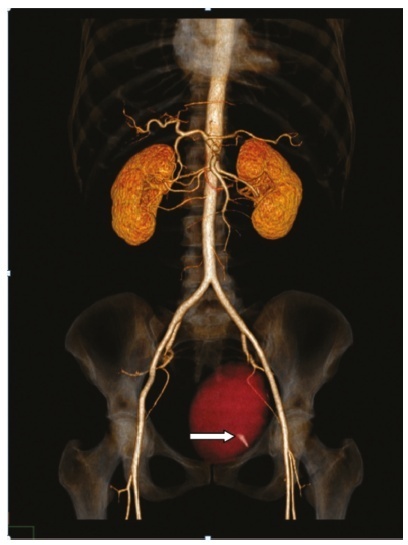
The placement of a suburethral sling is standard treatment for stress urinary incontinence. The transobturator technique (TOT) emerged as an alternative to minimize the risks of the blind insertion of needles, leading to a lower rate of perforation complications compared with the retropubic approach. We present a case of injury to a branch of the left obturator artery following the placement of a urethral sling using TOT, followed by intense bleeding and hemodynamic instability, which was treated with embolization.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):493-500
To examine women with pelvic floor dysfunction (PFDs) and identify factors associated with sexual activity (SA) status that impacts quality of life (QoL).
We conducted a cross-sectional study that includedwomen> 18 years old who presented with at least one PFD symptom (urinary incontinence [UI] and/or pelvic organ prolapse [POP]), in outpatient clinics specializing in urogynecology and PFD in Fortaleza, state of Ceará, Brazil, using a service evaluation form and QoL questionnaires.
The analysis of 659 women with PFD included 286 SA (43.4%) women and 373 non-sexually active (NSA) (56.6%) women, with a mean age of 54.7 (±12) years old. The results revealed that age (odds ratio [OR]= 1.07, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.03-1.12) and post-menopausal status (OR= 2.28, 95% CI 1.08-4.8) were negatively associated with SA. Being married (OR= 0.43, 95% CI 0.21-0.88) was associated with SA. Pelvic organ prolapse (OR= 1.16, 95% CI 0.81-1.68) and UI (OR= 0.17, 95% CI 0.08-0.36) did not prevent SA. SF-36 Health Survey results indicated that only the domain functional capacity was significantly worse in NSA women (p= 0.012). Two King’s Health Questionnaire domains in NSA women, impact of UI (p= 0.005) and personal relationships (p< 0.001), were significantly associated factors. Data from the Prolapse Quality-of-life Questionnaire indicated that NSA women exhibited compromised QoL.
Postmenopausal status and age negatively affected SA. Being married facilitated SA. Presence of POP and UI did not affect SA. However, NSAwomen with POP exhibited compromised QoL.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence - UI, fecal incontinence - FI, and pelvic organ prolapse - POP).
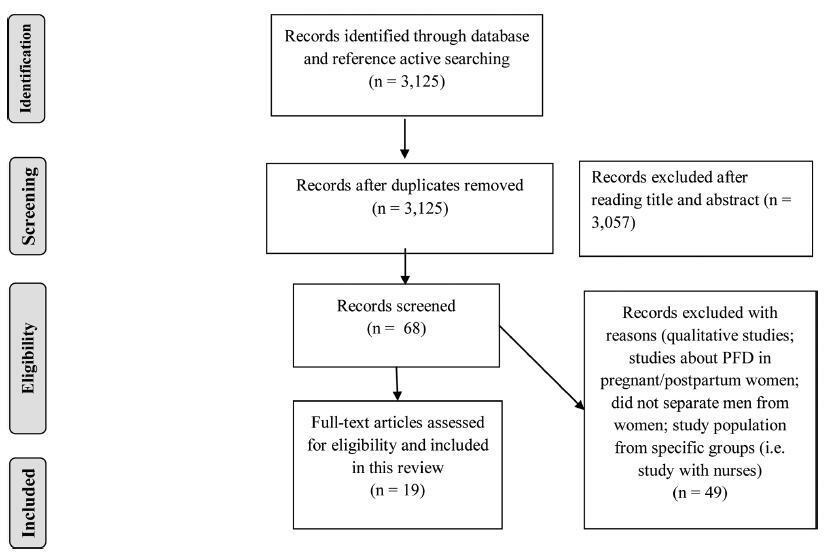
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):563-569
To describe a case of vesicouterine fistula and to review the literature related to this condition.
For the review, we accessed the MEDLINE, BIREME and LILACS databases; the references of the searched articles were also reviewed.
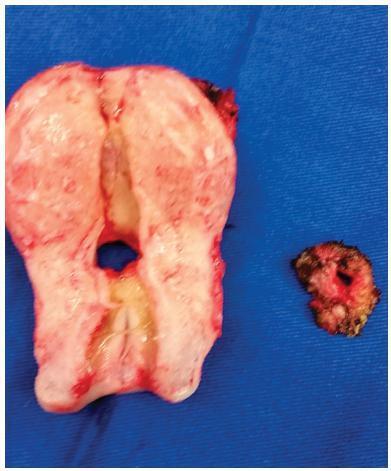
A 38-year-old woman, in the 1st day after her 3rd cesarean, presented heavy hematuria, which was considered secondary to a difficult dissection of the bladder. A total of 6 months after delivery, she failed to resume her regular menstrual cycles and presented cyclic menouria and amenorrhea. At this time, she had two episodes of urethral obstruction by blood clots. She remained without a correct diagnosis until about two years postdelivery, when a vesicouterine fistula was confirmed through cystoscopy. A surgical correction through open abdominal route, coupled with hysterectomy, was performed. After the surgery, the symptoms disappeared. The review showed a tendency of change in the relative frequency of the different types of genitourinary fistulae. Vesicovaginal fistulae, usually caused by inadequate care during labor, are becoming less frequent than those secondary tomedical procedures, such as vesicouterine fistulae. The most common cause of this latter kind of fistula is cesarean section, especially repeated cesarean sections. The diagnosis is confirmed through one or more imaging exams, or through cystoscopy. The most common treatment is surgical, and the routes are: open abdominal, laparoscopic, vaginal or robotic. There are some reports of success with the conservative treatment.
Vesicouterine fistulae are becoming more common because of the increase in the performance of cesarean sections, and the condition must be considered a possible complication thereof.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(10):534-540
The presence of bacteria in urine is called bacteriuria, which may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. The manipulation of the urinary tract during urodynamic study (UDS), which is an invasive procedure, can result in urinary tract infection (UTI). Studies on the use of prophylactic antibiotics for UDSs are contradictory. Some investigators concluded that they were valuable and others did not. The objective of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis before UDS. This is a placebo-control randomized double-blind study.
Two-hundred and seventeen women affected by urinary incontinence were eligible for this study. All patients had presented negative urine culture previous to the UDS. They were randomized in four groups: group A received placebo, group B received 500 mg of levofloxacin, group C received 80 mg trimethoprim and 400 mg sulfamethoxazole and group D received 100 mg of nitrofurantoin. A urine culture was performed 14 days after the UDS.
We observed asymptomatic bacteriuria after the UDS in five patients in group A, one in group B, one in group C and one in group D. Only one patient on group A had symptomatic bacteriuria.We didn’t observe statistical difference between the groups. When we recategorized the patients in two groups, the incidence of bacteriuria was significantly higher in the placebo group compared with the antibiotic group.
The conclusion is that antibiotic prophylaxis before the UDS did not reduce the incidence of UTI in women within the target population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):471-479
Using three-dimensional ultrasound (3D-US), we aimed to compare the tape position and the angle formed by the sling arms in different techniques of midurethral sling insertion for the surgical treatment of stress urinary incontinence, three years after surgery. In addition, we examined the correlations between the US findings and the clinical late postoperative results.
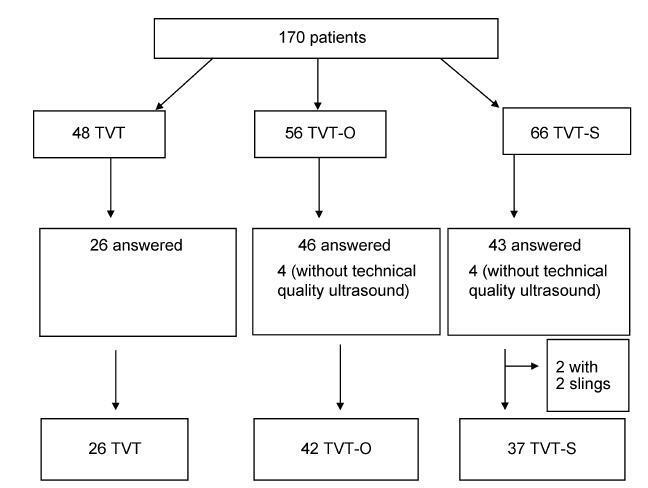
A prospective cross-sectional cohort study of 170 patients who underwent a sling procedure between May 2009 and December 2011 was performed. The final sample, with US images of sufficient quality, included 26 retropubic slings (tension-free vaginal tape, TVT), 42 transobturator slings (tension-free vaginal tape-obturator, TVTO), and 37 single-incision slings (tension-free vaginal tape-Secur, TVT-S). The images (at rest, during the Valsalva maneuver, and during pelvic floor contraction) were analyzed offline by 2 different observers blinded against the surgical and urinary continence status. Group comparisons were performed using the Student t-test, the chi-squared and the Kruskal-Wallis tests, and analyses of variance with Tukey multiple comparisons.
Differences among the groups were found in themean angle of the tape arms (TVT = 119.94°, TVT-O = 141.93°, TVT-S = 121.06°; p < 0.001) and in the distance between the bladder neck and the tape at rest (TVT = 1.65 cm, TVT-O = 1.93 cm, TVTS = 1.95 cm; p = 0.010). The global objective cure rate was of 87.8% (TVT = 88.5%, TVT-O = 90.5%, TVT-S = 83.8%; p = 0.701). The overall subjective cure rate was of 83.8% (TVT = 88.5%, TVT-O = 88.5% and TVT-S = 78.4%; p = 0.514). The slings were located in the mid-urethra in 85.7% of the patients (TVT = 100%, TVT-O = 73.8%, TVTS = 89.2%; p = 0.001), with a more distal location associated with obesity (distal: 66.7% obese; mid-urethra: 34% obese; p = 0.003). Urgency-related symptoms were observed in 23.8% of the patients (TVT = 30.8%, TVT-O = 21.4%, TVT-S = 21.6%; p = 0.630).
The angle formed by the arms of the sling tape was more obtuse for the transobturator slings compared with the angles for the retropubic or single-incision slings. Retropubic slings were more frequently located in the mid-urethra compared with the other slings, regardless of obesity. However, the analyzed sonographic measures did not correlate with the urinary symptoms three years after the surgery.